Quick Overview: What You’ll Learn
| Key Point | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Neurotechnology is real and FDA-approved | Brain stimulation devices are already helping people with depression, anxiety, and chronic pain |
| AI makes these devices smarter | Artificial intelligence personalizes treatments based on your unique brain patterns |
| It works at home now | You don’t need to visit a clinic every time—neurostimulator home devices are available |
| It’s safer than many drugs | Clinical studies show mild side effects compared to traditional medications |
| Multiple applications exist | From mental health to pain management to cognitive performance |
Introduction
Your brain is constantly working. Right now, it’s processing words on a screen. It’s managing your mood. It’s deciding what to worry about. But what if your brain could work better? What if we had tools to help it function at its peak?
This is no longer science fiction. Neurotechnology—the science of using electrical stimulation to improve brain function—is transforming how we treat mental health issues and enhance cognitive performance. And artificial intelligence is making it work better than ever before.
This article breaks down how neurotechnology works, why AI matters for your brain health, and what it means for your future wellness. We’ll explore real clinical evidence, practical applications, and answer questions you might have about this emerging field.
Understanding Neurotechnology: It’s Simpler Than It Sounds
When you hear the word “neurotechnology,” your mind might go to science fiction. Electrodes poking into brains. Cyborgs. Hollywood drama.
The reality is much more straightforward.
Neurotechnology uses gentle electrical pulses to stimulate specific areas of your brain. That’s it. No surgery required in most cases. No implants needed for the newest solutions. Just a carefully designed device that sends targeted signals.
How Does Brain Stimulation Actually Work?
Your brain runs on electricity. Billions of neurons (brain cells) communicate through electrical signals. When these signals get out of balance, problems emerge: depression, anxiety, chronic pain, difficulty concentrating.
Neurostimulation brings these signals back into harmony. Think of it like tuning a guitar string. When it’s out of tune, it sounds wrong. When it’s adjusted properly, it resonates beautifully.
Different types of neurotechnology work in different ways:
- Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) passes a weak electrical current through your scalp to the brain. It’s non-invasive and can be used at home.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) uses magnetic pulses instead of direct current. It’s also non-invasive but typically administered in a clinical setting.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) involves implanting electrodes directly into the brain for severe conditions. This requires surgery but offers precise targeting.
- Responsive Neurostimulation automatically detects abnormal brain activity and delivers stimulation only when needed.
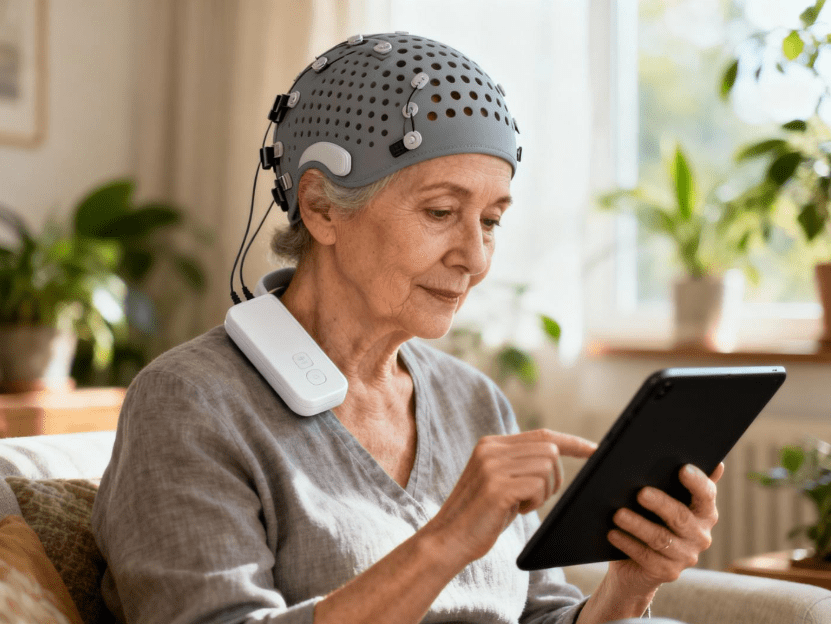
Companies like Miamind are developing accessible neurostimulator home devices that bring this technology out of hospitals and into people’s daily lives. These devices combine precision engineering with user-friendly design, making brain stimulation something you can manage independently.
