Vladimir Potapenko, Founder of software company Magora, discusses mobile application development for commercial companies, their costs, strategies, payoff, and success.
Will the popularity of mobile applications continue to grow?
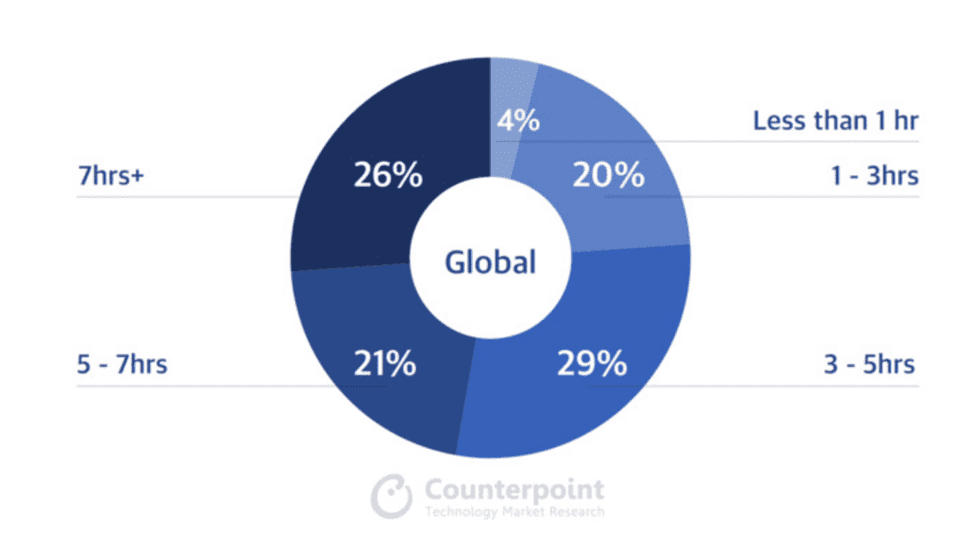
Mobile applications are one of the most promising channels of communication with an audience, as people spend more and more time on smartphones. Data provided by Counterpoint Research shows that only 4% of smartphone owners use their devices for less than one hour a day. 26% of users spend 7 hours or more—more than half of the time they are awake. Another 21% spend 5-7 hours on smartphones. I predict these numbers to continually increase in the future.
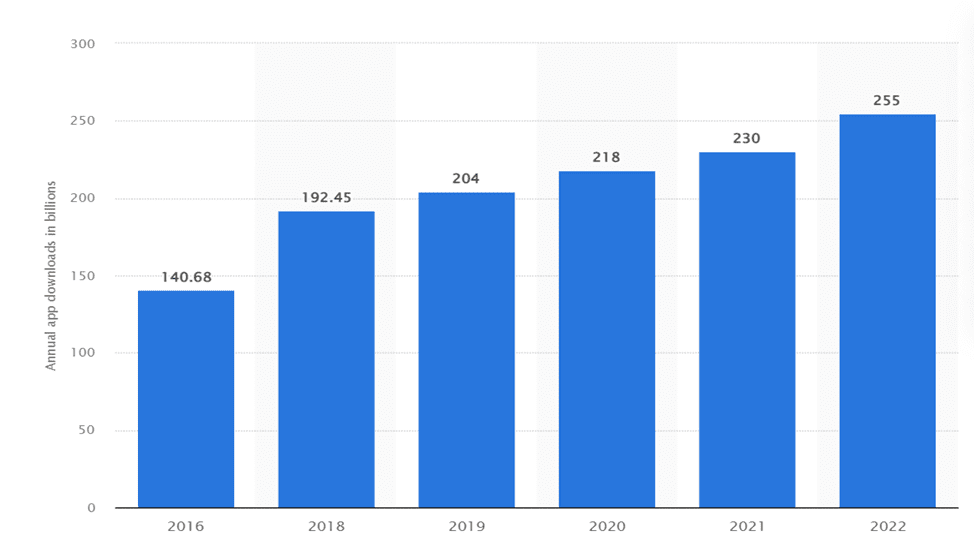
Moreover, the functionality of mobile application usage is quite wide: entertainment, communication, shopping, and everyday problem-solving. According to Statisa, the number of app downloads increased by 10% in 2022. That indicator has increased 1.8x since 2016.
In my opinion, the presence of a mobile application is more than just an advantage over competitors, allowing you to improve brand image and increase sales. Additionally, it is a way to connect with a new audience—those born in the 2000s will use smartphones all their adult lives.
How does a website compare to an app?
On mobile devices, applications are superior to websites—they have more adapted interfaces, are able to work offline, implement payment tools, and can access device functions like the camera, microphone, and NFC.
