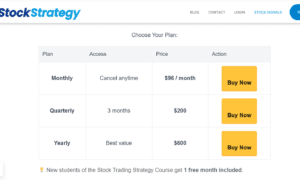
Introduction:
The stock market, often depicted as a bustling financial hub, is an integral cog in the machinery of the global economy. Whether you’re a novice investor eager to dip your toes into the world of stocks or simply intrigued by the intricate mechanisms behind it, this article is your guide to unraveling the mysteries of the stock market. In the following pages, we’ll take you on a journey to answer the question “What is a stock market” and the inner workings that propel it forward.
From the concept of ownership through shares to the pivotal role of stock exchanges and the importance of diversification, this comprehensive overview will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate this dynamic financial landscape. So, whether you’re planning to invest or simply seeking to demystify the world of stocks, fasten your seatbelt as we embark on this educational journey into the realm of the stock market.
Getting Started with Stock Market
The stock market is a fascinating financial ecosystem that plays a pivotal role in the global economy. If you’re new to investing or simply curious about the mechanics behind it, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of what a stock market is and how it operates.
What is a stock market?
A stock market, also known as an equity market, is a platform where individuals and institutions come together to buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. These shares represent ownership in those companies, and the stock market is the place where they change hands. It’s like a giant marketplace for company ownership.
How Does It Work?
Stock markets work on the principles of supply and demand. When a company goes public, it issues shares to raise capital. Investors can then buy these shares, making them shareholders in the company. The stock’s price fluctuates based on various factors, including company performance, economic conditions, and investor sentiment.
Key Players in the Stock Market
The stock market involves several key players, each with a unique role:
- Investors: Individuals and institutions who purchase shares.
- Stock Exchanges: These are the physical or digital platforms where trading occurs, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or NASDAQ.
- Brokers: Intermediaries who facilitate stock transactions for investors.
- Regulators: Government bodies like the SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission) that oversee and regulate stock markets.
The Role of Stock Exchanges
Stock exchanges are vital to the functioning of the stock market. They provide a structured and regulated environment for buying and selling stocks. Companies looking to go public list their shares on these exchanges. The two most prominent stock exchanges in the United States are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ.
Understanding Stock Market Orders
In the stock market, investors place orders to buy or sell shares. These orders come in various types, including market orders and limit orders.
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a stock immediately at the current market price.
A limit order allows investors to specify a particular price at which they want to buy or sell a stock, and the order is executed only when the market reaches that price.
Understanding these order types is crucial for effective stock market participation.
The Role of Brokers
Brokers are intermediaries that facilitate the buying and selling of stocks on behalf of investors. They execute orders, provide research and analysis, and offer investment advice. Brokers can be full-service or discount brokers, depending on the range of services they provide. Choosing the right broker is an important decision for investors, and it often depends on their level of experience and the services they require.
Market Regulation and the Role of Regulators
Stock markets are subject to regulation to ensure fairness and transparency. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is the primary regulatory body overseeing the securities industry. The SEC enforces securities laws, regulates securities markets, and protects investors. Its role is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the stock market.
Why Invest in the Stock Market?
Investing in stocks can offer the potential for long-term wealth accumulation. Historically, stock markets have outperformed many other investment options. However, it’s essential to understand that they also involve risks, and it’s important to diversify your investments to manage those risks effectively.
Diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading your investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. It helps reduce the impact of poor performance in any single investment and can enhance overall portfolio performance.
Conclusion
In this detailed exploration of the stock market, we’ve unraveled the basics of what a stock market is, how it functions, and the key players involved. Understanding the role of stock exchanges, the types of stock market orders, the importance of brokers, and the regulatory oversight of the market is crucial for successful investment. Additionally, we’ve emphasized the significance of diversification as a risk management strategy. The stock market can be a valuable tool for wealth creation, but it’s essential to approach it with knowledge and a diversified strategy.
Read More
Understanding the Dynamics of Stock Market: A Comprehensive Guide
The Intricacies of the Stock Market: A Comprehensive Guide to How the Stock Market Works
Understanding Stock Markets in the UK
Stock Market 101: Differentiating Dow Jones and Nasdaq for Beginners
Learn Risk Management At The Best Stock Market Institute in India