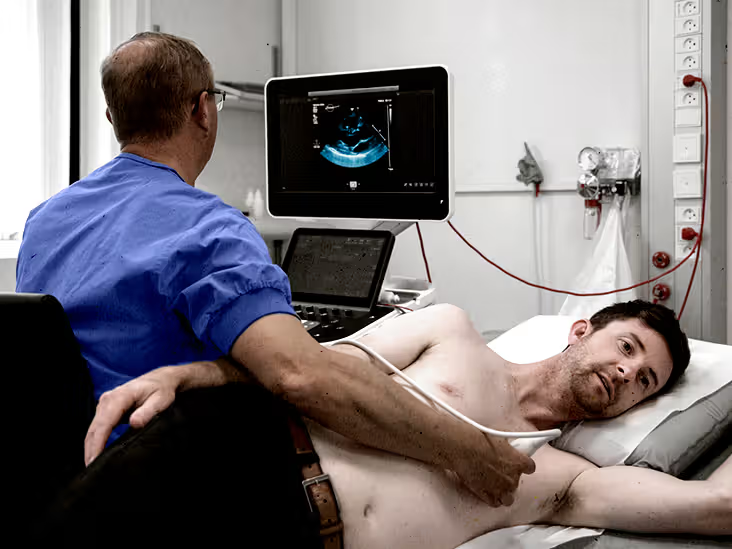
Heart conditions can be difficult to diagnose, often requiring specialised tools to provide a clear picture of a patient’s heart health. Among the most effective methods is the echo test for heart, also known as echocardiography.
This non-invasive imaging technique provides real-time images of the heart, allowing doctors to detect and evaluate a wide range of heart conditions. In this article, we will explore the significance of echo tests, their procedures, and how they contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases.
What is an Echo Test for Heart?
An echo test for heart, or echocardiogram, uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. It is a highly effective diagnostic tool for detecting heart abnormalities, as it provides a live, moving image of the heart in action.
The test allows doctors to observe the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow, giving them valuable insights into the heart’s performance.
How Does an Echo Test Work?
During an echo test, a device called a transducer is placed on the chest to send high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) into the body. These sound waves bounce off the heart’s structures and are converted into images that can be viewed on a monitor.
The procedure is typically painless and does not require any incision or surgery, making it a safe and non-invasive method for assessing heart health. Echo tests are used to evaluate heart size, pumping capacity, and the condition of the heart valves.
By providing detailed information about how well the heart is functioning, an echo test is instrumental in diagnosing heart conditions like heart failure, valve disorders, and congenital heart defects.
Types of Echo Tests
There are several types of echo test for heart procedures, each tailored to assess different aspects of heart health:
1. Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)
This is the most common type of echo test. It involves placing the transducer on the chest to capture standard images of the heart. It is typically used to examine heart size, function, and the health of the valves and walls.
2. Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
For more detailed images, especially when the transthoracic echocardiogram does not provide enough information, a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) may be performed. In this test, the transducer is inserted down the throat into the esophagus, which is closer to the heart.
This approach provides clearer images of the heart’s structures, particularly the back of the heart, which may be difficult to visualise with a standard TTE.
3. Stress Echocardiogram
This test combines an echo test with physical stress, usually from exercise or medication, to evaluate how the heart performs under stress. It is especially useful for detecting coronary artery disease and assessing the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively during increased physical demand.
4. Doppler Echocardiogram
A Doppler echocardiogram uses the same ultrasound technology as a standard echo test but also measures the speed and direction of blood flow through the heart. This is essential for evaluating valve function, detecting blood clots, and assessing the efficiency of blood circulation in the heart.
Why is an Echo Test Important in Diagnosing Heart Conditions?
An echo test for heart plays a pivotal role in the early detection and management of heart conditions. By providing real-time images of the heart, it allows healthcare providers to observe structural and functional abnormalities.
