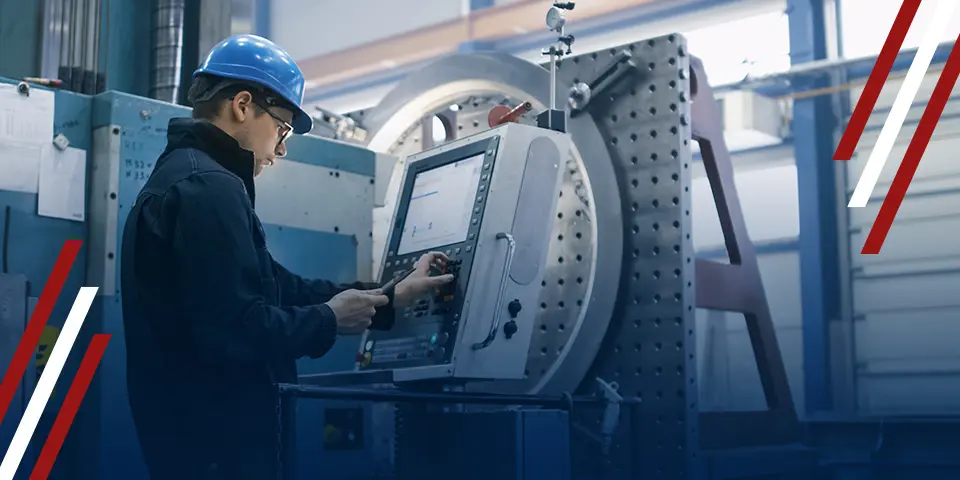
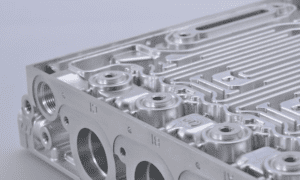
CNC machining is a way to make parts using computer-controlled machines. These machines follow a digital design to cut and shape materials like metal or plastic. Many businesses are now using CNC because it gives fast and accurate results.
It also helps reduce mistakes and saves time. In this article, we will look at why CNC machining is becoming more popular, how the technology is growing, where it is used, and how to choose the right service for your needs.
The Role of CNC in Manufacturing
CNC machining plays a big part in how products are made today. It uses smart machines to shape materials into the exact parts needed. This helps companies work faster, with fewer mistakes, and make better products. Many industries now depend on CNC to keep up with demand and quality.
How CNC Has Changed Production Standards?
CNC machining is very important in modern manufacturing. It helps companies make parts quickly and with the same quality every time. In the past, making parts by hand took more time and often had small errors.
Now, CNC machines can follow exact steps again and again, which saves time and improves quality. This change allows factories to work faster, reduce mistakes, and meet customer needs more easily. Many businesses are turning to online CNC service, which provides quick access to advanced machining technology without the need for large upfront investments.
Core Benefits:
- Makes parts faster than manual methods
- Keeps the same size and shape every time
- Works day and night without breaks
- Lowers mistakes and wasted materials
- Helps deliver products on time
- Let workers focus on design and planning
The Development of CNC Machining
CNC machining didn’t start out with computers. In the beginning, machines were controlled by people turning wheels and handles by hand. This method worked, but it was slow and not always accurate.
Things started to change in the 1940s and 1950s. During this time, there was a strong need to make parts faster and with better accuracy, especially for airplanes during wartime. So, engineers started using special codes on punched cards or tape to guide the machines automatically. This early method was called Numerical Control.
As time went on and computers became more common, they replaced those punched cards. By the 1970s, machines could be fully controlled by computers. This was a big step. It meant the machines could move more smoothly and follow more complex instructions with little help from humans.
From the 1980s onwards, software helped even more. Designers could create part shapes on a screen and send the exact instructions to the machine with just a few clicks. Over time, CNC machines became faster, smarter, and more precise. Today, cnc services are used in almost every industry, from cars to electronics, making high-quality parts quickly and with very little waste.