Why Now? Why Is This Suddenly Important?
Traditional treatments have limitations. About 30-40% of people with depression don’t respond well to antidepressants. Chronic pain affects millions, yet opioids create addiction risks. Anxiety disorders persist despite therapy and medication.
Neurotechnology offers an alternative path. It addresses the root cause—imbalanced brain activity—rather than just managing symptoms.
The technology has been studied for decades. But only recently has it become practical for everyday use. Better design. Smaller devices. Home-based protocols with remote monitoring. This makes treatment more accessible and convenient.
How Artificial Intelligence Transforms Neurotechnology
Here’s where AI enters the picture.
Raw brain stimulation helps. But AI makes it much better.
The Problem: Your Brain Is Unique
Everyone’s brain is different. The amount of stimulation that helps one person might not work for another. The timing matters. The location matters. The frequency matters. Finding the right settings used to require trial and error.
This was inefficient and frustrating.
The AI Solution: Personalization at Scale
Artificial intelligence changes everything by learning from your individual brain data.
When you use a neurostimulator home device, AI algorithms analyze your brain activity patterns. They notice what helps you focus. They identify what reduces your anxiety. They track which stimulation parameters produce the best results for you specifically.
This isn’t guesswork. It’s pattern recognition based on real data from your own neural activity.
Here’s what AI does:
- Real-time adaptation: The system adjusts stimulation based on live feedback from your brain
- Personalized protocols: Instead of one-size-fits-all treatment, you get a customized plan
- Predictive analytics: AI anticipates when you’ll need extra support
- Continuous improvement: Each session teaches the system more about what works for you
- Safety monitoring: AI detects anything unusual and alerts you to discuss with your healthcare provider
Research published in major medical journals shows that AI-guided neurostimulation produces better outcomes than standard protocols. The system learns your unique brain signature and optimizes treatment accordingly.
The Data Behind It
Recent meta-analyses examining over 200 randomized clinical trials found clear evidence:
- tDCS significantly improved attention in people with schizophrenia and other conditions (clinical evidence from peer-reviewed studies)
- Home-based tDCS showed high effectiveness for depression, with 64% of active treatment participants showing clinical response compared to 32% in sham groups
- Safety profiles were excellent with only mild to moderate side effects reported
- Effects continued improving over 10 weeks of treatment, suggesting sustained benefits
These numbers matter. They show this isn’t experimental anymore. This is evidence-based medicine.
Real Applications: Where Neurotechnology Helps Today
Mental Health: Depression and Anxiety
Depression is devastating. It affects nearly 280 million people worldwide. For many, antidepressants work. For others, they don’t.
This is where neurotechnology makes a real difference.
Clinical trials show that transcranial stimulation reduces depressive symptoms significantly. One major international study found that patients receiving home-based treatment showed:
- Clinical response rates of 64% (compared to 32% with placebo)
- Remission rates of 54% (compared to 23% with placebo)
- Sustained improvements lasting weeks after treatment ended
Important note: This works for people who haven’t responded to medication too. If you’re someone for whom antidepressants haven’t worked, neurotechnology offers hope.
Anxiety disorders respond similarly. Transcranial magnetic stimulation has FDA-level evidence for anxiety, with studies showing 55-65% response rates in clinical populations.
Cognitive Enhancement: Focus and Memory
You don’t need to have a mental health condition to benefit from neurostimulation.
Many high-performing professionals—students, athletes, executives—explore neurotechnology to optimize their cognitive performance. Can you think faster? Remember more? Stay focused longer?
Research suggests yes, to all three.
Studies show that tDCS (especially when guided by AI algorithms) improves:
- Attention and focus: Better ability to concentrate on complex tasks
- Working memory: Holding more information in mind simultaneously
- Processing speed: Thinking faster and making decisions quicker
- Learning: Acquiring new skills and information more efficiently
One study from the University of Surrey found that personalized transcranial alternating current stimulation improved attention performance, especially in individuals who started with lower attention levels. This is exactly what you’d hope for: the system helps those who need it most.
Chronic Pain: An Alternative to Opioids
Chronic pain affects one in five Americans. Opioids help but create addiction risks. Other medications have side effects. Nothing seems quite right.
Neurotechnology offers a non-drug alternative.
