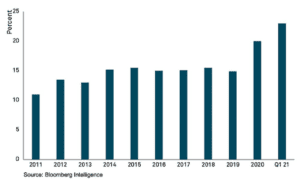
Switzerland has long been a global hub for financial services, known for its stability, innovation, and strong regulatory framework. The forex and derivatives trading sectors are no exception. Over the years, Swiss authorities have implemented strict regulations to ensure market integrity, protect investors, and maintain the country’s reputation as a leading financial center.
The Swiss Regulatory Landscape for Forex and Derivatives
Switzerland’s financial markets are governed by some of the most stringent regulations in the world. The Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) is the primary regulator overseeing forex and derivatives trading. FINMA ensures that all financial service providers comply with anti-money laundering (AML) laws, capital requirements, and transparency rules.
Additionally, Switzerland follows the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II), which harmonizes regulations across the European Economic Area (EEA). Although Switzerland is not an EU member, many Swiss brokers adhere to MiFID II standards to operate seamlessly in European markets.
Key Regulations Impacting Forex and Derivatives Trading
Strict Licensing Requirements
Before offering forex or derivatives trading services, brokers must obtain a license from FINMA. The application process is rigorous, requiring proof of sufficient capital, risk management protocols, and compliance with AML laws. This ensures that only reputable firms operate in Switzerland, reducing the risk of fraud.
Leverage Restrictions for Retail Traders
To protect retail investors from excessive risk, FINMA has imposed leverage limits on forex and derivatives trading. For major currency pairs, the maximum leverage is capped at 30:1, while for minor pairs and cryptocurrencies, it is even lower. These restrictions help prevent traders from taking on unsustainable losses.
Negative Balance Protection
Another crucial regulation is mandatory negative balance protection for retail clients. This means traders cannot lose more than their initial investment, shielding them from extreme market volatility. Brokers must automatically close positions before a client’s account goes into negative territory.
Transparency in Pricing and Fees
FINMA requires brokers to provide clear information on spreads, commissions, and other fees. Hidden charges are prohibited, ensuring traders can make informed decisions. This transparency fosters trust between brokers and their clients.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance
Switzerland has strict AML laws to prevent illicit financial activities. Brokers must verify client identities, monitor transactions, and report suspicious activities to the authorities. These measures help maintain the integrity of the financial system.
The Role of Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs)
Apart from FINMA, self-regulatory organizations (SROs) play a vital role in overseeing forex and derivatives trading. The Swiss Bankers Association (SBA) and the Swiss Trading and Brokerage Association (STBA) set industry standards and ensure members adhere to best practices.
These SROs work alongside FINMA to enforce compliance, investigate misconduct, and promote fair trading conditions. Their involvement strengthens Switzerland’s regulatory framework, making it one of the safest jurisdictions for forex and derivatives trading.
How Regulations Affect Traders and Brokers
For Traders: Enhanced Protection but Limited Flexibility
Swiss regulations provide traders with a high level of security, reducing the risk of broker insolvency or fraudulent activities. However, the strict leverage limits and compliance requirements may limit trading strategies, particularly for those seeking higher-risk opportunities.
For Brokers: Higher Compliance Costs but Increased Credibility
Brokers operating in Switzerland face significant compliance costs due to licensing fees, reporting obligations, and capital requirements. However, being FINMA-regulated enhances their credibility, attracting clients who prioritize safety over aggressive trading conditions.
The Future of Forex and Derivatives Regulation in Switzerland
Switzerland continues to refine its regulatory framework to keep pace with global financial trends. Emerging technologies like blockchain and AI are being integrated into compliance systems to improve monitoring and fraud detection. Additionally, Switzerland is aligning more closely with international standards to maintain its competitive edge.
Potential Changes on the Horizon
- Tighter Crypto Regulations: With the rise of crypto derivatives, FINMA may introduce stricter rules to mitigate risks.
- Enhanced Cross-Border Cooperation: Switzerland could strengthen ties with EU regulators to facilitate smoother market access.
- More Focus on ESG Compliance: Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors may influence future trading regulations.
Conclusion
Regulation plays a pivotal role in shaping forex and derivatives trading in Switzerland. FINMA’s strict oversight, combined with self-regulatory efforts, ensures a secure and transparent trading environment. While these rules impose certain limitations, they also enhance market stability and investor confidence. furthermore, Switzerland is likely to remain at the forefront of regulated forex and derivatives trading, balancing innovation with robust consumer protection.
For traders and brokers alike, understanding these regulations is crucial for navigating the Swiss market successfully. By adhering to compliance standards, stakeholders can thrive in one of the world’s most respected financial jurisdictions.