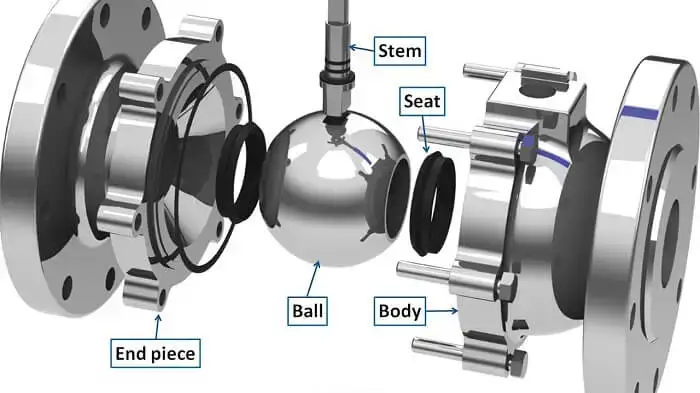
And a ball valve is used for controlling the Flow of Materials in a system. Its main part is a sphere with a hollow center; a 90· rotation of this ball aligns or misaligns the hole with the pipeline, hence regulating fluid flow. This construction makes them very popular in many industrial and some commercial applications.
The Basic Functions of a Ball Valve
As one of the key functions of valve balers is the opening and closing of fluid flow. When the hole matches the pipeline, the valve is open and fluid passes through. Through this valve, you have the ability to rotate the ball 90 degrees in the opening, perpendicular to the pipeline, which effectively closes the valve and creates a block of fluid moving through the valve. A quarter turn operation allows for rapid response times, making ball valves suitable for applications that require quick shut-off or flow adjustment.
Ball Valve Working Principle
These valves have a ball that rotates within the valve body. Rotating the ball so that the hole is perpendicular to the pipeline stops flow; aligning the hole with the pipeline allows fluid to flow. This straightforward mechanism offers consistency and effectiveness in managing fluid dynamics between pairs of systems.
Floating Ball Valve: here the ball is held between two sealing seats. Fluid pressure pushes the ball toward the downstream seat when applied, making the connection tight. It can be used for low to medium-pressure applications.
Trunnion Mounted Ball Valve: The ball is supported at the top and the bottom by trunnions or shaft on which the ball rotates, creating less operating torque, leading to improved sealing performance. Such a design is suited for high-pressure and large diameter applications.
V-Port Ball Valve — These types of valves have a V-shaped notch cut in the ball or the seat to modulate flow.
Basic Structure of the Ball Valve
Valve Body – It is a primary structural element in which all internal organs, and also connects the valve to the pipeline. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic.
Ball: The main component that flows the liquid — usually made of brass or stainless steel. It has a hole in the middle; if you align the hole with the pipeline, flow is allowed, while placing it at an angle stops flow.
Seat: This is the part found on both sides of the ball, aka; seats provide a tight seal when the valve is closed. Common materials include PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) and other elastomers.
Stem: A rod that links the ball and the actuator transmitting rotational movement. The stem usually contains sealing elements to avoid leaks.
Actuator: It is used to rotate the ball and can be manual (like a handle) or gear driven or powered by electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic sources.
Advantages of Ball Valves
Seamless operation: The ball valvue opens or closes with 90-degree rotation. They are well-suited for applications requiring emergency shut-off functionality.
Leak-proof Sealing: When in the closed position, ball valves create a tight seal that inhibits leakage. This is important for systems where fluid leakage is catastrophic.
Durable: Ball valves have a simple design and ability to resist the damage on valve components offering a longer service life as well as their ability to withstand high pressure and high temperature environments.
Low Operating Costs: The sturdy construction and simple architecture ensure low maintenance needs, which translates to lower costs to run.
Compatibility: Ball valves can handle various types of fluids, from water and oil to gases and corrosive materials, making them suitable for all branches of industry.
Applications of Ball Valves
Ball valves used in various industries:
On Oil and Gas: They help control the flow of oil and gas and make sure it all operates safely at high-pressure.
Chemical Processing: In industrial applications, ball valves are used to regulate the flow of different types of chemicals, allowing for accurate control and safe handling.
Water Treatment: Sometimes, in water treatment facilities, they regulate the flow of water and the addition of chemicals for treatment, allowing for effective water purification processes.
HVAC Systems: In HVAC applications, ball valves help control the flow of heating and cooling fluids, providing energy efficiency and improved temperature regulation.
Food and Beverage Sector: They control liquid and gas transfer in processing, maintaining cleanliness and adhering to safety regulations.
Ball Valve Selection Considerations
Here are some factors to consider when selecting a ball valve:
Material Selection: Use compatible materials with the controlled fluid, taking into account corrosion resistance and temperature tolerance.
33Considerations for Selecting Process Valves3Pressure and Temperature Ratings:1.
Connection Type: Choose a valve with suitable connection types (e.g., threaded, flanged, welded) to connect with the existing pipeline.
How about amending it to: Seal materials: Select seal materials that offer effective sealing for the specific fluid, taking into account parameters like chemical compatibility and temperature stability. Actuation Mechanism: Identifying the driving mechanism (manual/electrical/pneumatic/hydraulic) as per operational requirements.
Size and Flow Requirements: The size and flow of the valve must also match with the system so that the valve will perform well.
Ball valves are widely used in sectors such as chemical, oil and gas, water, power, and other industrial applications. By analyzing factors like what material it consists of, the pressure it can withstand, the temperature at which it can operate, the type of connection, the seal material, how it will get actuated, and the size you need, you can find the right ball valve for your system to function appropriately for longer.