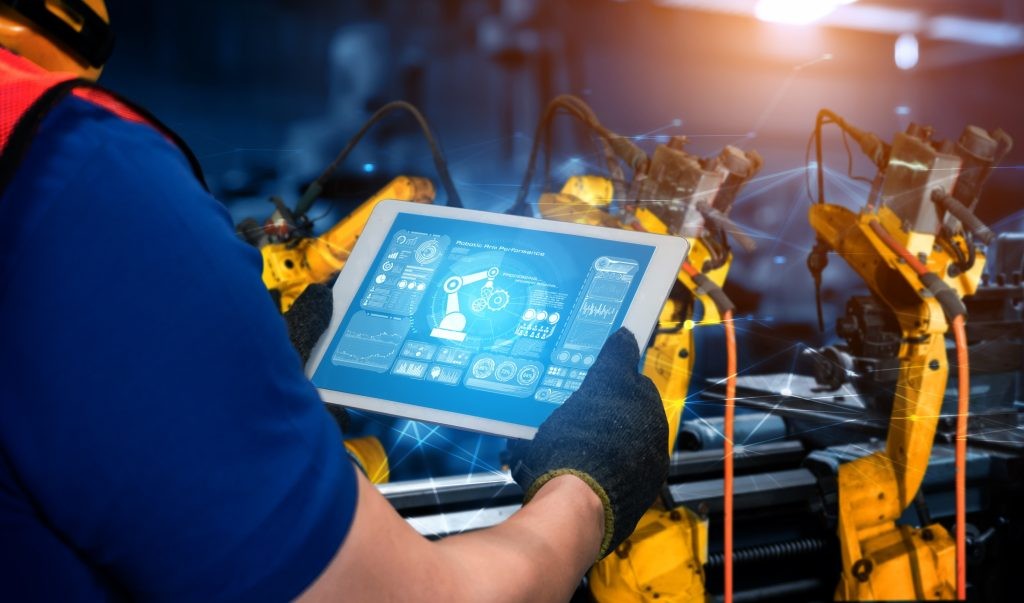
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, with automation at the heart of this transformation. While the concept isn’t new, its adoption has accelerated due to technological advancements and the pursuit of increased efficiency and ROI in digital transformation.
However, medium-sized manufacturers often face challenges, such as integrating real-time location systems (RTLS) with existing infrastructure and overcoming technical bottlenecks. This article explores how embracing automation can enhance operational efficiency, boost productivity, and maximize ROI.
The Evolution of Automation in Manufacturing
Automation in manufacturing dates back to the Industrial Revolution, which introduced mechanical advancements that reshaped production lines. The late 20th century saw the integration of computers and robotics, leading to more sophisticated and reliable manufacturing techniques.
Smart factories powered by automation, AI, machine learning, and real-time data analytics are the hallmark of Industry 4.0. RTLS in manufacturing enhances this evolution by providing the adaptability and efficiency needed to meet rising demands for quality and affordability.
Defining Automation in the Manufacturing Process
Automation in manufacturing involves using technology to perform tasks without human intervention. This includes implementing systems and software to control machinery and processes, minimizing human input, reducing errors, and increasing consistency.
Technologies such as robotics, computer numerical control (CNC) machines, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) target specific production aspects, streamlining operations and enhancing precision. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can focus on innovation and quality, leading to better products and a competitive advantage.
Key Drivers for Automation in Manufacturing
Several factors drive the push towards automation:
- Cost Reduction and Efficiency: Automation minimizes labor expenses and reduces waste, leading to significant savings.
- Increased Production Capacity: Automated systems allow for higher output without compromising quality.
- Improved Consistency and Quality: Automated processes ensure uniform product standards, crucial for customer satisfaction.
- Technological Advancements: Companies leverage cutting-edge solutions to innovate and stay competitive.
These drivers compel businesses to rethink traditional methods and embrace new technologies to remain competitive.
The Role of Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) in Automation
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) are transforming automated manufacturing environments by providing live data on asset and personnel locations. Maritime analytics platforms such as AXSMarine can enrich these insights by linking factory output with real‑time vessel schedules and port conditions, further reducing downstream bottlenecks. This precise tracking ensures components are where they should be, minimizing delays and errors, and streamlining the manufacturing process.