Additional advantages, which are not obvious at first glance, include the ability to communicate with users through push notifications. These allow you to send offers, conduct surveys, and promote events, without the client even logging into the app. This is useful for both promoting the brand and keeping in touch with users. Pushwoosh’s calculations show that push notifications receive a response from 70% of an audience.
Mobile phones are able to collect information about the owners. For example, data, time, and action tracking. This makes it possible to adapt the software to your audience. In general, people love mobile apps because they make them feel unique. When you visit a website, you are just a guest, but a well-designed mobile app can be highly personalized, instilling a sense of brand loyalty.
Lastly, mobile applications can be successfully monetized: purchases and advertising in programs, paid subscriptions, etc. If your application is of high quality, then these tools will be successful.
How do I determine if my business needs a mobile app?
Creating an application requires significant investments, and you will need to first understand what goals you are pursuing. To decide if you need an application, answer these questions:
1) Will an application help automate processes?
A mobile application can help you improve business processes and increase productivity, as it is able to take over both routine processes and document management, as well as work with personnel.
2) Are consumers coming back to you?
An application helps to retain customers. You can send users a push notification with a call to action, like offering a promo code for a discount.
3) Can an application solve customer problems?
Think about customer pain points and how an application can solve them. For example, IKEA was able to invite customers to “try on” furniture in their own home interiors.
4) Do you have a loyalty system?
By integrating a loyalty program into a mobile application, you can share promotions, discounts, and bonuses electronically.
5) Will an application allow you to do what your site cannot?
Ask yourself what new business opportunities an app will provide. Understand which new points of contact with the audience an application opens up and how they will make the user experience more successful.
6) Do your competitors have apps?
Know what your competitors are doing, whether they have mobile applications, what they can do, and whether they are convenient for a buyer. Look at the statistics in the App Store and Google Play. The number of downloads and reviews will tell you how customers are using competitors’ apps. If competing services are valued, you will need an application with similar or better functionality.
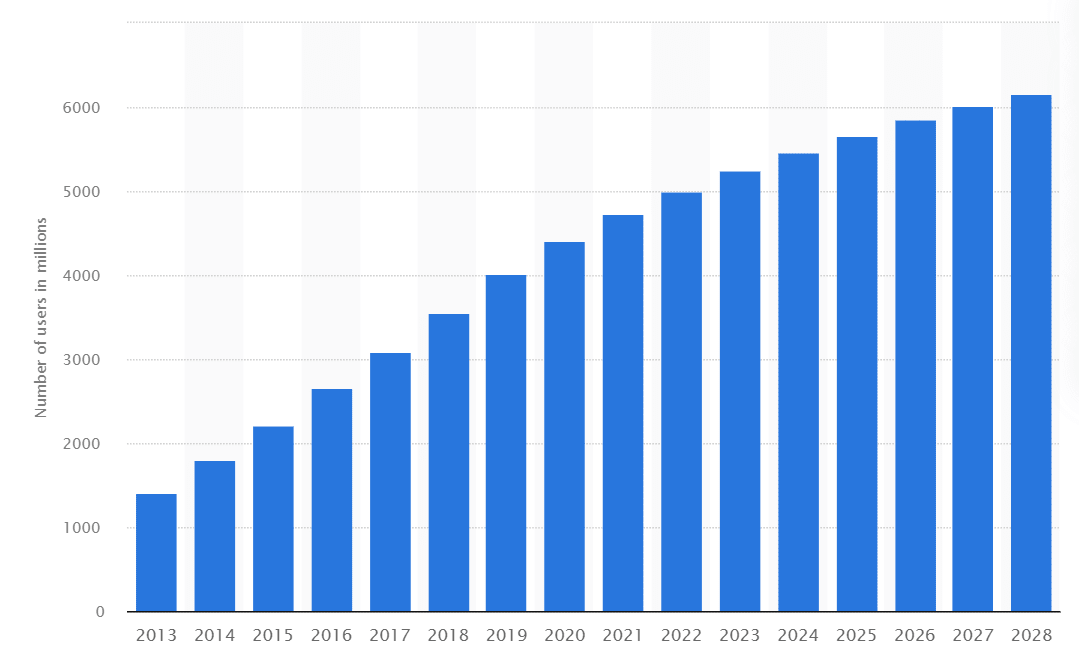
If you answered “yes” to even one question, consider developing a mobile application! According to Statista, the number of smartphone users will continue growing, and by 2028, the number will exceed 6 billion people.
Getting started:
The start of a successful project begins with the discovery phase. This point allows you to estimate how much time and money is necessary for development, and helps to predict risks. If you do not conduct a qualitative analysis, then the costs of creating a program will increase. The discovery phase can be compared to building a house: if you want to build a solid and reliable structure, then having the blueprints and the final design is the only way to do it.
- Determine the scope of the project, the main functions of the software, and business priorities.
- Carry out marketing research and competitor analysis.