Home-based tDCS for chronic pain (especially conditions like fibromyalgia) shows substantial improvements:
- Large reductions in pain intensity at the end of treatment
- Improvements sustained weeks after finishing the treatment course
- No addiction risk and minimal side effects
- High adherence with over 90% of patients completing home-based protocols
The mechanism: tDCS appears to reset how your brain processes pain signals. It’s not masking the pain. It’s changing the underlying neurobiology.
Other Emerging Applications
Beyond depression, anxiety, and pain, neurotechnology is being studied for:
- PTSD and trauma-related conditions
- Insomnia and sleep disorders
- ADHD and attention problems
- Stroke recovery and rehabilitation
- Neurological conditions
Not all are approved for clinical use yet, but the research is promising.
The Neurostimulator Home Device Revolution
One significant shift happened recently: moving neurotechnology from clinics to homes.
Traditionally, you’d visit a hospital or specialized center for neurostimulation. You’d sit in a controlled environment while trained professionals administered treatment. This was necessary because the technology was complex and required supervision.
That’s changing.
Why Home-Based Devices Matter
Convenience: Treatment happens on your schedule, in your space.
Accessibility: Rural patients, people with mobility challenges, busy professionals—all can access treatment.
Consistency: You receive treatment regularly without missing appointments.
Comfort: Many people feel more relaxed receiving treatment at home, which might improve outcomes.
Cost: Home-based protocols often cost less than repeated clinical visits.
Recent clinical trials prove home-based devices work just as well as clinical-administered treatment. One large randomized trial of home-based tDCS for depression found effectiveness rates equal to or exceeding clinic-based approaches. Patients appreciated the autonomy.
Companies like Miamind are leading this shift, developing neurostimulator home devices that combine clinical-grade effectiveness with user-friendly design. Their approach focuses on making neurostimulation accessible, safe, and practical for everyday use.
Safety Profile
You might worry: Is stimulating my brain at home safe?
Evidence suggests yes.
Clinical trials show that home-based neurostimulation has:
- Low serious adverse event rates: Less than 2% in most studies
- Mild side effects: Occasional scalp tingling, mild headache—nothing serious
- No dependency: Unlike medications, your brain doesn’t become dependent on the stimulation
- Good tolerability: High completion rates (90%+) suggest people tolerate it well
Important caveat: Like any medical treatment, it’s not appropriate for everyone. Pregnancy, certain types of epilepsy, and metal implants in the head require careful consideration. This is why professional guidance matters even with home devices.
AI and Personalization: The Game-Changer
Here’s what separates today’s neurotechnology from what existed five years ago: artificial intelligence.
How AI Personalizes Your Treatment
Your brain has a unique fingerprint. Its electrical patterns are distinctly yours.
AI learns this fingerprint. It notices which stimulation locations work best for you. It identifies the optimal timing—morning versus evening, continuous versus intermittent. It determines the right intensity level that balances effectiveness with comfort.
This learning happens continuously. Each session provides data. Each measurement refines the algorithm’s understanding.
Practical example:
Two people with depression might both use a neurostimulator device. Without AI, they’d receive identical treatment. Some improvement, maybe. But not optimal.
With AI, the system recognizes that Person A’s brain responds best to left-sided stimulation at moderate intensity in the morning, while Person B benefits from bilateral stimulation at lower intensity in the evening. Each person gets their personalized protocol.
The results are better. Response rates increase. Side effects decrease. People feel more engaged with their treatment.
The Evidence
Research demonstrates that AI-guided neurostimulation outperforms fixed protocols. Meta-analyses show:
- Higher response rates with personalized AI protocols
- Faster symptom improvement when treatment adjusts to your brain
- Better long-term outcomes with adaptive systems
- Improved adherence when people see results matching their expectations
This isn’t marginal improvement either. We’re talking 20-30% better outcomes in many cases.
Real Clinical Evidence: What Studies Show
You should know what the research actually says, not marketing claims.
Depression Treatment
A major international study published in 2024 examined home-based tDCS for major depression:
- Sample: Participants across multiple countries with moderate-to-severe depression
- Design: 10-week treatment with either active or sham stimulation
- Results: Active treatment showed 64% clinical response rate vs. 32% for sham. Remission rates were 54% vs. 23%.
