Within the constantly evolving energy sector, operational technology (OT) assumes a central role in optimizing the generation and distribution of power. The progress in OT has brought about substantial changes in how energy firms conduct their operations, providing improved automation, monitoring, and control systems. Nevertheless, these advancements come accompanied by distinct challenges that necessitate thoughtful attention. In this blog post, we will delve into the significance of OT in the energy sector, the most recent innovations, and the hurdles confronting companies involved in power generation and distribution.
Understanding Operational Technology
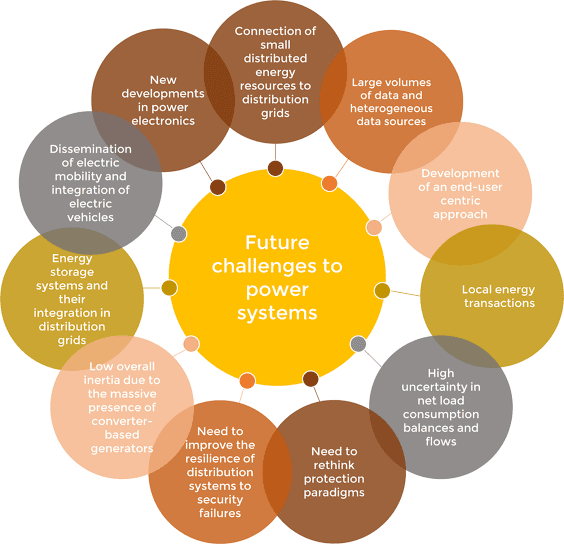
Operational technology encompasses both hardware and software applications utilized for the supervision and regulation of physical processes and equipment across diverse industries, including the energy sector. In the realm of power generation and distribution, OT encompasses an extensive array of technologies, including supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, sensors, actuators, and control systems. These technological components assume a pivotal role in safeguarding and enhancing the secure and efficient functioning of power plants, substations, and the overall energy infrastructure.
Advancements in OT for Energy
- Automation and Integration: Modern OT systems enable seamless automation and integration of various processes within power plants and substations. This automation reduces human intervention, leading to improved efficiency and reliability.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: OT advancements allow energy companies to monitor and control critical infrastructure remotely. This capability is particularly valuable for responding to issues promptly and reducing downtime.
- Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance:
Incorporating data analytics tools into operational technology systems empowers energy companies to gather and analyze extensive datasets sourced from sensors and equipment. This wealth of data serves as a valuable resource for predicting maintenance requirements, optimizing operational processes, and proactively averting costly breakdowns.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: As cyber threats continue to evolve, OT systems have also seen improvements in cybersecurity measures. Protecting critical infrastructure from cyberattacks is a top priority for energy companies.
- Smart Grids: The concept of smart grids, powered by advanced OT, has gained momentum. Smart grids enable real-time communication between utilities and consumers, leading to more efficient energy distribution and consumption.
Challenges in OT for Energy
While the advancements in OT have brought numerous benefits to the energy sector, they also bring unique challenges:
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: As OT systems become more interconnected and reliant on digital technologies, they become susceptible to cyberattacks. Energy companies must continuously invest in cybersecurity and operational technology together to protect critical infrastructure.
- Legacy Systems Integration: Many energy facilities still rely on legacy OT systems that may not easily integrate with modern technologies. Retrofitting and upgrading these systems can be costly and complex.
- Data Management: The vast amount of data generated by OT systems presents challenges in terms of storage, analysis, and interpretation. Energy companies need robust data management strategies to extract actionable insights.
- Skills Gap: There is a growing skills gap in the energy sector, with a shortage of professionals who possess the expertise to operate and maintain advanced OT systems effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Energy companies must adhere to stringent regulations and compliance standards. Ensuring that OT systems meet these requirements while staying technologically up-to-date can be challenging.
Conclusion
Operational technology is a driving force behind the efficient operation of power generation and distribution in the energy sector. As technology continues to evolve, the energy sector must adapt to remain competitive, reliable, and sustainable. The future of OT in energy promises even greater integration, efficiency, and resilience in the face of evolving energy demands and challenges. By embracing these advancements while proactively addressing associated challenges, the energy sector can continue to power our world effectively and responsibly.