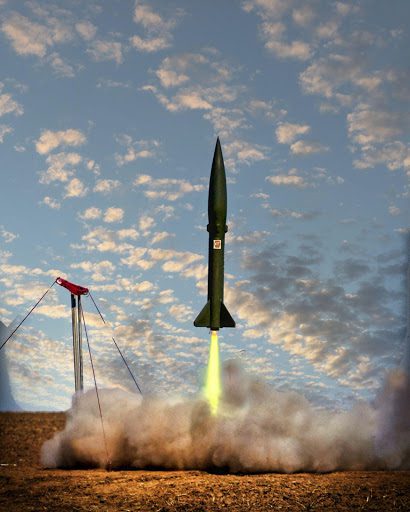
A small launcher, or a micro rocket, is a small, lightweight spacecraft that can only weigh only 500 kg or less. More and more micro rocket companies are emerging because they offer a more cost-effective alternative to launching satellites and other payloads in comparison to heavyweight vehicles. Besides, small carriers also have a lower cost of manufacturing, which makes all future space launches more affordable.
Micro Rocket Applications
Micro rockets have enabled small-scale researchers, as well as different private companies, to launch their satellites in space. Small launchers are perfect for carrying small or micro satellites, but more importantly they can carry different payloads at once because spacecraft are becoming ever smaller. All of these factors further help to bring down overall launch costs.
Small or micro rockets are not only economical, but are also perfect for certain space missions, where bigger carriers would fail.
The first application of micro rockets is to develop constellations of satellites for low orbit data transmission. They can also be used to inspect bigger satellites in space. As smaller satellites work by building a network in space, it is possible to collect data from multiple points using a constellation. For example, a constellation of satellites could provide Internet connection to remote areas where wire is economically unwise. Since each of the satellites in a constellation is small, deploying a constellation of satellites does not call for a large, heavyweight launcher. Then, we have university students and small-scale researchers who can benefit from using a small launcher to send their SmallSat into space for purely research purposes. Usually, researchers do not have large budgets, so they could benefit from micro rockets’ low launch cost and quick launch preparation.
What are Micro Rockets?
Another application of micro rockets is to try out new hardware and specs before using them for larger projects. More and more researchers are resorting to this method, which helps them avoid possible losses due to unforeseen accidents and anomalies.
Development for micro satellites has been on the rise since this concept was first developed. Long before we designed 1-50 kg SmallSats, launch operators worked with 50-100 kg and heavier spacecraft.
During 2000-2005, more than 30 small satellites were launched in space. In 2006 this figure rose to 36. Then, it dropped to 34 in 2012 and rose to 93 the next year. According to an estimate, the total market value for all SmallSats launched in space during 2015-2019 is way over $7.4 Billion.
Even a decade ago, small satellites were considered as a secondary payload on large launch vehicles. However, micro rockets for SmallSats recently changed this situation and ever more small sats now act as the primary payload.
The advantage of having SmallSats is that now companies do not have to wait for their turn to take off. They can schedule launches according to their timetable. The very first CubeSats that left our planet’s orbit for interplanetary use were the micro sats used for the Mars Cube One space mission.
How does a Micro Rocket engine Work?
A micro rocket engine does not require the same amount of fuel and thrust. Due to its small size, it can reach the Earth’s outer orbit with little propulsion. However, this does not mean that micro rocket engines are weaker than those of larger carriers. In fact, in many instances, these engines are much stronger.
Different companies that are working on SmallSat projects have different approaches to building the most reliable spacecraft. Scientists from China are using stainless steel for building a rocket’s outer body. And, European researchers are using Iridium as it is both lightweight and fire-resistant.
How does a Motor of a Micro Rocket Work?
Just like any regular rocket, micro rockets have to follow some rather strict rules. Depending on the purpose of a micro rocket launcher, it may need from one to three stages or booster. The first booster will be the most powerful one because it needs enough thrust to overcome drag in our planet’s atmosphere. The second stage may be used for navigating in orbit, while the final, third one is used to accurately deploy cargo in orbit.
Payloads, generally satellites, follow their rules, too. For example, CubeSat got their name because they consist of scalable units. This standard is referred to as the 1U. The smallest Nano Satellites can be only a few centimeters in length. You could easily hold such a satellite in the palm of your hand.
These satellites are often designed to fulfill very specific objectives, such as taking pictures or relaying signals from another satellite orbiting the Earth. Since they are so small, you can easily deliver them with various micro rockets. Unlike the big large carriers, micro rockets will never be as big as reusable rockets developed by many large space agencies.
However, unlike large carriers, micro rockets offer unprecedented launch flexibility and reduced launch cost. That is why so many commercial aerospace companies develop micro launchers to service all sorts of customers, i.e., small satellite makers and research organizations.