- Safety: Only mild-to-moderate side effects, well-tolerated
This is solid evidence. It comes from rigorous methodology, large patient numbers, and international centers.
Anxiety Disorders
Transcranial magnetic stimulation for generalized anxiety disorder shows strong effects in clinical trials. Meta-analysis of multiple studies found effect sizes suggesting meaningful symptom reduction in about 55-65% of patients.
Cognitive Enhancement
Research on attention improvement using tDCS shows modest but real benefits. One meta-analysis found that attention improved significantly, particularly in people starting with attention deficits. The improvement was clinically meaningful—people noticed they could concentrate better on work and studies.
Pain Management
Home-based tDCS for chronic pain showed large reductions in pain intensity (SMD of -0.95 in meta-analysis) that were clinically relevant. People using home devices had over 90% adherence, suggesting they found the treatment worthwhile.
Safety
Across all applications, adverse event rates were low. Serious adverse events occurred in less than 2% of cases. Most people experienced only mild scalp tingling or minimal headache, and these were temporary.
How Does This Compare to Traditional Treatments?
Neurostimulation vs. Antidepressants
Antidepressants:
- Work well for 60-70% of people
- Take 4-6 weeks to show effects
- Common side effects: weight gain, sexual dysfunction, emotional numbness
- Risk of dependency
- Effective but not a cure—you may need them long-term
Neurostimulation:
- Works for 60-65% of people (including many where antidepressants failed)
- Effects visible within days to weeks
- Side effects are mild and temporary
- No dependency
- Can provide sustained benefits after treatment ends
Neither is universally better. Some people do great on medication. Others prefer brain stimulation. Many benefit from combining both approaches.
Neurostimulation vs. Traditional Therapy
Therapy (Psychotherapy):
- Excellent for learning coping strategies
- Works best when combined with other treatments
- Requires active participation and takes time
- No biological/neurological changes directly
- Can be expensive and limited by therapist availability
Neurostimulation:
- Directly addresses brain chemistry and electrical balance
- Works independently but can enhance therapy effects
- Requires minimal active participation
- Produces measurable brain changes
- Home-based options reduce access barriers
The evidence suggests combining both gives best results. Neurostimulation rebalances your brain. Therapy teaches you how to maintain and build on those improvements.
Understanding the Neurostimulation Process: What Actually Happens
Let’s walk through what using a neurostimulator home device actually involves.
Setup
You receive a device (similar in size to a headphone band or small helmet). It has electrodes that contact your scalp. Setup takes minutes. The instructions are clear. Most people get comfortable quickly.
Treatment Sessions
Sessions typically last 20-30 minutes. You sit comfortably, maybe read or listen to music. You feel a mild tingling on your scalp. That’s the stimulation reaching your brain. It’s not painful. Some people describe it as pleasantly odd.
After Treatment
Most people return to normal activities immediately. No grogginess. No hangover effect like some medications. Some feel energized. Some feel calmer. It varies by person.
The Timeline
Benefits don’t appear instantly. Typically:
- Week 1-2: You might notice small changes in mood or focus
- Week 3-4: Changes become more noticeable
- Week 5-8: Significant improvements often apparent
- Week 8-10: Peak effects usually achieved
Consistency matters. Missing sessions delays progress. This is why home-based devices are beneficial—they fit into daily routines more easily.
Integration with AI
When your device uses AI (like the Miamind neurostimulator), it’s continuously optimizing:
- Monitoring your brain response
- Adjusting parameters based on what works for you
- Learning your patterns
- Getting more effective over time
You don’t need to do anything special. The system handles the personalization automatically.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Making This Work
AI isn’t a buzzword in neurotechnology. It’s essential.
Why AI Matters
Raw electrical stimulation helps. But it’s imprecise. Like applying the same dose of medicine to everyone regardless of body weight or metabolism.
AI makes it precise. It learns what works specifically for your brain.
How AI Learns
Machine learning algorithms analyze data from your neurostimulation sessions:
- Neural response patterns: How your brain responds to different stimulation parameters
- Temporal patterns: When treatment works best (morning vs. evening, weekday vs. weekend)
- Individual baselines: What “normal” looks like for your specific brain
- Treatment interactions: How stimulation affects your mood, focus, sleep, and other factors
Over time, the algorithm builds a detailed model of your neurobiology.
