In the vision systems of automated equipment, industrial lens are core components for image acquisition, and their performance directly impacts inspection accuracy, recognition efficiency, and system stability. Choosing the right industrial lens requires a comprehensive consideration of equipment requirements, environmental conditions, and technical parameters. The following details the selection process from multiple perspectives.
Identify the Application Scenario and Core Requirements
First, determine the specific application scenario for the automated equipment. Lens requirements vary significantly across different scenarios. Measurement equipment (such as dimensional inspection and position positioning) prioritizes lens distortion and resolution, generally requiring distortion below 1% and resolution matching the camera’s pixel density. Defect inspection equipment (such as surface scratch detection) prioritizes lens contrast and detail reproduction. High-speed sorting equipment places higher demands on lens frame rate compatibility and dynamic imaging quality.
Also, it’s important to clearly define the characteristics of the inspection target: target size determines the lens focal length (focal length = working distance × sensor size / field of view); target material (reflective/absorbent) influences lens coating selection; and motion speed influences lens shutter synchronization performance.
Matching Camera and Sensor Parameters
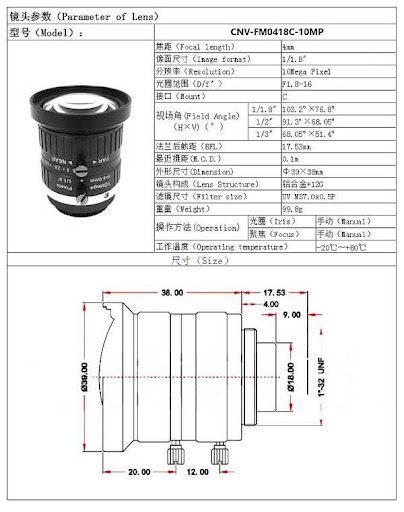
Machine Vision Lens and camera compatibility is a fundamental prerequisite. Ensure that the lens’ optical format (e.g., 1/2.5″, 1/1.8″, or 2/3″) is larger than or equal to the camera sensor size to avoid image edge cropping. Regarding pixel matching, the lens resolution should be slightly higher than the camera’s (e.g., an 8-megapixel camera should be paired with a 10-megapixel lens) to avoid “wasted pixels” or a “resolution bottleneck.”
The lens’ mount type should also be standardized. Mainstream industrial FA lenses mounts include C-mount, CS-mount, and F-mount. Automation equipment often uses C-mount and CS-mount (the two differ only in flange focal distance and are compatible via adapters). When selecting a lens, ensure it matches the camera’s mount to minimize light loss and errors caused by the adapter.
Critical Optical Parameter Selection
Focal length is the core parameter that determines the field of view. Short focal lengths (e.g., 2.8-12mm) are suitable for scenarios with a large field of view (e.g., package identification in logistics), while long focal lengths (e.g., 50-100mm) are suitable for long-distance, small-target inspection (e.g., pin inspection of electronic components). Zoom lenses (e.g., 10-50mm) are suitable for multi-product inspection scenarios requiring flexible field of view.
The working distance must match the equipment’s mechanical structure. For close-range inspection (such as PCB inspection), a macro lens (working distance 10-50mm) is recommended, while for long-range production line monitoring, a telephoto lens (working distance 1-5 meters) is required. Depth of field requirements must also be considered. Lenses with a large depth of field (such as a small aperture design) are suitable for inspecting uneven objects, avoiding the impact of frequent refocusing on efficiency.
Industrial environments are complex, and lenses must possess appropriate protection. For dusty environments, choose lenses with IP65/IP67 protection ratings. For equipment with severe vibration (such as stamping lines), choose lenses with anti-vibration structures (capable of withstanding 10-20G vibrations). For high-temperature environments, consider the lens’s temperature stability (operating temperature range -10°C to 60°C).
Lighting conditions must also be considered. For bright light environments, a lens with an ND filter can be used. For low-light environments, a large aperture lens (f-number F≤1.8) is required to maximize light intake and avoid excessive image noise that could affect inspection.
Special Functional Requirements
For high-precision measurement scenarios, telecentric lenses are ideal. They eliminate perspective error, ensure consistent image size at varying distances, and achieve measurement accuracy down to 0.01mm. Line scan lenses for line scan cameras require high resolution (single pixel size ≤ 3.5μm) and uniform image plane illumination, making them suitable for continuous inspection of coils and sheets.
In addition, for automated equipment requiring rapid switching between inspection modes, motorized zoom/zoom lenses can be selected, with program-controlled parameter adjustment eliminating the need for manual intervention. For multispectral inspection scenarios, customized lens coatings are required to ensure high transmittance at specific wavelengths.
Balancing Cost and Reliability
While meeting performance requirements, the cost-effectiveness of a lens must be comprehensively considered. Standard FA lenses can be used for general inspection scenarios, while specialized lenses are required for high-precision applications. Long-term lens stability should also be considered, with metal materials and precision assembly processes being selected to minimize equipment downtime caused by lens drift.
Finally, Cnomax Vision recommends verifying the selection effect through actual testing, checking the imaging quality, edge clarity and consistency of the lens under simulated working conditions, and ensuring that the selected lens can stably meet the operating requirements of the automation equipment in the long term.