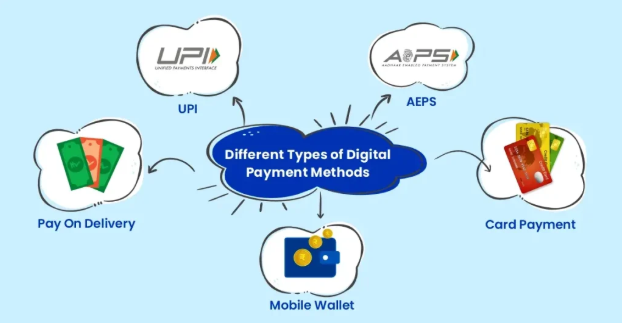
India’s digital payment ecosystem is evolving rapidly, driven by increased online transactions and regulatory advancements. As businesses integrate digital payments, ensuring payment gateway security in India is crucial to prevent fraud and protect customer data. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mandates strict security protocols, aligning with its Payments Vision 2025, which aims to make digital payments more secure and efficient.
A secure payment gateway in India must comply with PCI-DSS, enable encryption, implement fraud detection mechanisms and ensure data privacy. Indian businesses must adopt robust security measures to maintain compliance and build customer trust.
Below is a comprehensive guide on how payment gateways in India enable businesses to navigate cross-border transactions seamlessly while ensuring secure and compliant payment processing.
Why it is important to keep payments in India secure
As cyber threats evolve, businesses must adopt robust security protocols to prevent fraud, data breaches and regulatory non-compliance. India’s digital payments sector is projected to reach $10 trillion by 2026, making security a top priority for businesses. With increasing online transactions, threats such as phishing, data breaches and card fraud pose significant risks.
To protect customer data, payment gateways in India must implement robust security measures, comply with RBI and SEBI guidelines and leverage AI-driven fraud detection.
A strong security framework ensures:
- Customer trust: Secure payments boost consumer confidence.
- Regulatory compliance: Adhering to RBI guidelines prevents penalties.
- Fraud prevention: Strong security reduces cyber threats.
- Business continuity: Preventing breaches protects revenue and reputation.
Key security challenges in digital payments
Online transactions are vulnerable to cyber threats, necessitating strong security protocols. Some key challenges include:
- Data breaches: Hackers steal sensitive information, causing financial and reputational loss;
- Fraud: Card cloning, phishing and identity theft threaten digital payments;
- Chargeback fraud: Disputed transactions increase financial risks;
- Regulatory non-compliance: Violating RBI guidelines leads to penalties;
- Malware attacks: Cybercriminals steal data or disrupt transactions.
Best practices for secure payment gateway transactions
Businesses must adopt stringent security practices to safeguard transactions, prevent fraud and meet regulatory requirements. The following security measures ensure secure payment processing.
- Compliance with PCI-DSS and RBI regulations
A payment gateway in India must adhere to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) to protect card transactions. Additionally, RBI mandates key security measures, including:
- Tokenisation: Encrypts card details, reducing data exposure;
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Prevents unauthorised online transactions;
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance: Verifies identities and detects fraud.
- End-to-end encryption for data security
Encryption ensures payment data remains secure during transactions, preventing unauthorised access. Essential encryption methods include:
- SSL and TLS encryption: Protects sensitive data during transmission;
- AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard – 256-bit) encryption: Ensures advanced encryption for transaction security.
- AI-driven fraud detection and risk management
Modern payment gateways in India use AI and machine learning to detect fraud in real time. These systems analyse transaction patterns and prevent suspicious activities using:
- Behavioural analysis: Detects unusual spending patterns to identify potential fraud;
- Geolocation tracking: Flags high-risk transactions from suspicious locations;
- Device fingerprinting: Prevents unauthorised payments by analysing user device history.
- Secure customer authentication methods
To enhance security, payment gateways integrate multiple authentication layers, including:
- One-Time Passwords (OTPs): Ensures transaction authorisation;
- Biometric authentication: Enhances security with fingerprint or facial recognition;
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requires multiple verification steps for protection.
- Tokenisation for card security
Tokenisation is an RBI-mandated security measure that ensures safe card storage and processing. The key benefits include:
- Prevents data breaches: Replaces actual card details with secure tokens;
- Ensures compliance: Enables businesses to store card details while remaining RBI compliant.
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
Businesses must conduct periodic security audits to identify and mitigate potential threats. Recommended practices include:
- Penetration testing: Simulates cyberattacks to detect vulnerabilities;
- PCI compliance audits: Ensures adherence to security standards;
- Real-time monitoring: Detects and prevents fraudulent activities instantly.
- Adopting secure APIs and payment infrastructure
A secure payment gateway in India should provide secure API integrations to prevent vulnerabilities. Best practices include:
- OAuth-based authentication: Enhances security for third-party integrations;
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Restricts access based on user roles;
- Secure coding practices: Prevents cyber threats such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
Regulatory compliance: SEBI’s Third-Party Validation (TPV) requirement
For businesses in Securities, Broking and Mutual Funds, compliance with SEBI’s Third-Party Validation (TPV) guidelines is essential.
TPV ensures that investors transact only from their registered bank accounts, reducing fraud risks. A payment gateway in India must support TPV verification to help businesses comply with SEBI requirements while maintaining payment security.
RBI’s Payments Vision 2025 and its impact on payment security
The RBI’s Payments Vision 2025 focuses on strengthening digital payment security through:
- Expanded tokenisation: Secures UPI and Aadhaar-based payments;
- AI fraud detection: Monitors banking networks for risks;
- Secure cross-border payments: Ensures global compliance;
- Data localisation: Protects sensitive payment data.
Ensuring secure payment gateway transactions
A secure payment gateway in India not only protects businesses from fraud but also enhances payment success rates. By implementing robust security measures, businesses can achieve:
- Higher success rates: Reduces payment failures;
- Encryption & tokenisation: Secures financial data;
- AI fraud detection: Prevents unauthorised transactions;
- Seamless APIs: Enables secure payments.
Enhance your payment gateway security today
Ensuring payment gateway security in India is critical as digital payments continue to grow. Businesses must adopt best practices to safeguard customer data, prevent fraud and comply with RBI guidelines.
By adopting tokenisation, encryption and AI-driven security, businesses ensure seamless, secure payments, reduce risks and build long-term customer trust in India’s evolving digital economy.
A secure payment gateway such as Plural enhances transaction success rates, ensures seamless API integrations and provides advanced fraud detection. Implementing these measures strengthens overall payment security.