When the sun sets and the world goes dark, modern defense and security doesn’t slow down—they rely on thermal cameras. Across borders, ports, and remote installations, military-grade security cameras are giving operators a new kind of sight—one that cuts through smoke, weather, and complete darkness to reveal what the human eye could never see.
It’s a quiet revolution in vision. What used to be a single night-vision scope has become a network of intelligent surveillance systems, powered by thermal imaging, advanced sensors, and AI analytics that spot heat signatures before anyone else can.
Built for the Toughest Environments
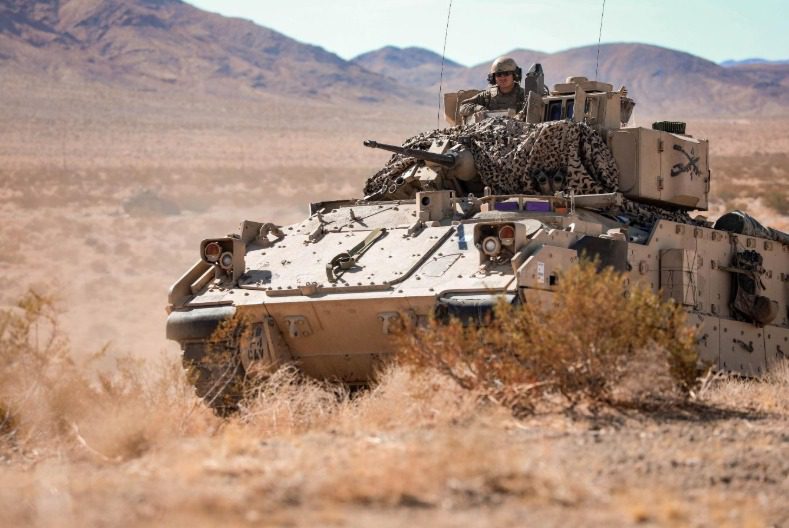
These aren’t your neighborhood security cameras. Military-grade systems are built for the harshest environments on Earth—salt spray at sea, desert sandstorms, or the freezing altitudes of an unmanned aircraft. Every component must verify that it can survive vibration, dust, and shock while keeping optical clarity and efficiency.
Industry leader Clear Align engineers these cameras and systems for endurance. Each thermal camera features proprietary thin-film optical coatings that boost light transmission and protect delicate optics from sand and salt. The result: durable imaging equipment that keeps working long after commercial products would fail.
This level of engineering rigor matters. In a real mission, there are no second chances—border patrols, armored convoys, and reconnaissance aircraft depend on cameras that perform every time, no matter the conditions. Each system is tailored to meet operational demands, from long-range detection to compact airborne surveillance, making these devices as adaptable as the missions they serve.
How Thermal Imaging Turns Heat into Vision
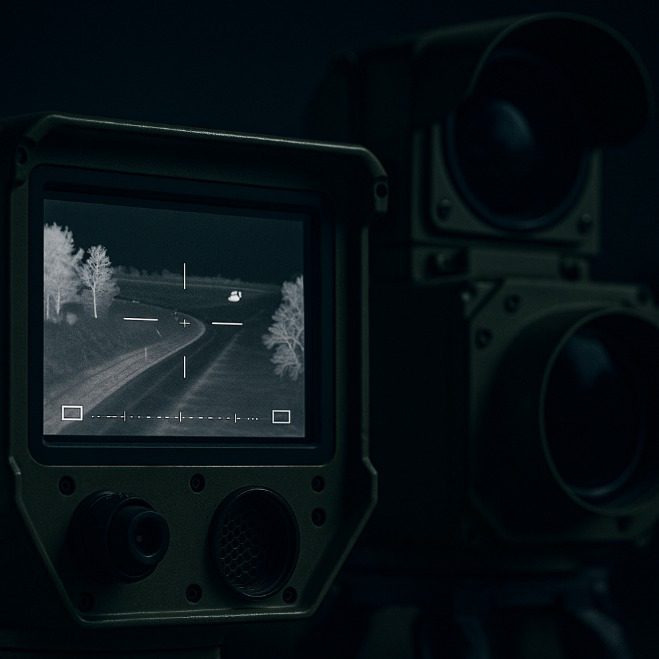
The magic of thermal imaging lies in heat. Everything on earth emits heat—foliage, rocks, water, people, engines, buildings—but it is not visible to the human eye. Thermal cameras detect that heat radiation and convert it into a visible view of the world that glows with temperature contrast.
