Introduction:
Retirement services play a pivotal role in helping individuals plan and secure their financial future during their post-working years. With an aging population and evolving retirement needs, the landscape of retirement services has witnessed significant changes.
Exhibit 1: Source-Adobe stock photos
Here are the few types of Retirement solutions available for the aging population:
- Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans: Employers offer retirement plans such as 401(k)s, 403(b)s, or similar plans to their employees that allow them to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income to a retirement account, often with employer matching contributions. These plans are widely used and serve as a significant retirement savings vehicle for millions of Americans.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): IRAs are individual retirement savings accounts that individuals can set up independently. They offer tax advantages, either as traditional IRAs (with tax-deferred contributions) or Roth IRAs (with tax-free withdrawals in retirement). IRAs offer additional flexibility for retirement savings beyond employer-sponsored plans.
- Social Security: Social Security is a government program that offers retirement benefits to eligible individuals. Workers contribute a part of their income to the Social Security system during their working years, and upon retirement, they become eligible to receive benefits based on their earnings history. Social Security serves as a foundational source of retirement income for many Americans.
- Pension Plans: Traditional pension plans, also known as defined benefit plans, were common in the past but have become less prevalent in recent years. These plans promise a fixed benefit amount based on years of service and salary. Today, most private-sector employers have shifted to defined contribution plans like 401(k)s, which place the investment risk on the employees.
- Annuities: Annuities are financial products offered by insurance companies that provide a guaranteed income stream in retirement which are designed to offer lifetime or fixed-term payments to individuals who purchase them. Annuities can be a valuable tool for retirees seeking predictable income and protection against longevity risk.
Now let us explore the current situation of retirement services, identify opportunities for carriers, and address the challenges they must tackle to thrive in the retirement market.
Current Situation of Retirement Services:
- Shifting Demographics: The US population is experiencing a significant demographic shift, with the Baby Boomer generation reaching retirement age and Generation X and Millennials increasingly planning for their retirement. This diversification of the market demands tailored retirement services from the carriers that cater to the unique needs and preferences of each age group.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of digital technologies has transformed the way retirement services are delivered. Carriers are using artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics to personalize retirement plans, streamline processes, and enhance customer experiences. Digital platforms have made it easier for individuals to access retirement information and manage their accounts remotely.
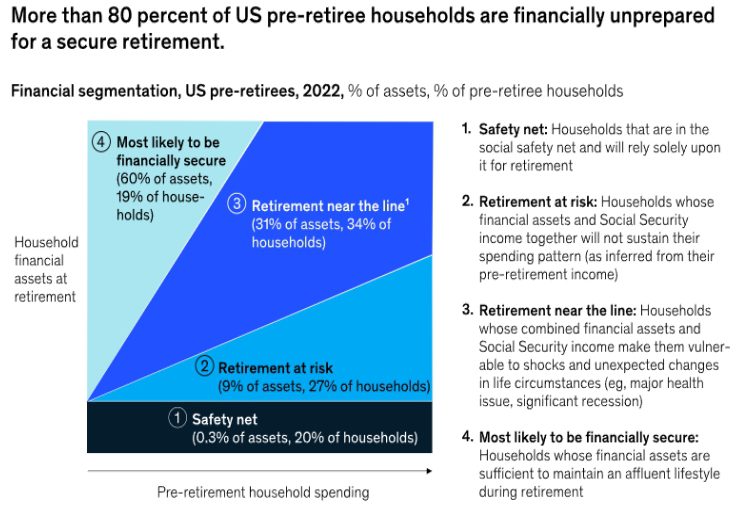
- Retirement Savings Gap: Despite the availability of retirement plans like 401(k)s and IRAs, a sizable part of the population still faces a retirement savings gap. Many Americans are not saving enough for retirement, leading to concerns about their financial security during retirement. Carriers must address this gap and develop strategies to encourage increased savings. Many pre-retirees are running out of time to accumulate sufficient retirement assets. Just over 80 percent of baby boomers may be unprepared for retirement, according to McKinsey’s surveys in 2021 and 2022 (Exhibit 2). (“From saving to spending: A second front emerges in the US retirement …”) The surveys asked about respondent’s financial sufficiency in retirement (asking whether households have sufficient assets to cover expected spending), as well as their retirement confidence (whether they feel adequately prepared to manage their finances). Approximately 47 percent of households nearing retirement report that they have not achieved financial sufficiency, including 20 percent who are in the safety net, reliant heavily on Social Security for retirement income, and 27 percent who are financially at risk of not supporting their working years’ standard of living. Another one-third of households are financially near the line, in that their assets leave little to no margin for shocks like market downturns, continued inflation, or family health changes. “That leaves only 19 percent of pre-retirees likely to be fully financially secure.” (“From saving to spending: A second front emerges in the US retirement …”)
—————————————————————————————————————————————–
Exhibit 2: Source-McKinsey Retirement Readiness survey, April 2022
——————————————————————————————————————————————
Opportunities for Carriers in Retirement Services:
- Personalized Retirement Solutions: The advancements in data analytics and AI present a unique opportunity for carriers to offer personalized retirement solutions. By analyzing customers’ financial situations, risk tolerance, and retirement goals, carriers can tailor retirement plans that suit individual needs, promoting increased participation and contribution rates.
