Losing hair can feel like losing a part of your identity, affecting confidence and how you face the world daily. While traditional hair transplants involve surgery and downtime, non-surgical hair transplant methods are gaining attention as less invasive alternatives that deliver noticeable results. Understanding these options can help anyone seeking hair restoration make an informed choice.
Let’s break down the concept of non-surgical hair transplant, explore the most effective procedures available, and share important insights backed by real-world examples. If you’re curious about alternatives to surgical hair restoration, this guide is for you.
What Is a Non-Surgical Hair Transplant?
A non-surgical hair transplant refers to treatments that restore hair or simulate hair regrowth without invasive surgery. Unlike traditional hair transplants, where follicles are physically moved from one scalp area to another, non-surgical methods use advanced technology or topical solutions to promote hair growth or create the illusion of thicker hair.
These treatments often require little to no downtime and carry fewer risks of complications. For many, non-surgical options serve as an introduction to hair restoration or a solution when surgery isn’t viable.
Why Consider Non-Surgical Hair Transplant Methods?
Hair loss affects approximately 50% of men and women worldwide by age 50. Traditional surgery isn’t always an option due to cost, recovery time, or medical conditions. Non-surgical methods:
- Minimise discomfort and recovery time
- Are often more affordable
- Allow gradual, natural-looking results
- Suit a wider range of hair loss stages
Common Non-Surgical Hair Transplant Procedures
Below is an overview of the leading non-surgical hair transplant approaches, highlighting how each works and who it benefits most.
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)
SMP involves applying tiny dots of pigment to the scalp, mimicking the appearance of hair follicles. It creates the illusion of thicker hair or a closely shaved scalp.
- How it works: Specialised tattooing techniques deposit pigment on the scalp’s surface.
- Benefits: Instant visual density without altering hair growth.
- Limitations: Does not promote actual hair regrowth, results fade over time, and require touch-ups.
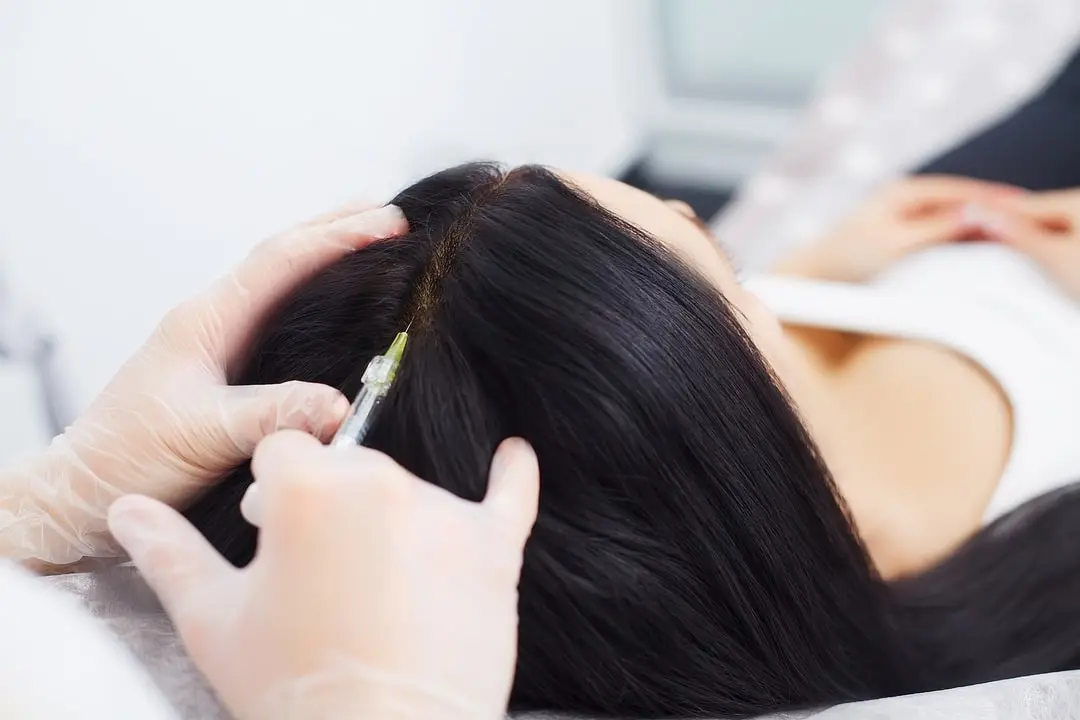
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP uses a patient’s own blood components to stimulate hair follicles naturally.