- Create a workflow for an effective software solution, taking into account the product monetization strategy.
- Identify unambiguous program functions and user roles.
- Develop strategies for expansion and reproduction of software for growing business needs.
- Identify and cover risks.
- Develop the concept of visualization of the future solution.
Next steps:
You need to complete a number of stages. These can be divided into four main groups.
- Prototyping
The analyst must consider how the program will work. At the same time, marketers should express their wishes, focusing on the target audience and tasks. When everything is ready, the specialist coordinates the prototypes with the customer, makes corrections, and passes them to the designer, who determines the design style and graphic elements. The function of the prototype is to help the designer, customer, and user to check the correctness and feasibility of the project. It is not necessary to perceive the prototype as an equivalent of the final product.
- Development
Move on to development once you have clear terms of reference, and the main hypotheses have been tested on the prototype. Designers should work on page layouts, develop graphic elements, and think through the interface. When you have a “shell” of an application without functionality, the developers will begin to create code that will lead your customers to the end goal.
- Testing
The application should be able to cope with the tasks for which it is designed—this is the first thing you must check. Then, test how the program works on various devices and operating systems, and evaluate whether its interface is understandable. Try to test development in difficult conditions: with a large number of users, with weak Internet, on not very powerful devices, and so on. Don’t forget to check if your development is protected from cyber dangers. All shortcomings must be eliminated. After that, you can publish the application in the App Store or Google Play.
- Marketing
You must interact with users from the moment your application is launched and throughout their continued use. You must convince customers to install the application, encourage them to take the first action in your program, and keep them interested. You can use different tools: ASO (improving the visibility of an application in app stores), social media marketing, influencers, paid advertising, etc.
How much will it all cost in the end?
The information you gather during the discovery phase will give you a rough idea of how much money your project will cost and what it takes to achieve payoff. Return to your calculations after each stage.
Think about how many people you need on your team, and which stages the development process will require. Do not forget about additional costs—fees, linking payment systems, marketing, etc. It is important to remember that development is usually only one third of the cost; the rest goes to promotion, support, and integration of services. Also include support costs: updates and bug fixes.
Profitability largely depends on the tasks that you identify during the discovery phase. At Magora, we had a customer who needed a solution that would allow medical specialists to study the neurocognitive functions of a person. As a result, we developed an Android game for patients that collected all the necessary information. Based on the data captured, the doctor could form recommendations for patients. In order to make it convenient for physicians to analyze results, we developed a special web platform. The main task was to make the test results as accurate as possible. In total, eight people worked on the application—a designer, a PHP developer, two Android developers, a project manager, an account manager, and two quality control specialists. The project budget amounted to €66.65 thousand, or $73,880. We spent five months on development. Because we were able to achieve the main goal and reached an accuracy rate of 94%, the project paid off in a year.
Which areas are in high demand for mobile applications?
The service sector has the most demand for mobile apps. For example, travel and restaurant industries use apps for booking, ordering, aggregators, and catalogs. The Starbucks app, launched in 2009, enables users to find nearby locations, learn about the menu, and customize drink recipes. Over time, the company moved its loyalty program to users’ smartphones using the Card mobile app. Customers can place an order in advance for pickup, allowing the chain to increase revenue and reduce costs. Starbuck’s net profit for the 2022-2023 fiscal year reached $855.2 million.
Another area where mobile development is becoming extremely popular is healthcare. Apps allow you to conduct quick examinations of patients, provide virtual consultations, and identify diseases from images. At Magora, we developed a project that helped speed up the process of testing for COVID-19 and receive travel certificates remotely. When registering, the user indicated passport data and a phone number, then an express test was delivered to their home. At the user’s convenience, a video call with a consultant was scheduled, then the user scanned a QR code on the test, and passed verification and direct testing. Once tested, the result was recorded in the user’s personal account and confirmed by the specialist. With a negative test, the user was able to download the PCR test certificate.
What technologies are relevant now?
Over the past year, artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies have shown a leap in development. AI can optimize application performance, improving both efficiency and security, while machine learning helps analyze user behavior and predict preferences. These opportunities may be in demand for medicine, transport, and marketing.
Another trend is the growth of the market for mobile payments and fintech applications that offer faster payment methods, including NFC technologies, QR codes, and blockchain. Biometric payment methods such as fingerprints, face scanning, and voice recognition are also expected to gain popularity in the future.
In addition, the trend towards creating real-time applications capable of processing large amounts of data will continue to expand due to the spread of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart devices. For example, in agriculture, this can be used to increase productivity, improve crop quality, and monitor weather conditions by installing IoT sensors in fields to collect information about temperature, humidity, pressure, and rainfall. IoT can also help improve urban infrastructure such as traffic light management, waste management, water management, and more.



