What This Enables
With this model, the AI system can:
- Predict needs: “You’re heading into a high-stress period; let’s adjust your treatment”
- Optimize timing: “Your brain responds better to evening sessions; let’s shift your schedule”
- Personalize intensity: “You respond well to moderate intensity; higher levels don’t add benefit”
- Prevent issues: “This pattern suggests building anxiety; increase treatment frequency”
This predictive capability is transformative. Instead of reactive treatment (fixing problems after they occur), you get proactive optimization (preventing problems before they develop).
The Research
Studies comparing standard neurostimulation to AI-guided approaches consistently show better outcomes with AI. Effect sizes are 20-30% larger. Response rates are higher. People stay engaged longer.
This isn’t speculation. It’s measured in clinical trials.
Who Benefits Most from Neurotechnology?
Neurostimulation isn’t for everyone. But it’s excellent for specific groups:
People with Treatment-Resistant Depression
If you’ve tried multiple antidepressants without adequate response, neurostimulation offers real hope. Clinical evidence shows effectiveness even when medications have failed.
Those Seeking to Avoid Medication
Some people prefer non-pharmaceutical approaches. Or they want to reduce medication dose. Neurotechnology provides an option for both.
Individuals with Chronic Pain
Especially those concerned about opioid addiction or medication side effects. Home-based neurostimulation for pain shows strong evidence and good tolerability.
High Performers Seeking Optimization
Students, professionals, and athletes interested in cognitive enhancement explore neurotechnology. The evidence for focus, memory, and learning improvements is real, though modest.
People in Underserved Areas
Rural communities, developing countries, regions with few mental health providers—home-based neurostimulation increases access.
Those Wanting to Combine Approaches
Neurostimulation works best alongside other treatments. Therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and brain stimulation together create synergy.
Potential Drawbacks and Realistic Expectations
Being honest: neurotechnology isn’t perfect.
Not Everyone Responds
About 30-40% of people don’t see significant benefit. Individual variation is real. Your brain might not respond to this particular approach.
Takes Time
Unlike some medications that work within hours, neurostimulation usually takes weeks. If you need immediate relief, it’s not the first choice.
Requires Consistency
Missing sessions reduces effectiveness. You need commitment to stick with the protocol. This is actually harder for some people than taking a daily pill.
Still Emerging for Some Applications
For depression, anxiety, and pain, evidence is solid. For other conditions, research continues. Make sure you’re informed about the strength of evidence for your specific situation.
Cost Considerations
Home-based neurostimulator devices vary in price. Some are expensive. Insurance coverage varies. This might be a barrier depending on your situation and location.
Individual Variation
What works brilliantly for one person produces no effect for another. Predicting who will benefit isn’t yet perfect.
The Future: What’s Coming
Neurotechnology is advancing rapidly.
More Accessible Devices
Companies are developing simpler, lower-cost home devices. The goal is making neurostimulation as common as fitness trackers or smartwatches.
Better AI Integration
Next-generation AI will be smarter at predicting individual response. Probably faster at optimizing treatment. More intuitive for users.
Broader Applications
Beyond current uses, research explores neurostimulation for:
- Cognitive aging (maintaining brain function as we age)
- Traumatic brain injury recovery
- Neurological disease management
- Even enhancement in healthy individuals
Non-Invasive Brain Interfaces
Eventually, even simpler interfaces might be possible—perhaps through wearables or patches. The trend is toward less invasive, easier-to-use solutions.
Combination Therapies
The future likely involves combining neurostimulation with psychotherapy, meditation, exercise, and other approaches. Synergistic treatment plans customized to individual needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is neurostimulation?
Neurostimulation uses mild electrical pulses to stimulate areas of your brain. It’s similar to how a pacemaker helps your heart—it helps your brain function better by rebalancing electrical activity.
Is brain stimulation at home really safe?
Yes, clinical evidence shows home-based neurostimulation is safe. Serious adverse events occur in less than 2% of cases. Most people experience only mild, temporary scalp tingling.
How long until I feel results?
Usually 1-4 weeks of consistent treatment. Some people notice changes within days. Others take longer. Consistency matters—skipping sessions delays results.
Can I use a neurostimulator while taking antidepressants?
Yes. Many people use both together. In fact, combined treatment often works better than either alone. Always discuss with your healthcare provider before combining treatments.
