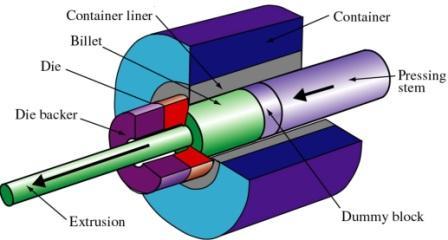
Metal extrusion is a process where a block of metal is forced through a die to create a specific shape. The method has been used in manufacturing for more than a century. It allows factories to make complex profiles with high accuracy and efficiency. There are many forms of extrusion, such as hot extrusion, cold extrusion, direct, and indirect methods. One form that stands out for speed and versatility is impact extrusion.
Impact extrusion takes the basic idea of extrusion and adapts it for soft metals, quick cycles, and precise shapes. It is often used to make everyday products that most people do not realize are created this way. Understanding how it works helps both beginners and experienced professionals see its role in modern production.
What is Impact Extrusion
Impact extrusion is a cold working process. It uses a high speed press to force a slug of metal into a die with one quick stroke. The metal flows around the punch and takes the shape of the cavity in the die. The action happens in a fraction of a second, which is different from slower methods of extrusion that apply steady pressure.
This process usually works with softer metals such as aluminum, tin, zinc, and lead. Steel and harder alloys can also be used, but they require stronger equipment and special lubricants. The speed and force make impact extrusion unique compared to other forming methods.
How the Process Works
The steps of impact extrusion can be broken down in a simple way:
1. Preparing the slug
A slug is a small cylindrical piece of metal cut from a rod or sheet. The slug must be clean and free of oxides or dirt. In many cases, lubrication is applied to help the metal flow smoothly in the die.
2. Positioning the slug in the die
The slug is placed into the bottom of a die cavity. The die is made of hardened steel to handle the repeated force of the press.
3. The punch stroke
A punch, attached to a high-speed press, strikes the slug with great force. This impact forces the metal to flow around the punch and into the die cavity. Depending on the design, the metal can flow backward or forward relative to the punch movement.
4. Ejecting the part
Once the press retracts, the shaped part is removed from the die. The part may need trimming, heat treatment, or surface finishing depending on the application. This entire sequence can happen in less than a second, which makes impact extrusion ideal for mass production.
Types of Impact Extrusion
Impact extrusion is not a single uniform process. There are a few variations depending on how the metal flows:
- Forward impact extrusion: The slug flows in the same direction as the punch.
- Backward impact extrusion: The slug flows opposite to the punch direction, forming hollow shapes like tubes or cans.
- Combined impact extrusion: Uses both directions of flow in one stroke to form complex parts.
Backward impact extrusion is the most common method because it creates seamless hollow shapes that are useful in many industries.
Why Impact Extrusion Matters
Impact extrusion offers several benefits that make it important in manufacturing. These advantages explain why the process is used widely across industries.
- High production speed. The process is fast, with cycle times measured in fractions of a second.
- Material efficiency. There is little waste because the slug is almost fully shaped into the final product.
- Strength improvement. The cold working effect increases hardness and tensile strength of the metal.
- Precision. The method produces parts with close tolerances and smooth surfaces.
- Seamless designs. Hollow parts made without welding or joining have better strength and reliability.
Common Applications and Industries
Packaging
One of the most visible uses of impact extrusion is in packaging. Aluminum beverage cans, deodorant containers, and aerosol cans often come from backward impact extrusion. The seamless design prevents leakage and ensures strength while keeping the container lightweight.
Automotive
The automotive industry uses impact extrusion to produce lightweight but strong components. Examples include brake cylinders, sensor housings, fuel system parts, and electrical connectors. Using aluminum or other soft metals keeps weight down while ensuring durability.
Electronics
Impact extrusion is useful in making housings for capacitors, battery cases, and connectors. These parts need precision and consistency, which the process provides. The seamless nature of the parts also ensures safety for batteries and electronic components.
Medical Devices
Some medical containers and components are made with impact extrusion. Aluminum tubes for ointments and inhalers are common examples. The process ensures cleanliness, reliability, and the ability to produce in high volume.
Limitations of Impact Extrusion
Although it has many advantages, impact extrusion also has limits. These following factors must be considered when deciding if impact extrusion is the right method for production.
- Material choice. Softer metals are better suited. Harder metals are possible but increase tool wear and energy costs.
- Tooling costs. Dies and punches must be made from high-strength steel and replaced after wear. Initial costs can be high.
- Part size. Impact extrusion works best for small to medium-sized parts. Large components are not practical.
- Surface finishing. Some parts need secondary finishing to remove surface marks left by the die or lubricant.
Comparison to Other Extrusion Methods
Traditional extrusion methods, such as hot extrusion, work with a wide range of materials and larger parts. They use steady pressure and heat to form the metal. This allows for complex shapes but takes more time.
Impact extrusion, in contrast, is faster and more suitable for small precision parts. It is a specialized process rather than a replacement for all extrusion. Manufacturers choose it when speed, strength, and seamless design matter more than shape complexity or material range.
The Role of Lubrication and Heat Treatment
Lubrication plays a key role in impact extrusion. It reduces friction, prevents sticking, and protects the tooling. Common lubricants include zinc stearate, graphite, and oil-based compounds. Without proper lubrication, tool life drops and part quality suffers.
Heat treatment may also follow the process, especially for aluminum parts. Annealing can restore ductility lost during cold working. This balance of forming and treatment ensures that the final product has the right combination of strength and workability.
The Future of Impact Extrusion
The process continues to evolve with better tooling materials, automated presses, and improved lubricants. Manufacturers also focus on sustainability by recycling aluminum and reducing energy use. As industries push for lighter materials and faster production, impact extrusion remains a reliable method.
In Conclusion
Impact extrusion is a specialized form of metal forming that combines speed, precision, and strength. By forcing a slug of metal into a die with a single stroke, manufacturers can create seamless, lightweight, and durable parts. Industries from packaging to automotive rely on it for mass production of essential components.
While it has limits in material choice and tooling costs, its advantages in speed and quality keep it relevant in manufacturing. The first step in learning about the process is asking, how does impact extrusion work, and then exploring its stages. For both beginners learning about metal forming and professionals, impact extrusion shows how a simple idea, shaping metal through impact, can support industries worldwide.