Introduction
AI agents are transforming how businesses operate, delivering autonomous solutions that tackle complex challenges with precision and efficiency. For companies seeking to harness intelligent automation, understanding the diverse types of AI agents is critical. This guide explores seven essential AI agent categories, detailing their unique features and practical applications across industries like healthcare, retail, and logistics. Learn how the best AI agents can revolutionize your workflows in 2025 and beyond.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are intelligent systems that sense their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional automation, they range from basic rule-driven systems to advanced adaptive models, enabling flexibility in dynamic settings. In healthcare, they assist with diagnostics; in retail, they personalize shopping experiences; in logistics, they streamline supply chains. Tools like AI web scraper platforms enhance their capabilities by extracting real-time data, making them vital for businesses aiming to stay competitive in a fast-evolving digital landscape.
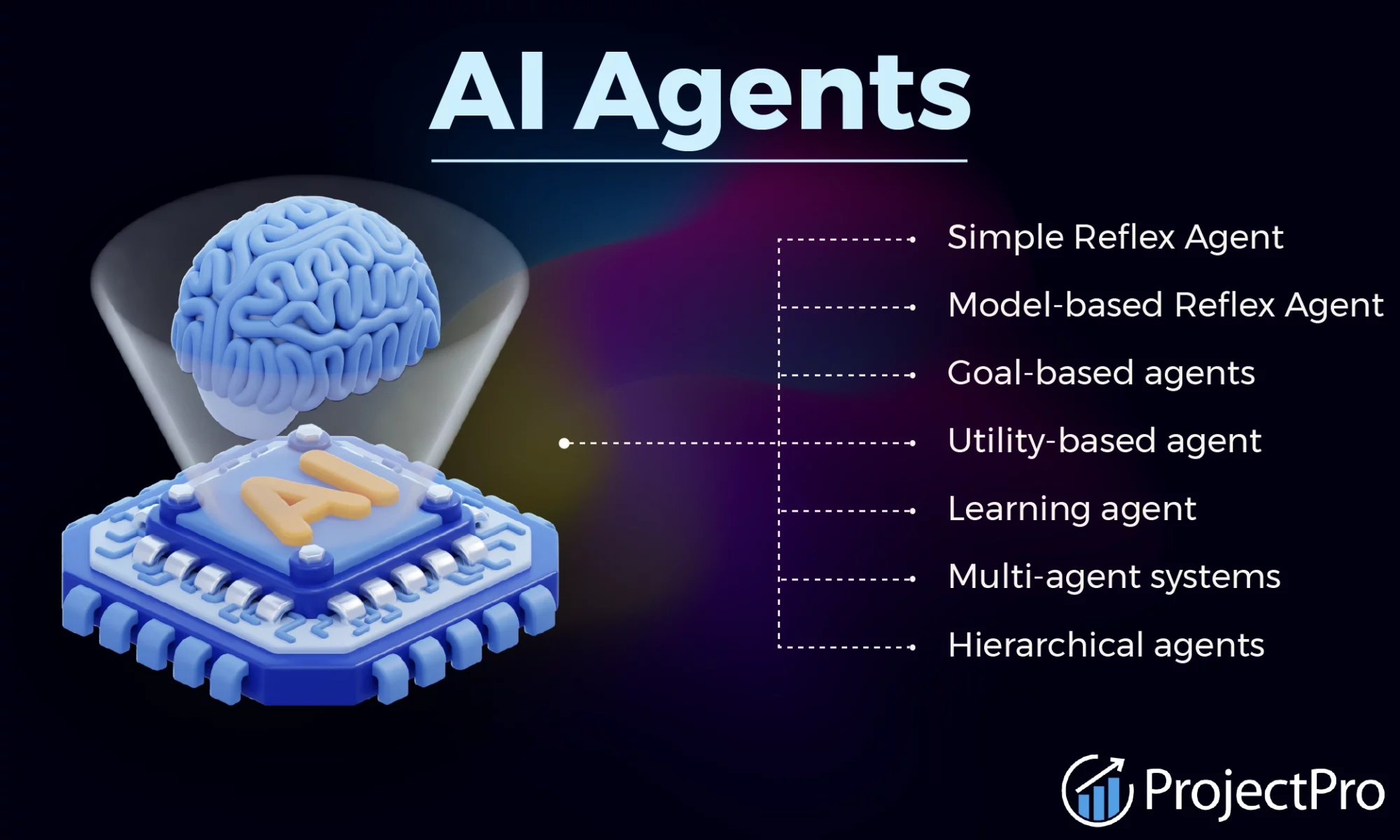
7 Types of AI Agents
1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents respond instantly to specific triggers using predefined rules, without memory or context. They excel in predictable, repetitive tasks where speed is key.