- How it works: Blood is drawn, processed to concentrate platelets, and injected into the scalp.
- Benefits: Encourages existing follicles to grow thicker and stronger.
- Limitations: Requires multiple sessions, results vary, and are gradual.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses low-intensity laser light to stimulate hair follicle activity.
- How it works: Laser devices, often worn as caps or combs, emit light that promotes cellular activity in hair follicles.
- Benefits: Pain-free, non-invasive, can be done at home.
- Limitations: Requires ongoing use for maintenance, and effectiveness depends on individual response.
Topical Treatments with Minoxidil and Finasteride
While not transplants, these FDA-approved topical and oral treatments are often grouped under non-surgical hair restoration because they encourage regrowth without surgery.
- How they work: Minoxidil improves blood flow to follicles, and finasteride blocks DHT, a hormone linked to hair loss.
- Benefits: Clinically proven to slow hair loss and regrow hair in many users.
- Limitations: Requires continuous use with possible side effects.
Hair Fibers and Concealers
Temporary, cosmetic solutions using colored keratin fibers that cling to existing hair strands.
- How it works: Fibers attach to hair, instantly masking thinning areas.
- Benefits: Quick, non-invasive, and easy to apply.
- Limitations: Washes out daily. It is purely cosmetic with no regrowth effect.
Insights About Non-Surgical Hair Transplant Options
Below, you can find unique insights on non-surgical hair transplant options:
- Patient Suitability Varies Widely: Non-surgical treatments generally work best for early to moderate hair thinning, rather than complete baldness. For advanced hair loss, they often complement surgical options or serve as a maintenance strategy after surgery.
- Results Depend on Consistency: Treatments like PRP, LLLT, and topical applications require multiple sessions or daily use. Commitment impacts outcomes more than any one-time procedure.
- Combining Treatments Can Increase Effectiveness: Some clinics design programs combining PRP with LLLT and topical solutions, achieving better hair density than single treatments alone.
- Non-Surgical Methods Often Avoid Scarring and Downtime: Compared to follicular unit extraction (FUE) or strip surgery (FUT), these approaches allow patients to maintain normal activities immediately after treatment.
Patient Case Studies
Real-life cases show how non-surgical hair transplant methods can deliver noticeable improvements in hair density and appearance.
Case Study 1: PRP Therapy Success
A 45-year-old man with androgenic alopecia underwent six PRP sessions over three months. Follow-up photos showed a 25% increase in hair density, improving confidence and reducing reliance on hair fibers.
Case Study 2: Scalp Micropigmentation for Visual Density
A female patient with diffuse thinning used SMP to reduce scalp visibility. The treatment took three sessions and created a subtle, natural appearance that eliminated the patchy look.
What to Expect from Non-Surgical Hair Transplant Treatments
Understanding the process and outcomes helps set clear expectations for non-surgical hair transplant treatments.
Treatment Duration and Frequency
- SMP: Usually 2-4 sessions lasting 2-3 hours each.
- PRP: Multiple sessions, typically monthly for 3-6 months, then maintenance every 3-6 months.
- LLLT: Daily or several times weekly sessions, lasting 10-20 minutes.
- Topical treatments: Twice daily application ongoing.
Side Effects and Risks
Most non-surgical methods have minimal risks compared to surgery. Possible mild side effects include:
- Temporary redness or swelling with PRP injections.
- Mild scalp irritation with minoxidil.
- Pigment fading or allergic reaction with SMP.
How to Choose the Right Non-Surgical Hair Transplant Method for You
Choosing the best non-surgical hair transplant method depends on your unique hair loss situation and personal goals.
- Assess Your Hair Loss Stage: Early thinning may respond well to topical treatments and LLLT. More advanced cases may require SMP or a combined approach.
- Consider Your Lifestyle and Budget: Non-surgical options involve less downtime but may require ongoing sessions and maintenance costs.
- Consult a Hair Restoration Specialist: Professional assessment helps determine which procedures suit your hair type, scalp condition, and expectations.
- Research Clinic Credentials: Choose clinics with verified experience, positive reviews, and transparent before-and-after photos.
Say Hello to Fuller Hair Today
Non-surgical hair transplant methods provide a less invasive alternative to surgery, helping stimulate growth, hide thinning, or support surgical results. Treatments like PRP, LLLT, and SMP require realistic expectations and commitment.
They offer subtle but meaningful improvements, restoring confidence without the risks of surgery. If hair loss impacts your life, consulting a trusted specialist about these options is a smart next step.