How long people take on their digital devices has a direct impact on various areas of the brain. Nowadays, the overuse of technology is predominantly well-spread among youth. More than half of teenagers are addicted to computer and mobile devices. Because the human brain continues maturing until the age of 25 years, too much exposure early in life could hamper its growth. In the Ruston documentary, digital media was found shown to have a drug-like effect that is felt at any age. It is more pronounced in the teen years.
Since studies on technologies influence on the brain are relatively new, many people who are hesitant to limit their screen time. For example, even after spending many hours working on computers, people continue using tech devices like smartphones and tablets at home.
The main question that people have at the back of their minds is: “How long should one take behind the screen without damaging the brain?” This post takes a closer look at how the overuse of technology influences different cerebral areas.
Facts about Technology Overuse
- At the age of 4 years, about 75% of children have mobile devices
- Over 50% of teenagers are addicted to computers and mobile devices.
- Nielsen Report indicates that adults spend more than 11 hours on the screen every day.
- Adults between the age of 18 and 36 years spend over 17.5 hours with varying types of media such as computers and smartphones.
- Young adults who take a lot of time playing video games and television are twice as likely to develop attention disorders.
Areas of the Brain Affected by Technology Overuse
To appreciate how technology overuse impacts, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the brain areas and functions. See the image below:
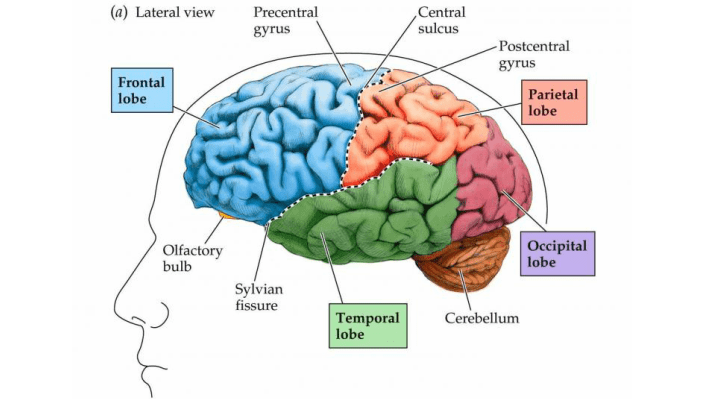
Image 1: Diagram of a human brain courtesy of PublicSource.Org
A human brain develops based on the way it is used. For example, teens should only have 60 minutes of screen time for optimal brain development. It is also crucial to note that surfing the internet and texting impacts different parts of the brain than speaking or reading.
Breaking Down of Ties between Different Parts of the Brain
The prefrontal cortex that occupies the frontal lobe of the brain controls cognition, personality, and social behavior. The parietal lobes control language and word interpretation, while cerebellum regulates a human’s muscular activity like those linked to language. These controls mean that the three parts are tied together.
Excessive use of technology results in a breakdown of ties between the prefrontal cortex the cerebellum, and parietal lobes. The impact of this breakdown is that people find it difficult to process information and interact with others. For example, some find it difficult to remember events or pay attention.
Scholars recommend reducing the time people spend on tech devices to improve argumentative skills. As Jonathan Haidt once has said: “the article is one of my favorite papers of the last ten years. I believe that they have solved one of the most important and longstanding puzzles in psychology: why are we so good at reasoning in some cases, but so hopelessly biased in others?” From our perspective, the answer lies in the correlation between screen time and argumentative the brain function of a particular person. The dependence between them is quite simple – the screen spends more time, the person could provide the worse arguments on a specific issue. That’s why those students who are not “screen-addicted” tend to master persuasive essay format better, than those with high daily usage of smartphones and tablets. Why do people neglect their possibilities to think broadly? Unfortunately, there is no answer to that question.
Gray Matter Atrophy
Studies have demonstrated that the overuse of gadgets causes shrinking of the brain tissues, especially in the gray matter. These are the areas where information processing takes place. The most affected parts are the frontal lobe, cortex, and subcortex that govern executive functions such as organizing, prioritizing, and planning.
Another part of the brain that shrinks due to the use of computing devices is the striatum. This is mainly involved in reward pathways and suppressing unacceptable impulses. But the damage to the insula, the part responsible for the development of compassion and empathy, has drawn a lot of concern from scholars. They are worried that addiction to media devices could result in violent behavior.
Reduction in Cortical Thickness
In their study, Hong and colleagues found that excessive gaming is associated with a decrease in the thickness of the frontal lobe. The researchers also established that the effect of internet addiction was similar to other disorders. This implies that if one is addicted to the internet, the likelihood of developing other disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity desease (ADHD).
Increased Cravings and Impaired Dopamine Function
Studies have demonstrated that people release dopamine when gaming. In their research, referred to as The Neural Basis of Video Gaming, Kuhn and colleagues found that most people start gaming as a recreational activity but later develop a serious craving.
Kuhn also established that some effects of excessive gaming are similar to those of drug addiction. For example, gamers could also end up losing sleep or work hours to gaming.
A Dissenting Voice: Technology could Enhance Communication
While most researchers and psychologists appear to agree that using technology has serious negative implications, Professor Shyam Sundar of communication at Penn State College of Communication differs sharply. He argues that critiques of computing advances are missing the point by treating face-to-face to be the standard.
Sundar posits that times are changing and people should appreciate tech advancement that enables talking, entertainment, and chatting without limitation of time or space. His argument was supported by Professor Frank Vee of Microsoft Research Center for Social Natural User Interface.
Vee posits that technology is aimed at augmenting social interactions and well-being. Therefore, he sees a brighter future of computer technology. It has raced fast from keyboard commands to mouse and touch devices. Now, Wii devices have taken over, and it is possible to walk into a screen-free future. Therefore, he posits that a human brain can be trained to rewire itself.
Conclusion
Today, a lot of people are overusing technology. However, it has negative impacts on their brain and lifestyles. Whether a person is left brain dominant or right brain dominant, overusing technology raises the danger of breaking ties between the different sections, reducing the gray matter, and shrinking the cortical thickness.
Even the dissenting voice of the tech minds appear to agree that people should use less time on technology. This is important in helping the brain to develop and reduce tech-related damage.

































