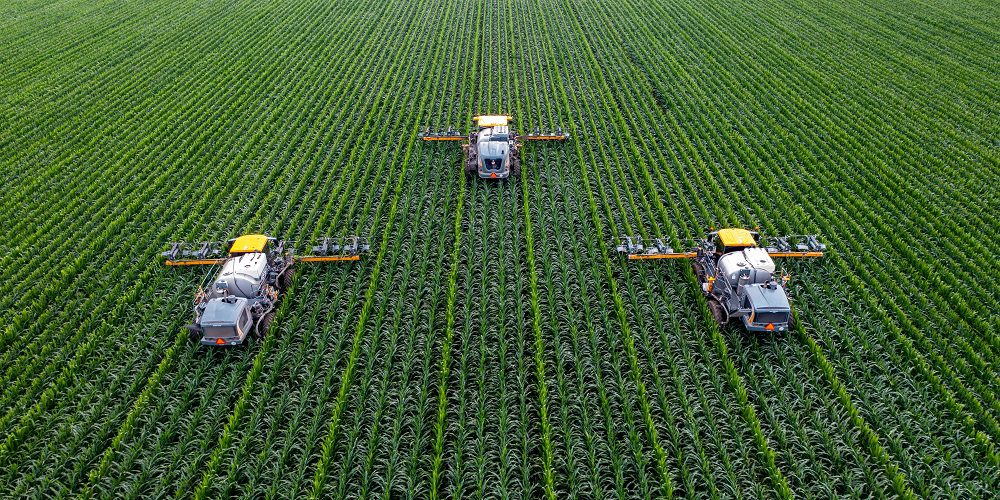
Welcome to the age of revolutionized agriculture! In this fast-paced era of technological advancements, traditional farming methods are making way for cutting-edge AgTech solutions. From drones monitoring crop health to AI-powered systems optimizing irrigation, farmers around the globe are embracing these innovative tools to increase efficiency and maximize yields. But with great opportunities come unique challenges, and that’s precisely what we’ll be exploring in this blog post.
Introduction to AgTech:
AgTech, or agricultural technology, refers to the use of technology in agriculture to improve farming processes and increase efficiency. It encompasses a wide range of tools, techniques, and methods that aim to modernize traditional agricultural practices. From precision farming and automated irrigation systems to drones and artificial intelligence, AgTech has the potential to revolutionize the way we grow crops and raise livestock.
The Advantages of AgTech for Farmers
AgTech, also known as agricultural technology, has been rapidly gaining momentum in recent years as a viable solution to the challenges faced by farmers in traditional agriculture practices. This innovative approach utilizes modern technology and data analysis to increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency in farming operations. In this section, we will discuss some of the key advantages that AgTech offers to farmers.
1. Improved crop management:
One of the major benefits of AgTech is its ability to provide real-time data on crop growth and health. Through the use of sensors, drones, satellites, and other advanced technologies, farmers can monitor their crops at every stage, from planting to harvesting. This helps them make informed decisions about irrigation schedules, fertilization needs, disease detection, and pest management. By having access to accurate and timely information about their crops, farmers can optimize their resources and ensure maximum yields.
2. Precision Farming:
With AgTech tools like GPS-guided tractors and automated machinery, farmers can now practice precision farming with incredible accuracy. This means that inputs such as seeds, pesticides, and fertilizers are applied only where needed instead of across entire fields or crops. As a result, there is less waste of resources, which translates into cost savings for the farmer while also reducing environmental impact.
3. Weather Monitoring:
Weather plays a crucial role in agriculture, and any unexpected changes can have significant impacts on crop yield. With AgTech solutions such as weather monitoring systems and predictive analytics software, farmers can receive accurate and real-time weather data specific to their location. This helps them plan ahead for potential risks and make necessary adjustments to their farming practices.
4. Increased Efficiency:
AgTech automates many labor-intensive tasks, reducing the time and effort required by farmers. For example, automated irrigation systems can be programmed to water crops at specific times and in precise amounts, eliminating the need for manual labor. Similarly, robotic harvesters can efficiently pick and sort produce, saving farmers valuable time and resources.
5. Cost Savings:
By optimizing inputs, reducing waste, and increasing efficiency, AgTech can help farmers save on costs in the long run. Precision farming techniques also result in higher crop yields, which means more produce to sell and increased income for farmers.