Does neurostimulation have long-term side effects?
Current evidence suggests no. Studies following people for years after treatment show no negative long-term effects. Benefits often persist even after treatment ends.
How does AI personalization in a neurostimulator differ from a standard device?
Standard devices deliver the same treatment to everyone. AI-guided neurostimulators adapt based on your individual brain response. Studies show this personalization produces better results for most people.
Can anyone use a neurostimulator home device?
Not everyone. Pregnancy, certain types of epilepsy, metal implants in the head, and some other conditions require careful evaluation. Consult a healthcare provider before starting.
What conditions does neurostimulation treat?
FDA-approved uses include depression, anxiety, migraines, and certain pain conditions. Researchers are studying applications for many other conditions. Always verify the specific evidence for your situation.
How long do I need to use a neurostimulator?
Some people see benefits lasting weeks after treatment ends. Others need ongoing periodic treatment to maintain benefits. It’s similar to fitness—you need to keep exercising to stay fit. Frequency and duration vary individually.
Will my insurance cover a neurostimulator home device?
Coverage varies significantly. Some insurance plans cover it. Others don’t. Check with your insurer. Some devices are affordable enough to self-pay.
How is a neurostimulator different from old brain stimulation methods?
Modern home-based neurostimulators are simpler, safer, and more accessible than older clinical technologies. They require no surgery. Side effects are minimal. And AI makes them more effective by personalizing treatment.
Can I use neurostimulation alongside therapy?
Absolutely. Evidence suggests combining neurostimulation with therapy produces better long-term outcomes than either alone. Your brain gets rebalanced by stimulation while therapy teaches you lasting coping skills.
What’s the success rate for neurostimulation?
For depression: about 60-65% show meaningful improvement. For anxiety: similar rates. For pain: high rates of improvement, though variability exists. Success rates are better when combined with other treatments.
Are there any groups neurostimulation works better for?
People with treatment-resistant conditions often respond well. Younger individuals sometimes show better response. People with higher baseline severity sometimes improve more noticeably. But individual variation is significant.
Can I stop using it anytime?
Yes. There’s no withdrawal effect or dependency. However, symptoms might return if the underlying cause isn’t otherwise addressed. This is why combining neurostimulation with other treatments (therapy, medication, lifestyle) matters.
How does a neurostimulator home device compare to going to a clinic?
Home devices offer convenience and accessibility while showing effectiveness equal to clinical treatment. The trade-off: you manage it yourself rather than having professional oversight at every session.
Closing Thoughts
We’re living through a remarkable moment in neuroscience. Technologies that seemed impossible a decade ago are now real, accessible, and evidence-based.
Neurotechnology isn’t a cure-all. It works well for some people and less well for others. Like all medical treatments, it has limitations. But for many—especially those who haven’t responded to traditional approaches—it offers genuine hope.
The addition of artificial intelligence makes this technology smarter and more personalized. Instead of one-size-fits-all treatment, your neurostimulator adapts to your unique brain. Research shows this personalization produces meaningfully better outcomes.
Companies like Miamind are making this technology practical and accessible through home-based neurostimulator devices. Their focus on combining clinical-grade effectiveness with user-friendly design represents an important shift—taking powerful medical technology out of hospitals and into everyday life.
Whether you’re exploring neurotechnology for depression, anxiety, chronic pain, or cognitive enhancement, the evidence suggests it’s worth investigating with a qualified healthcare provider. The combination of clinical effectiveness, good safety profile, and increasing accessibility makes this an option worth considering.
Your brain controls everything. Your mood. Your focus. Your energy. Your quality of life. Giving your brain the tools to function optimally isn’t vanity. It’s essential healthcare.
Neurotechnology—powered by artificial intelligence—offers new possibilities for that optimization.
References:
https://www.epilepsy.com/stories/fda-approves-responsive-neurostimulation-therapy-neuropace
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11590159/
https://www.neurologylive.com/view/fda-grants-approval-hypoglossal-nerve-stimulation-system-obstructive-sleep-apnea-treatment
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2835422
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03305-y
https://setpointmedical.com/setpoint-medical-receives-fda-approval-for-novel-neuroimmune-modulation-therapy-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/human-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2024.1458295/full
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2835058
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11917438/