- Holistic Retirement Planning: Carriers can expand their services beyond traditional retirement products and provide holistic retirement planning solutions. This can include offering advice on managing healthcare costs, Social Security optimization, long-term care planning, and estate planning. Providing comprehensive retirement planning can strengthen customer relationships and loyalty.
- Embracing ESG Investing: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing has gained traction among investors who seek to align their retirement savings with their values. Carriers can seize this opportunity by incorporating ESG investment options in their retirement plans, attracting socially responsible investors and fostering long-term client engagement.
- Emphasis on Financial Education: Educational initiatives on retirement planning and financial literacy can help carriers empower individuals to make informed decisions about their retirement. By providing workshops, webinars, and educational resources, carriers can build trust and credibility, ultimately increasing customer retention.
Challenges faced by Carriers in the context of providing Retirement Services:
- Regulatory Compliance: The retirement industry is subject to various regulatory requirements from federal agencies like the DOL and the SEC. Carriers must comply with these regulations while also navigating potential changes in legislation that can impact retirement offerings and investment options.
- Managing Longevity Risk: With life expectancy increasing, carriers face the challenge of managing longevity risk, which is the risk of outliving retirement savings. Offering annuities or other lifetime income solutions can mitigate this risk, but it requires careful planning and underwriting.
- Retaining Customer Trust: The retirement market is highly competitive, with numerous carriers vying for customers’ attention. Building and maintaining customer trust is essential for carriers to remain relevant and successful in this landscape. Addressing concerns related to fees, transparency, and performance is crucial in earning and retaining customer trust.
- Technological Adoption: While technological advancements present opportunities, they also pose challenges in terms of implementation and integration. Carriers must invest in modernizing their systems and processes to deliver seamless digital experiences to customers while ensuring data security and privacy.
Conclusion:
US retirement services industry is experiencing a paradigm shift due to changing demographics, technological advancements, and evolving customer expectations. Carriers of today have an incredible opportunity at hand to shape the future of retirement services by expanding their product & service offerings, leveraging on technological and AI advances and ensuring personalization for their clients.
Additionally, they should recalibrate themselves to handle regulatory compliance, manage longevity risk, build consumer trust, and focus on digital adoption. Carriers may position themselves as trusted partners in helping individuals reach their retirement objectives and create a financially secure future.
About the Author:

Neeraj Kaushik, Principal Consultant, is a Product Manager for the Infosys® McCamish NGIN platform initiative at Infosys McCamish Systems.
Neeraj is an innovative and effective leader recognized for achieving exceptional results in highly competitive environments requiring continuous improvement and has driven the business of large-scale technology projects based out of the US, UK, India, and China Geography for the last 18+ years. He has an excellent business domain, architecture, design, and implementation skills in various life insurance administration as well as producer management & compensation systems. He is a published author and though leader in US Insurtech space.
Prior to this, Neeraj was part of Big 4 Consulting firms where he led digital transformation programs for the Insurance Industry. He has led strategic consulting and transformation initiatives across the Life, Annuities, and Property & Casualty Insurance space.
He holds a master’s degree in insurance & risk management from BIMTECH (India) and the designations of ALMI (LOMA) and Fellow (III India).
Contact Details:
https://www.linkedin.com/in/neerajkaushikprincipalconsultant/