6. Access to Global Markets:
With the help of e-commerce platforms and online marketplaces, AgTech has made it easier for farmers to reach global markets. This has opened up new opportunities for small-scale farmers who previously had limited access to large markets due to logistical barriers. With AgTech solutions like online marketplaces and digital payment systems, farmers can now sell their products directly to consumers or businesses worldwide.
Challenges Faced by Farmers When Adopting AgTech:
Farming has always been a challenging profession, requiring hard work, careful planning, and a deep understanding of natural systems. With the emergence of AgTech, or agricultural technology, farmers now have access to new tools and techniques that can help improve their productivity and efficiency. However, adopting these technologies also presents its own set of challenges for farmers.
1. Cost of Implementation:
One major challenge faced by farmers when adopting AgTech is the cost associated with implementing these technologies. Many modern farming technologies, such as precision agriculture systems, drones, and smart irrigation systems, can be quite expensive to purchase and install. This can be particularly challenging for small-scale farmers who may not have the financial resources to invest in these technologies.
2. Lack of technical knowledge:
Another hurdle for farmers is the lack of technical knowledge required to operate and maintain AgTech devices. Farmers are often used to traditional farming methods, which do not require much technical expertise. Therefore, it may take time for them to learn how to use new AgTech devices effectively.
3. Access to a Reliable Internet Connection:
Most AgTech devices rely on an internet connection to function efficiently. However, many rural areas where farming takes place do not have reliable internet connectivity or even electricity supply at all times. This can hinder the proper functioning of AgTech devices and limit their effectiveness on farms.
4. Integration with Existing Systems:
Farmers may face difficulties integrating new technological systems with their existing ones seamlessly. For instance, if a farmer adopts a precision agriculture system but does not have accurate maps of their farm, it can be challenging to use the system effectively.
5. Resistance to Change:
Farming is a traditional profession, and many farmers may be resistant to change or new methods of farming. Some may prefer to stick to their traditional ways of farming rather than adopting new technologies, which can lead to slower adoption rates.
6. Maintenance and upkeep:
AgTech devices require regular maintenance and upkeep for them to function efficiently. This can be a challenge for farmers who may not have the technical expertise or resources to troubleshoot and repair these devices when needed.
Overcoming the Challenges
The AgTech revolution has brought about numerous benefits for farmers, such as increased efficiency, improved productivity, and cost savings. However, it also presents its fair share of challenges. Fortunately, governments around the world have recognized the potential of AgTech and are taking steps to support its growth and adoption in the agricultural sector.
Government Initiatives:
One of the main challenges faced by farmers is access to technology. Many small-scale farmers do not have the resources or knowledge to invest in expensive technologies. To address this issue, governments are implementing various initiatives aimed at providing financial assistance and training programs to help farmers adopt AgTech.
For instance, in India, the government launched a program called “Digital India” with a budget of $480 million to promote digital literacy among rural communities. This initiative includes providing subsidies for buying smartphones and offering free digital training courses for farmers to learn how to use agricultural apps and other digital tools effectively.
Similarly, in Africa, where smallholder farming is prevalent, governments are investing in mobile phone networks and internet connectivity in rural areas. This enables farmers to access information on weather forecasts, market prices for their crops, and best farming practices through their phones.
Partnerships:
Another challenge that often arises when implementing new technologies is bridging the gap between tech companies and traditional agriculture businesses. To overcome this issue, partnerships between private tech companies and government agencies have been formed.
For example, Silicon Valley-based startup Plenty has partnered with several government agencies in Singapore to build a vertical farming facility that will help the country reduce its reliance on food imports. The government has provided funding and support for this project, which will also provide job opportunities for local farmers.
Similarly, in the Netherlands, Wageningen University & Research has partnered with various government institutions to develop smart farming technologies that can be implemented by Dutch farmers. This collaboration has led to the development of precision agriculture tools such as drones and sensors that help farmers optimize their crop production.
Support:
Governments are also providing support for AgTech startups and entrepreneurs through funding programs, tax incentives, and other forms of assistance. In the United States, the Department of Agriculture (USDA) provides grants and loans to small businesses developing innovative solutions for agriculture.
Additionally, governments are creating regulatory frameworks and policies to promote the adoption of AgTech while ensuring data privacy and security. For example, the European Commission’s Farm-to-Fork strategy includes plans to support digitalization in agriculture while protecting farmers’ interests.
Conclusion
The challenges faced by AgTech startups and farmers require collaboration between governments, tech companies, and traditional agricultural businesses. By implementing initiatives, forming partnerships, and providing support, governments play a crucial role in driving the growth and adoption of AgTech.