The sense of smell plays a vital role in daily life—helping us enjoy food, detect danger, and connect with the world around us. When that sense is diminished or lost altogether, it can have a significant impact on quality of life. For patients experiencing smell disorders, a rhinologist is often the most qualified medical specialist to diagnose and treat the problem effectively.
Specialists in Smell and Sinus Health
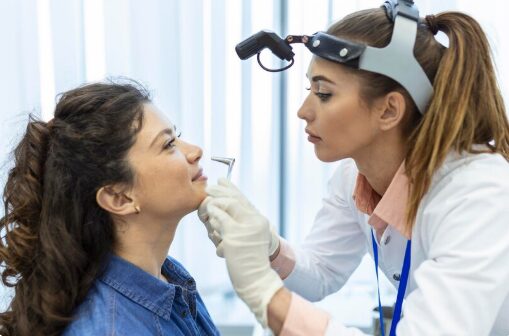
A rhinologist is a subspecialist within the field of otolaryngology (ENT) who focuses specifically on diseases and conditions of the nose, sinuses, and related structures. This includes nasal obstruction, chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, deviated septum, and critically—olfactory (smell) dysfunction.
While general ENT physicians address a broad range of ear, nose, and throat concerns, rhinologists bring advanced expertise in complex nasal and sinus issues that may require detailed evaluation, medical therapy, or surgical intervention.
Understanding Smell Disorders
Smell disorders—known medically as olfactory dysfunction—can present in several forms:
- Hyposmia: A reduced sense of smell
- Anosmia: Complete loss of smell
- Parosmia: Distorted sense of smell
- Phantosmia: Smelling odors that aren’t present
These issues can result from viral infections (such as COVID-19), chronic sinus disease, nasal obstructions, head trauma, neurological conditions, or prolonged exposure to environmental irritants.
How a Rhinologist Helps
A rhinologist plays a central role in identifying and treating the underlying causes of smell disorders. Their process typically involves:
1. Comprehensive Evaluation
This includes a detailed medical history, smell testing, and nasal endoscopy—a minimally invasive procedure using a small camera to examine the nasal passages and sinus openings.
2. Advanced Imaging
If necessary, imaging such as a CT scan may be ordered to assess for structural abnormalities, inflammation, or sinus disease contributing to the dysfunction.
3. Targeted Medical Treatment
Depending on the cause, treatment may involve:
- Anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., nasal corticosteroids)
- Oral or topical antibiotics
- Saline rinses
- Olfactory training (a therapy involving repeated exposure to specific scents)
4. Surgical Intervention
If conservative treatment fails, a rhinologist may recommend procedures such as endoscopic sinus surgery to remove blockages, nasal polyps, or correct anatomical issues that restrict airflow and olfactory access.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Many patients delay seeking care for smell loss, assuming it will resolve on its own. However, early intervention can greatly improve outcomes—particularly when smell loss is linked to treatable conditions like chronic sinusitis or nasal polyps. In cases of post-viral anosmia, prompt medical management and olfactory training can increase the likelihood of recovery.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Many patients delay seeking care for smell loss, assuming it will resolve on its own. However, early intervention can greatly improve outcomes—particularly when smell loss is linked to treatable conditions like chronic sinusitis or nasal polyps. In cases of post-viral anosmia, prompt medical management and olfactory training can increase the likelihood of recovery.
Conclusion
Smell disorders can be frustrating and life-altering, but they are not without hope. A rhinologist offers specialized care tailored to the complex structures of the nose and sinuses, providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatment options. If you’re experiencing persistent changes in your sense of smell, consulting a rhinologist may be the first step toward restoring a vital part of your sensory experience.