- Examples: IFTTT automates tasks like sending email alerts when a sensor detects a change. Google’s Dialogflow powers basic chatbots for e-commerce FAQs.
- Pros: Fast, simple to implement, low resource demands.
- Cons: Limited to known conditions, struggles with complexity.
- Use Case: Ideal for real-time monitoring, like website uptime checks or automated replies.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
These agents maintain an internal model of their environment, enabling decisions despite incomplete data. They track changes and predict outcomes, making them suited for dynamic settings.
- Examples: Waymo’s autonomous vehicles model traffic patterns to navigate safely. Nest thermostats adjust heating based on user habits and weather data.
- Pros: Handles partial data, reduces redundant actions.
- Cons: Complex design, potential for inaccurate models.
- Use Case: Perfect for AI web scraper tools like Octoparse or smart home systems requiring state awareness.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents plan actions to achieve specific objectives, evaluating multiple paths to find the best strategy. They adapt to obstacles, making them ideal for multi-step processes.
- Examples: Google Maps calculates optimal routes based on traffic. Amazon’s Kiva robots navigate warehouses to retrieve items efficiently.
- Pros: Strategic, flexible for complex tasks.
- Cons: High computational needs, struggles with conflicting goals.
- Use Case: Suited for project management tools like Monday.com or robotic automation in manufacturing.
4. Utility-Based Agents
These agents optimize decisions by evaluating outcomes against a value metric, balancing trade-offs for maximum benefit. They excel in scenarios with competing priorities.
- Examples: Netflix’s recommendation engine tailors content based on user preferences. Uber’s dynamic pricing adjusts fares by weighing demand and supply.
- Pros: Optimizes performance, handles uncertainty well.
- Cons: Complex utility functions, resource-heavy.
- Use Case: Ideal for financial trading platforms or ad optimization systems like Google Ads.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents improve over time by analyzing feedback and adapting to new patterns, reducing the need for manual updates.
- Examples: Spotify refines playlists by learning from user interactions. PayPal’s fraud detection adapts to emerging threats by analyzing transactions.
- Pros: Highly adaptive, reduces maintenance.
- Cons: Risk of biased learning, unpredictable during early training.
- Use Case: Best for evolving environments like customer support or predictive analytics.
6. Hierarchical Agents
Organized in layers, hierarchical agents delegate tasks from high-level planning to low-level execution, ensuring coordinated outcomes in complex systems.
- Examples: Amazon’s logistics network plans delivery routes while robots execute tasks. Smart factories integrate planning and production for seamless operations.
- Pros: Scalable, efficient for multi-tiered tasks.
- Cons: Complex to design, potential coordination challenges.
- Use Case: Suited for large-scale operations like supply chain management or industrial automation.
7. Multi-Agent Systems
Multiple agents collaborate to solve large-scale problems, leveraging specialized roles for collective intelligence and scalability.
- Examples: IBM’s Supply Chain Intelligence Suite optimizes global operations. Surtrac’s traffic system manages city-wide intersections for smoother flow.
- Pros: Scalable, fault-tolerant, powerful for distributed tasks.
- Cons: Complex management, risk of agent conflicts.
- Use Case: Ideal for enterprise solutions like smart cities or cross-functional automation.
The Future of AI Agents
The best AI agents are set to redefine business efficiency by 2025, with advancements in autonomy, collaboration, and adaptability. Multi-agent systems will dominate complex tasks, from optimizing global supply chains to powering smart cities. Learning agents will evolve faster, adapting to market shifts and consumer trends. Tools like AI web scraper platforms will enhance data-driven decisions, enabling businesses to unlock new levels of innovation and gain a competitive edge in an AI-driven world.
Conclusion
From simple reflex to collaborative multi-agent systems, AI agents offer powerful solutions for modern automation challenges. By understanding their unique strengths and applications, businesses can select the right type to transform operations in retail, healthcare, logistics, and beyond. For those seeking a no-code solution, BrowserAct’s AI web scraper—offering no-code, AI-powered data extraction from any site—promises cost-effective, reliable results for your best AI agents. Launching soon, join the BrowserAct waiting list to automate web scraping effortlessly.
Read More From Techbullion