Here are the key reasons why echo tests are important:
1. Early Detection of Heart Conditions
Many heart conditions, including those that are asymptomatic in the early stages, can be detected with an echo test. For example, heart murmurs, which may be indicative of valve problems or congenital heart defects, can be observed early, allowing doctors to initiate early treatment and prevent further complications.
2. Accurate Diagnosis of Valve Diseases
Heart valve diseases, such as aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation, and mitral valve prolapse, are often diagnosed with the help of an echo test. The test allows doctors to evaluate how well the heart valves open and close and whether there are any issues like valve leakage or narrowing.
3. Monitoring Heart Function
An echo test for heart is a valuable tool in assessing heart function over time. It can help monitor the heart’s pumping capacity, especially in patients with heart failure.
The test provides an ongoing assessment of how well the heart is managing the body’s circulatory demands, helping doctors adjust treatments as necessary.
4. Assessment of Congenital Heart Defects
For infants and children with congenital heart defects, an echo test is a crucial diagnostic tool. It helps determine the presence of abnormal structures or blood flow within the heart.
Early detection of congenital heart defects allows for timely intervention, improving long-term health outcomes for affected individuals.
5. Detecting Blood Clots and Tumors
In addition to evaluating the heart’s function, echo tests can also identify abnormalities like blood clots or tumours within the heart. These conditions can pose serious health risks, including strokes or heart failure, and require immediate attention.
Common Heart Conditions Diagnosed with an Echo Test
An echo test for heart is instrumental in diagnosing a variety of heart conditions. Some of the most common heart problems that can be identified include:
1. Heart Failure
Echo tests help evaluate the heart’s pumping ability and determine if the heart is failing to pump blood efficiently, a hallmark of heart failure. The test can measure the ejection fraction (the percentage of blood pumped out of the heart with each beat), a critical indicator of heart function.
2. Coronary Artery Disease
Although coronary artery disease is primarily diagnosed using other tests like angiography, an echo test can still provide valuable information about how well the heart is functioning, particularly if the patient has been diagnosed with a history of heart attacks or blocked arteries.
3. Valve Disorders
As mentioned earlier, valve disorders such as stenosis, regurgitation, or prolapse can be accurately diagnosed using an echo test. The procedure allows doctors to see the structure of the valves and assess any issues with blood flow.
4. Pericardial Disease
Diseases affecting the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart, can also be detected using an echo test for heart. Conditions like pericarditis or pericardial effusion can be observed and treated early to prevent complications.
5. Atrial Septal Defects (ASD)
ASD is a congenital condition in which there is a hole in the wall separating the heart’s upper chambers. An echo test can identify these defects, which may cause symptoms like shortness of breath or irregular heart rhythms.
How is an Echo Test Performed?
There is usually no special preparation required for an echo test for heart. However, patients may be asked to remove any clothing covering the chest and wear a hospital gown. It’s important to inform the doctor about any implanted devices, such as pacemakers, as these may affect the test’s results.
What Happens During The Test?
The test is typically performed while the patient is lying on an examination table. A technician will apply a gel to the chest area to help the transducer make contact with the skin. The device will then be moved around the chest to capture various angles of the heart. For a TEE, a thin tube with the transducer will be passed through the throat.
Post Test Procedure
The results of the echo test are typically available within minutes or hours, depending on the complexity of the exam. The images will be reviewed by a cardiologist, who will provide a diagnosis based on the findings. If necessary, additional tests or follow-up exams may be recommended.
Conclusion
An echo test for heart is a powerful diagnostic tool that plays a critical role in the detection, diagnosis, and monitoring of heart conditions. Its non-invasive nature, along with its ability to provide detailed images and measurements, makes it an invaluable asset for healthcare providers.
Whether identifying structural issues like heart valve diseases, monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for heart failure, or detecting congenital disabilities, echo tests contribute significantly to improving patient outcomes.
By offering real-time insights into heart function, they provide the necessary data to guide treatment decisions, ultimately leading to better heart health and quality of life.