You might have read that Ethereum 2.0 is about to switch to Proof of Stake. It’s time to have Proof of Stake explained!
Most current blockchains utilize Proof of Work. Both of these terms represent consensus algorithms. They are the core of many blockchain systems, and they have even been around before Bitcoin. Decentralized networks have no single source of trust. Instead, participants need to agree on how to validate all transactions and information sharing. So, continue reading to discover how proof of stake works.
Proof of Work
Proof of Stake is an alternative to Proof of Work, so let’s first mention the latter. It is currently used in cryptocurrency giants like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Both currencies are really popular today, and this information is vital if you are about to exchange Bitcoin or Ethereum.
In PoW systems, miners invest energy to perform complex computations. Essentially, your mining rig decrypts transactions the hard way. The first miner who verifies the block can add it to the blockchain. He is also rewarded with the blockchain’s cryptocurrency.
It’s a secure system, and it works well. However, there are some issues to consider:
- Mining is difficult
To become a miner, you’ll need a powerful mining rig that’s capable of performing the computations. Also, make sure you account for electricity costs for powering the mining rig and its cooling system.
- Possible centralization
People who live in countries with cheaper electricity prices and lower air temperatures have the advantage in mining. It can lead to centralization in such countries. Mining pools are a great solution, but things can go wrong if a simple mining pool controls the blockchain.
- Efficiency
Blocks are added one-by-one. During high-volume periods, users might have to wait several hours until the transaction goes through.

Cost of Bitcoin mining against its price (US)
Proof of Stake
Now, let’s see what is the Proof of Stake. The proof of stake algorithm (PoS) takes on a different approach. Instead of mining, validators commit specific amounts of the blockchain’s cryptocurrency (stake) to create blocks.
Validators commit a cryptocurrency amount on the network and enter a pool of possible users that can propose the next block. The validator who will propose the block is often chosen randomly.
Other validators attest that they’ve reviewed the block. Once enough validators attest, the block is added, and everyone receives certain rewards. Not fulfilling your obligations on the network results in mild penalties. In turn, being responsible (online) when the time is right will lead to more rewards than penalties. If someone tries to attack the blockchain(by proposing a fake block), their stake is confiscated, and they are banned.
How Can PoS Resolve PoW Problems?
We have mentioned three significant problems with PoW blockchain networks. Here is how Proof of Stake works to resolve these problems:
- Mining is difficult
There is no mining in PoS. However, PoS networks require a minimum amount of cryptocurrency you have to possess to become a validator. For example, Ethereum 2.0 blockchain requires validators to own at least 32 ETH, which is around $13.3K at the time of writing.
- Possible centralization
To get started, you only need to register and own enough cryptocurrency. Your geographical location has no impact, and the fear of centralization is removed. Also, PoS blockchains are immune to 51% attacks. More on this type of attack below!
- Efficiency
PoS alone doesn’t provide a new approach to improve efficiency. However, PoS networks allow for sharding, a method that divides the blockchain into many smaller chains. It powers the network to process transactions parallelly. If the blockchain is divided into 10 smaller chains, it can analyze ten transactions simultaneously!
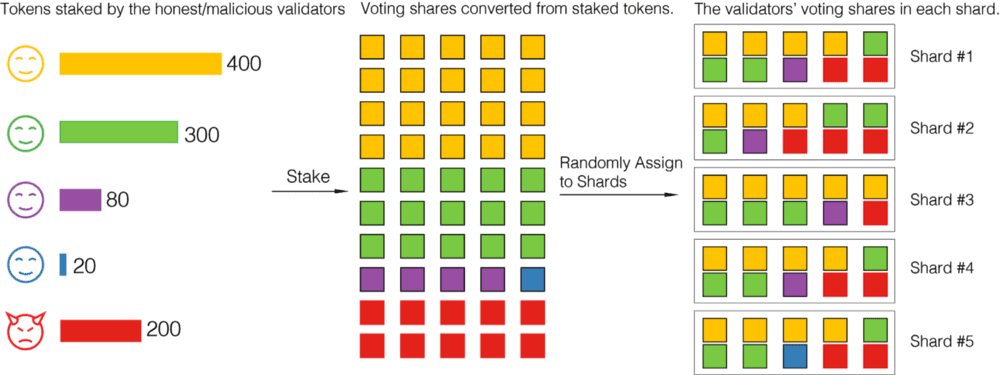
51% Attack
One day, when miners mine almost all Bitcoins, there will be little or no block reward. Instead, miners will be rewarded from transaction fees, which will also probably be lower. It will require fewer miners than ever. Someone may create a mining pool that represents over 51% of the network’s computation power. This allows the pool to create fake transactions and place them on the blockchain. For example, they can just create a transaction where you send all of your money to them. Since they’ll be the first to mine it, they can validate it and cause you harm.
In PoS networks, to own 51% of power, you need to own 51% of the cryptocurrency. Indeed, in PoW networks, power comes from investing energy whereas, in PoS networks, power comes from owning cryptocurrency. If someone hypothetically accumulated 51% of a cryptocurrency, he wouldn’t perform any suspicious actions on the network, as it would plummet the value of the cryptocurrency and harm him.
Final Thoughts
Here is a short explanation of what is proof of stake. It might not be better than Proof of Work in some networks. But, it’s a step forward from mining and investing gigantic amounts of energy. It might lead to more people adopting cryptocurrencies and switching their operations to the blockchain.



































