Why Cybersecurity Is Critical in Hybrid and Remote Work Environments
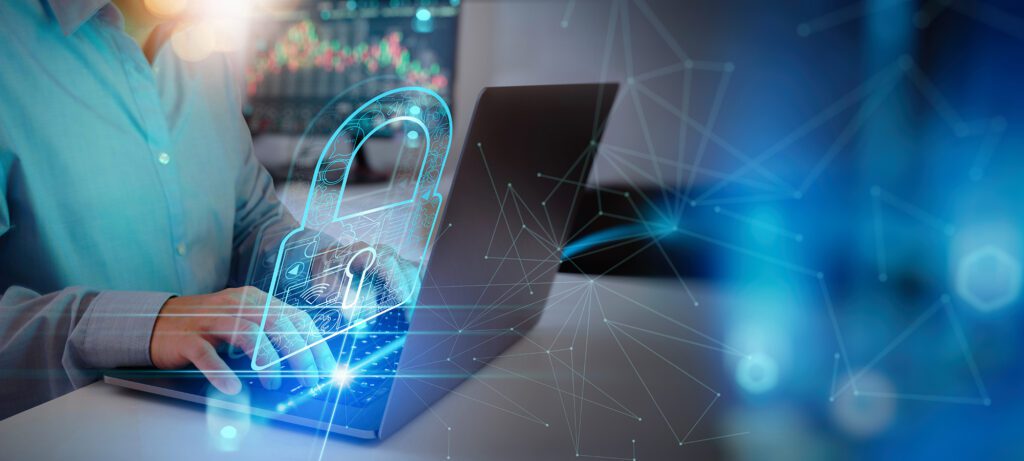
Hybrid and remote working have reshaped business operations, expanding the digital footprint and increasing exposure to cyber threats. The decentralisation of the workplace has created more entry points for attackers, making robust cybersecurity essential for business resilience.
Cybersecurity enables secure and flexible operations by protecting digital assets, securing data exchanges, and ensuring only authorised users gain access to critical systems. For cloud architects, remote employees, and CISOs, secure access is the foundation of a productive hybrid model.
Without the right protections in place, distributed teams risk data breaches, service disruption, and regulatory violations. Strong cybersecurity frameworks reduce these risks and support business continuity.
Understanding New Risks in a Decentralised Workforce
Cybersecurity protects remote work environments by managing the unique threats they face. Common risks include:
- Phishing attacks targeting users through email and messaging platforms
- Malware infections from unsecured downloads or compromised websites
- Unauthorised access due to weak credentials or shared devices
- Data breaches caused by unsecured home or public networks
Each remote device introduces a new potential vulnerability. Unmanaged endpoints and poorly configured networks increase risk, especially when employees access business systems from personal devices or open networks.
Threat actors exploit these gaps using social engineering, ransomware, and credential theft. Effective cybersecurity strategies monitor, isolate, and respond to these threats in real time.
Key Cybersecurity Tools and Practices for Remote Teams
Remote teams rely on layered protection supported by a range of security tools. Businesses that adopt scalable, multi-layered defences reduce their exposure to attacks and maintain better visibility over distributed assets.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Secure encrypted access for remote connections
- Firewalls: Block unauthorised traffic and monitor incoming/outgoing data
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Verifies user identity beyond passwords
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Monitors and secures individual devices
- Cloud access control tools: Manage user privileges across cloud applications
IT teams are responsible for implementing and maintaining these tools across multiple devices and networks. Many rely on cybersecurity services to manage the complexity, improve response times, and support ongoing compliance.
Securing Endpoints and Devices at Scale
Endpoints are among the most targeted assets in remote environments. Endpoint-specific tools help detect threats, enforce updates, and block unauthorised activities.
Patch management ensures that all devices run updated software. Antivirus software identifies known threats, while continuous monitoring detects anomalies that may signal intrusion attempts.
Visibility across all endpoints is essential. IT teams must track device health, activity logs, and policy compliance in real time. Scalable endpoint management platforms support proactive responses to new vulnerabilities.
Encryption, Authentication, and Access Control
Encryption protects data as it moves across devices, networks, and cloud platforms. It renders data unreadable without the correct decryption key, protecting sensitive information in transit and at rest.
Employees access systems through secure VPNs that establish encrypted connections between endpoints and enterprise networks. This reduces the risk of interception, especially over public internet connections.
Authentication systems enforce secure logins using multi-factor protocols. Access control systems define who can view or edit data, limiting exposure in case of compromise.
Creating and Enforcing Security Policies for Remote Work
Security policies ensure that remote employees follow consistent procedures when accessing business systems. Centralised control enables administrators to enforce these policies regardless of employee location.
Best practices include:
- Defining role-based access control
Using secure file sharing platforms
Requiring regular password changes
Enforcing endpoint compliance standards
HR departments and compliance officers work with IT teams to ensure policies align with legal obligations and company values. Governance frameworks provide clarity on acceptable use and help detect violations early.
Training and Awareness for Remote Employees
Employee training is one of the most effective tools for preventing cyber incidents. Regular education reduces risk by equipping staff with the knowledge to spot phishing, social engineering, and suspicious links.
Training programmes should cover:
- Identifying suspicious emails and attachments
- Creating and managing secure passwords
- Updating devices and software promptly
- Reporting incidents through proper channels
Proactive education supports a culture of security. When employees understand how their actions affect risk, overall threat exposure is reduced.
Compliance and Legal Considerations in Hybrid Security
Remote working does not exempt businesses from data protection laws. Organisations must ensure full compliance with regulations such as GDPR, ISO 27001, HIPAA, or sector-specific standards.
Cybersecurity infrastructure must support secure data handling, maintain detailed records, and provide clear audit trails. Failure to meet these requirements can lead to fines, loss of customer trust, and legal challenges.
Documenting access logs, managing encryption keys, and proving breach detection capabilities are all vital components of a compliant cybersecurity setup.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements Remotely
Remote compliance is achievable through well-designed infrastructure and reliable partners. Cloud platforms often include built-in compliance tools such as encryption, data region controls, and automated reporting.
Secure handling of sensitive data across borders requires local storage options and adherence to regional standards. Managed service providers and cloud security partners assist in configuring systems that meet these demands.
Auditable systems ensure that every access, update, or transfer is logged and traceable. This transparency is essential during audits or breach investigations.
Benefits of Strong Cybersecurity for Distributed Workforces
Strong cybersecurity brings long-term value to hybrid and remote work models. It improves business continuity, protects sensitive data, and builds trust with clients and partners.
Key benefits include:
- Resilience against downtime, breaches, or disruptions
- Scalability to support growing teams and evolving tools
- Accessibility that maintains speed and usability without sacrificing security
A secure digital environment ensures that teams can collaborate effectively across locations, without compromising compliance or performance.
Supporting Productivity and Secure Collaboration
Cybersecurity enables productive collaboration by providing secure access to cloud services, communication platforms, and shared resources. Teams work confidently, knowing that data is protected.
Infrastructure that integrates seamlessly with productivity tools reduces friction. File-sharing, video conferencing, and task management all function securely when protected by appropriate authentication and data controls.
Remote teams operate more efficiently when security supports, rather than hinders, their daily workflows.