RTLS in manufacturing also enhances safety by monitoring the location of workers and equipment, identifying potential hazards promptly. Integrating RTLS with automation systems boosts overall efficiency, enabling quick decision-making and reducing downtime.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency Through Automation
Automation significantly boosts operational efficiency by streamlining workflows and reducing cycle times. Automated systems execute tasks with high precision, minimizing human errors and leading to higher-quality outputs.
Additionally, automation allows for better use of equipment and facilities. Machines can operate at optimal speeds, reducing wear and tear while maximizing output. Real-time data insights enable proactive management of manufacturing processes, leading to quicker issue resolution and refined process optimization.
Productivity Gains from Automated Manufacturing
Incorporating automation leads to significant productivity improvements:
- Continuous Operation: Automated systems operate without breaks, increasing output.
- Better Allocation of Human Resources: Machines handle routine tasks, allowing skilled workers to focus on complex activities.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance features foresee equipment failures, avoiding costly interruptions.
Automation transforms the manufacturing landscape by optimizing labor allocation, reducing downtime, and enabling continuous operation.
Addressing Workforce Dynamics in an Automated Environment
Automation alters workforce dynamics, requiring a focus on developing new skills suited to an automated environment. Upskilling the existing workforce becomes crucial, with training programs facilitating this transition.
Automation also presents an opportunity to improve job satisfaction by eliminating monotonous tasks, encouraging creativity and problem-solving, and leading to a more motivated and efficient workforce.
Overcoming Challenges in Automation Implementation
Transitioning to an automated manufacturing system involves challenges:
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Careful evaluation is needed to identify areas requiring upgrades or replacements.
- Technical Bottlenecks: Issues like outdated hardware or software incompatibilities require proactive troubleshooting.
- Change Management: Addressing employee resistance through strategic planning and communication is essential.
Developing a roadmap that includes regular assessments and feedback loops can ensure smooth adoption.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Integrating automation with current systems is complex. Prioritizing interoperability ensures new automation solutions communicate seamlessly with legacy systems, avoiding disruptions.
Collaboration between IT and operations departments is crucial to identify potential integration pitfalls early. Thorough planning enhances productivity without system incompatibilities, laying the foundation for successful automation.
Technical Bottlenecks and Solutions
Technical bottlenecks can stall automation projects. Conducting comprehensive audits of existing technologies can reveal potential weaknesses. Regular updates to software and hardware mitigate common problems.
Leveraging advanced analytics highlights areas of inefficiency, and predictive maintenance tools powered by AI can foresee potential failures. Cultivating a knowledgeable technical team ensures effective handling of technical challenges.
Case Studies: Successful Automation in Manufacturing
Real-world examples highlight automation’s potential:
- BMW: Implemented robotics to enhance precision and reduce error rates, streamlining assembly processes.
- John Deere: Incorporated advanced IoT sensors for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime.
- Honda: Used AI-powered inspection systems to improve product quality and reduce waste.
- US Military: Integrated autonomous vehicles for logistics, increasing operational efficiency and safety.
These case studies demonstrate automation’s transformative power in modern manufacturing.
Maximizing ROI from Automation Investments
To maximize ROI from automation:
- Tailor Solutions: Align technology investments with specific business objectives.
- Phased Implementation: Gradually introduce automation to manage costs and adjust processes.
- Continuous Evaluation: Monitor performance metrics and refine processes to enhance efficiency and productivity.
This proactive approach ensures automation investments yield sustainable value and competitive advantage.
The Future Trends in Manufacturing Automation
Manufacturing automation is rapidly evolving, bringing transformative trends:
- Collaborative Robots and Digital Twins: Robots working alongside humans and virtual replicas of physical systems enhance efficiency.
- Smart Factories and Industry 4.0: Interconnected systems automate and refine manufacturing processes.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Used in training and maintenance to enhance workforce capabilities.
- Blockchain Technology: Enhances supply chain transparency and security through immutable records.
These trends point to a future where manufacturing is more efficient, adaptable, and responsive to market demands.
For additional insights on Industry 4.0 and logistics transformation, you may enjoy How Technology Is Reshaping the Logistics Industry.
Conclusion: Preparing for a Digitally Transformed Future
Embracing automation is a strategic imperative. A digitally transformed future demands adaptability, continuous learning, and innovative thinking. Leadership commitment is crucial to foster an environment that encourages new technologies while ensuring employee engagement.
Balancing technology with human insights is key. Integrating automation thoughtfully, maintaining a customer-centric approach, and ensuring each investment translates into tangible value will create resilient, agile, and efficient operations, securing a competitive edge and fueling sustainable growth.