In practical terms, that means soldiers or border agents can see a person hiding in shadows, track a vehicle through haze and smok, or follow footprints cooling in sand.
Infrared technology works in several bands:
- LWIR (Long-Wave Infrared): Ideal for detecting subtle temperature differences through dust, sand, smoke or mist.
- MWIR (Mid-Wave Infrared): Ideal for detecting subtle temperature differences through dust and smoke, but also humid air, maritime environments, haze, weather.
- SWIR (Short-Wave Infrared): Reflects light like the visible spectrum—perfect for maritime environment, light fog, haze and dust
Each band serves a different mission, but together they deliver a continuous imaging providing information in whatever field of view and range is selected.
The science behind it is stunningly elegant. Every frame of thermal data comes from photon-level variations in emitted or reflected radiation. Sophisticated algorithms process that data to create thermal maps that can distinguish living beings from mechanical heat, even at great distances. It’s one of the few technologies where physics and art intersect—showing the world in a different light making the invisible into a visible image with scientific precision.
Thermal Imaging vs. Night Vision: What’s the Real Difference?
Many people think Thermal Imaging and Night Vision are the same, but the difference is more than just the band
- Night vision amplifies what little light exists.
- Thermal cameras don’t need light at all—they see heat, not reflection.
That makes them capable of seeing through at night and even camouflage nets. A handheld thermal camera, or a helmet mounted camera, or even weapon mounted camera can reveal events that are critical to the mission.
A good example is Clear Align’s Cooled Thermal Cameras, where cryogenically cooled detectors cut background noise, offering longer range and sharper detail. These high-performance cameras aren’t just useful—they’re mission-critical.
The distinction explains why thermal cameras are now appearing in more civilian applications. Firefighters use them to locate trapped people in burning buildings; pilots rely on them for landing in low-visibility conditions; and power-plant inspectors use them to find overheated transformers before they fail. What began as military technology now touches countless aspects of public safety and industrial efficiency.
Integration: Building a Connected Defense Network
Today’s security systems are designed to connect. When thermal cameras are installed across a border or airfield, they form a situational awareness network—each camera feeding live surveillance data into command centers that is processed by AI/ML algorithms that help the operator act quickly.
The connection between sensors, software, and operators is where the real power lies. AI algorithms interpret heat patterns, trigger alerts, and coordinate with radar or drones. The systems are often tailored to the specific site, giving every installation a customized defense layer that’s both efficient and responsive.
Experts describe this as “sensor fusion”—a term that means security equipment can provide information that is actionable instead of just data.
In the Field: From the Battlefield to the Backyard
While designed for defense, thermal cameras now appear in everything from critical infrastructure protection to wildlife monitoring and disaster response. The same high-performance cameras used by soldiers to track vehicles in dust storms help firefighters find survivors in smoke-filled buildings.
Handheld thermal cameras make field inspection easy, offering engineers, police, and rescue teams a portable means of detecting heat leaks, machinery faults, or hidden intruders. The growing sales of this technology reflects its value—reliable, adaptable, and increasingly essential.
Beyond pure surveillance, these systems can also support predictive maintenance by spotting heat anomalies in engines or turbines, preventing failures before they happen.
Clear Align’s Quiet Edge
Behind many of these breakthroughs is Clear Align, a U.S.-based thermal imaging innovator that supplies military and industrial customers around the world. The company’s vertically integrated process—design, assembly, and testing—gives it precise control over performance and cost.
These thermal cameras are used in unmanned systems, intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, and aerospace applications, reflecting a reputation built on clarity, efficiency, and mission-ready engineering.
The Future of Seeing Clearly
As threats become more complex, vision technology must keep up. The integration of thermal imaging, AI, and multi-spectral sensors is redefining what’s possible in security systems.
Whether mounted on a vehicle, tower, integrated into an aircraft, or carried in the palm of a soldier’s hand, the new generation of military-grade security cameras will continue to serve one goal: transforming darkness into data.
In a world where seeing means surviving, thermal cameras don’t just capture images—they offer insight, speed, and the power to act in real time.
Quantum Sensors
The next evolution may go beyond vision altogether. Engineers are exploring quantum sensors that could detect changes at the molecular level, giving even greater information content and precision. Combined with AI, such systems could one day provide automated threat classification within seconds—an innovation that would further shrink the gap between detection and response.