The Fourth Industrial Revolution, characterized by the fusion of digital technologies and physical systems, is transforming industries across the globe. In this era of advanced automation and data-driven decision-making, precision manufacturing services play a crucial role.
In a post by Medical Plastics News, it was mentioned that the challenge of achieving precise geometric dimensioning and tolerancing is resolved through precision machining. This is because the manufactured parts are now consistently aligned with the 3D model down to the micron level. In this article, we will explore the key contributions of precision manufacturing services in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
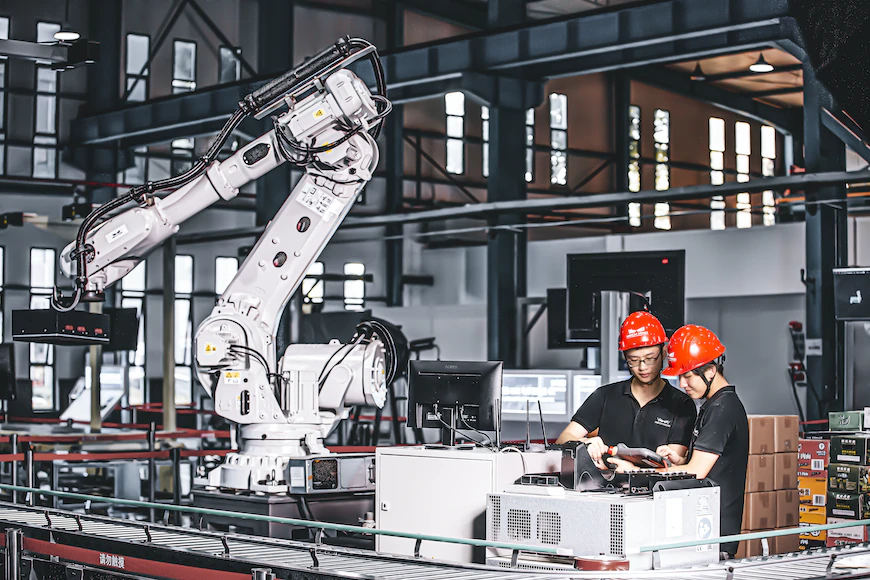
Advanced Robotics and Automation
Precision manufacturing services leverage advanced robotics and automation to streamline production processes. According to L&T Precision, robots with artificial intelligence and machine learning skills can do difficult jobs with precision and speed, lowering the possibility of mistakes.
Automated systems facilitate continuous production, leading to improved productivity and reduced costs. By automating repetitive tasks, manufacturers can allocate their human resources to more complex and creative endeavors. Click here to discover how the integration of robotics and automation enhances operational efficiency and enables manufacturers to meet the demands of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
IoT Integration
Precision manufacturing services embrace the Internet of Things (IoT) to connect machines, sensors, and devices on the shop floor. This connection enables real-time monitoring and data sharing, resulting in a more integrated industrial ecosystem.
Manufacturers obtain important insights into their operations by gathering and analyzing data from numerous sources, leading to better decision-making and proactive upkeep. IoT integration also enables remote monitoring, allowing manufacturers to optimize production processes and minimize downtime. The ability to harness IoT technology enhances efficiency and responsiveness in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Additive Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry has been transformed by additive manufacturing, sometimes known as 3D printing. Precision manufacturing services utilize this technology to build complex and customized components, prototypes, and even finished products. By layering materials based on digital designs, additive manufacturing eliminates many traditional manufacturing constraints.
According to Springer, additive techniques can aid in the identification of underlying flaws in goods that are costly to repair in later stages of manufacturing. These technologies enable the manufacturing of complex-shaped objects directly from computer data in a very short period of time utilizing the most automated procedures.
With additive manufacturing, manufacturers can achieve greater design flexibility, faster time to market, and cost-effective production, making it a key enabler in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Big Data Analytics
Precision manufacturing services leverage big data analytics to extract valuable insights from large volumes of data generated during the production process. By analyzing data related to machine performance, product quality, and supply chain, manufacturers can optimize operations, improve product quality, and enhance decision-making.
Predictive analytics helps identify potential equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and reduced downtime. Furthermore, data analytics enables manufacturers to identify trends, customer preferences, and market demands, aiding in product innovation and customization. The integration of big data analytics empowers manufacturers to adapt to the dynamic landscape of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
AR in Manufacturing
Precision manufacturing services employ augmented reality (AR) technology to enhance various aspects of the production process. AR systems provide real-time visual information, overlaying digital data onto the physical environment. In manufacturing, AR can assist in assembly tasks, quality inspections, and training processes.
According to an Automation World article, it is interesting to note that implementing AR can be more challenging compared to virtual reality (VR) because AR systems require a way to accurately position virtual elements in the real world. To address this, developers in the manufacturing sector have been adopting technologies from the computer-game industry, which has already tackled many of these issues.
AR in manufacturing enables workers to access relevant information, such as assembly instructions or maintenance procedures, hands-free. AR also facilitates remote collaboration, allowing experts to provide guidance from a distance. By incorporating AR technology, precision manufacturing services improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance worker productivity in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Cybersecurity in Precision Manufacturing
With increased connectivity and data exchange, precision manufacturing services face cybersecurity challenges in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Protecting sensitive data, intellectual property, and operational systems becomes paramount. Manufacturers need robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard their networks, IoT devices, and production processes from cyber threats.
Encryption, access control, network segmentation, and regular security audits are some essential practices. Additionally, training employees on cybersecurity best practices is crucial to maintain a secure manufacturing environment. Cybersecurity ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and technologies, enabling precision manufacturing services to thrive in the digital era.
Key Takeaways
Precision manufacturing services, through using modern technology to change the manufacturing business, are playing a critical role in the future of Industry 4.0. Manufacturers are attaining better levels of precision, efficiency, productivity, and creativity by integrating robots, automation, IoT, additive manufacturing, big data analytics, and augmented reality.
Real-time monitoring, data-driven choices, customization, and increased worker productivity are all possible with these services. However, cybersecurity safeguards are required to protect sensitive data and systems. Finally, precision manufacturing services are propelling the growth of manufacturing in the digital era, transforming processes, and helping enterprises to prosper in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.