CNC Technology
CNC technology works by using machines, computer programs, and control systems. The machines follow instructions given by the software. These instructions help the machines cut, shape, or drill materials with great accuracy.
CAD and CAM programs help designers make digital models. These models are then used to guide the machines. This makes the work faster and more correct.
Modern CNC machines can also check their work while running. Real-time systems help find mistakes and fix them quickly. This keeps the final product clean and exact.
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is used in many industries around the world. It helps make strong, accurate, and detailed parts. Because it’s fast and precise, many companies rely on CNC machines to improve their products and save time.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry uses CNC machines to make parts for airplanes, rockets, and satellites. These parts must be very strong but also lightweight. CNC machines help create them with great care and accuracy.
Automotive
In the car industry, CNC machines are used to make engines, gears, and other important parts. They help companies produce vehicles faster while keeping high quality.
Medical
Hospitals and doctors need tools that are clean, safe, and well-shaped. CNC machines make surgical tools, implants, and medical devices that are both strong and precise.
Electronics
CNC machines help create small and detailed parts used in electronics like computers, phones, and circuit boards. These parts need to be tiny but perfect in shape and size.
Defense
The defense industry uses CNC machines to build parts for military vehicles, weapons, and protective gear. These parts must be tough, reliable, and made exactly right.
Why Do Businesses Use CNC?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. It means machines are controlled by computers instead of people. This helps factories make things faster, better, and with less waste.
- High Precision and Consistent Quality: CNC machines can make the same part again and again with the exact size and shape. They don’t make mistakes like people sometimes do.
- Faster Production with Less Waste: These machines work fast and don’t stop often. They also use the right amount of material, so there’s less waste.
- Cost-Effective in the Long Run: Even though CNC machines can cost more at first, they save money later. You need fewer workers, and there’s less need to fix or redo parts.
- Flexibility for Different Industries: CNC machines can make many different products. It’s easy to change the design or material if needed.
How is the CNC Machining Industry Evolving?
The CNC machining industry is undergoing significant changes as technology advances and global demand for precision manufacturing rises. This evolution is driven by the increasing need for high-quality, customized parts across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
As a result, manufacturers are adopting smarter machines, integrating automated systems, and striving to meet rising demand for precision and speed.
Market Growth
The demand for CNC machining is growing due to increased automation in manufacturing processes and the need for higher precision in various sectors, especially automotive, aerospace, and healthcare.
Resourcing
One major challenge in the industry is the shortage of skilled labor, as CNC machining requires specialized knowledge and training. Companies are facing difficulties in finding qualified technicians to operate and maintain advanced CNC equipment, which can limit production efficiency.
Technological Advancements
The industry is seeing the rise of smarter CNC machines that incorporate AI, IoT, and machine learning to optimize operations and reduce downtime. These innovations allow machines to self-monitor and adjust, improving both productivity and precision.
What Are the Main Trends Shaping the Future of CNC Machining?
The future of CNC machining is being shaped by several key trends focused on automation, smart technology, and data-driven operations. These trends are helping businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance production capabilities. As technologies like robotics, AI, and IoT continue to advance, they are revolutionizing the way CNC machines are operated, monitored, and optimized.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are allowing for unmanned shifts and robotic handling of parts, which increases production efficiency and reduces human error. “Lights-out manufacturing,” where machines run 24/7 without human intervention, is becoming more common, driving cost savings and higher output.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are enabling predictive maintenance, helping machines anticipate and fix issues before they cause downtime. Smart quality control powered by AI ensures higher consistency and fewer defects in produced parts.
Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
The integration of IoT in CNC operations allows machines to communicate with each other and with centralized systems, improving coordination. Real-time data sharing and analytics provide valuable insights that help manufacturers make faster, more informed decisions to optimize performance.
Conclusion
CNC machining is rapidly evolving, offering greater precision, efficiency, and flexibility across industries. As technology advances, trends like automation, AI, and smart manufacturing are reshaping how products are made, making production faster and more accurate. The future of CNC machining is bright, offering exciting opportunities for both businesses and manufacturers.