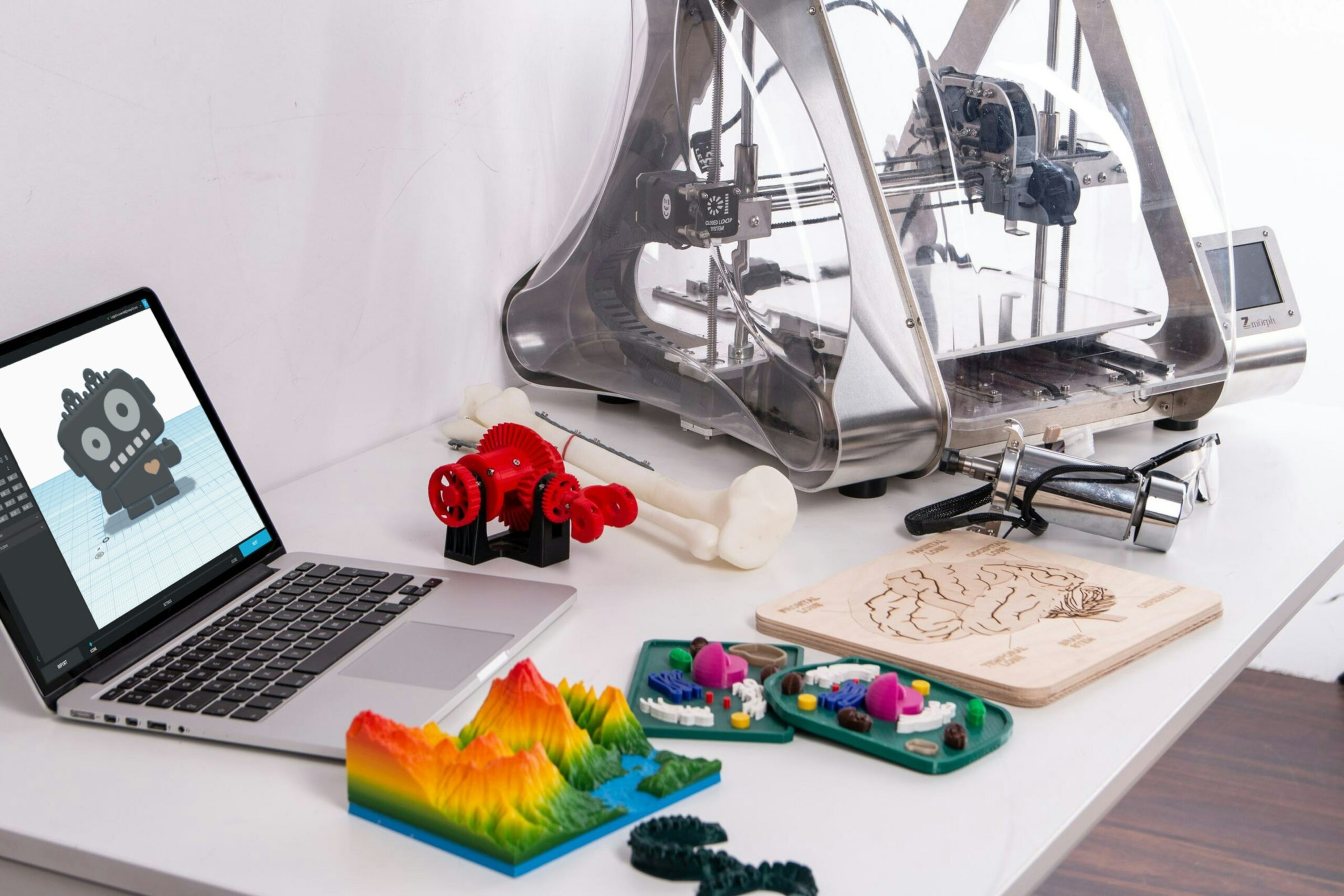
Few know that 3D printing has actually been around since the 1950s. Now, this once-niche technology is revolutionizing home construction, with processes like using computer 3D models to guide printers to layer materials into houses and buildings.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects from digital models. It is “additive” because it does not require a big block of material or a mold to make objects. Instead, it just stacks thin layers of material and fuses them together. With lower costs, this method can make shapes and other complex shapes faster than traditional factory machines.
3D printers can also build more complicated designs than normal manufacturing tools. New printing materials are always being developed. In addition, 3D printing is used a lot in engineering to test design ideas and make lightweight parts quickly. The 3D printers stack and glue thin sheets of plastic, metal, or other materials to create a physical object based on a computer model.
What sort of homes can be built this way?
3D printing allows unique and innovative homes to be built quickly and cheaply. Small printed homes can have the walls done in less than 24 hours. Larger single-family houses take 10-45 days to finish. This very fast process is possible by automating construction with special 3D printers.
These printers can use materials like concrete, clay, foam, or polymers to form the home layer-by-layer based on a computer model. Concrete is very common because it makes solid, sturdy structures. The automated additive process only uses the required amount of material in each area, reducing waste much compared to traditional building methods.
3D-printed homes are also designed to be energy efficient and withstand weather extremes like storms or floods. For example, the world’s biggest 3D printed housing development built in Austin, Texas, will have curved concrete walls reinforced to withstand climate conditions.
The affordable and sustainable printed homes in this “Genesis Collection” neighborhood showcase the huge potential of 3D printing technology to quickly build high-quality housing tailored to the owners’ needs and adapted for local conditions.
Beyond single-family houses, attached multi-residence buildings like duplexes can also utilize 3D printing for rapid, affordable housing. With further development, the automated layering method may unlock creative architectural expressions across diverse property types – from studios to apartments to elaborate mansions.
What are the benefits?
3D-printed homes are one step closer to reality as construction companies increasingly test and adopt this next level of technology in the home building industry. Here are some key benefits of using 3D printing to build homes:
Speeding up home building: 3D printing allows homes to be built much faster compared to traditional construction methods. Small homes can be printed in less than a day, while bigger single-family homes may take up to 45 days at most.
Reducing costs: 3D printing can lower home building costs by needing less manual labor and wasting fewer materials. For example, the construction costs for a duplex in Sydney can cost between $600,000 to $1.5 million. However, 3D printing technology can automate many processes and help save money.
Customizing easily: 3D printing empowers intricate, bespoke home designs catered to an owner’s lifestyle wishes or spatial needs. This new tech permits architectural originality that is traditionally hard to attain.
Promoting eco-friendliness: 3D printed homes encourage sustainability by reducing building refuse and facilitating the use of renewable materials, like resilient, energy-thrifty concrete.
Boosting resilience: 3D-printed houses can be engineered for maximum endurance against extreme weather incidents. Austin’s Genesis Collection displays printed dwellings with heightened disaster resistance.
Enabling affordability: Streamlined 3D printing construction can enable more budget-friendly housing by cutting the manual efforts required.
What are some of the challenges of 3D printing?
While 3D printed homes have benefits, there are still challenges slowing widespread use across home building.
Cost: The printers and special materials are very expensive, putting the technology out of reach for many smaller builders and financially risky for construction companies. 3D printing requires high-quality materials as well as machines.
Quality: Ensuring 3D-printed homes that are consistently strong and durable enough is difficult. You need to consider many things, like layer bonding, integrating wiring, and curing methods. Materials like concrete require lots of testing to meet construction standards.
Legal issues: Builders must deal with intellectual property rules on printer designs. Printed houses must also follow many local codes and regulations before people can live in them.
As 3D printing processes advance, it could potentially revolutionize mainstream home construction – using automation to enable creative, quick solutions to the global housing shortage.