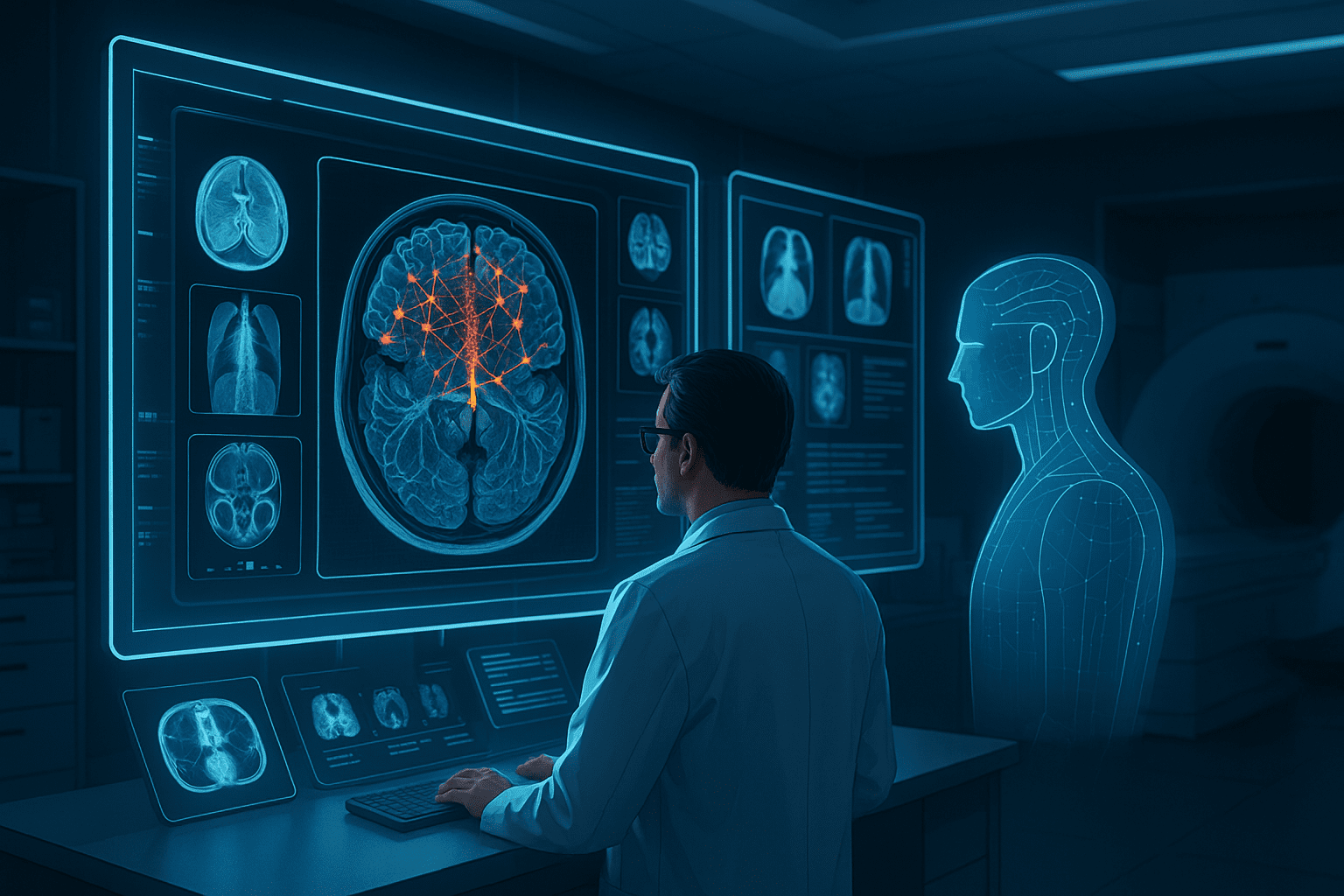
Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping healthcare. From diagnostic imaging and clinical decision support to workflow automation and population health analysis, AI systems promise to improve accuracy, efficiency, and access to care. Yet despite significant progress in algorithms and computing infrastructure, many medical AI projects struggle to reach reliable clinical deployment.
The limiting factor is rarely the model architecture itself. In most cases, the success or failure of medical AI systems depends on the quality of the annotated imaging data used during training. Without accurate, consistent, and clinically relevant annotations, even advanced deep learning models cannot deliver dependable results in real-world healthcare settings.
Why medical imaging data is uniquely challenging
Medical imaging data differs fundamentally from consumer or industrial imagery. Modalities such as MRI, CT, X-ray, ultrasound, and digital pathology capture complex anatomical structures that require expert interpretation. Variability across scanners, protocols, patient populations, and acquisition settings further increases complexity.
Unlike general computer vision tasks, medical imaging often involves subtle patterns that are difficult to detect. Small variations in tissue density, shape, or texture can indicate clinically significant conditions. These nuances place high demands on both annotation precision and domain expertise.
As a result, medical AI systems are particularly sensitive to annotation quality. Inaccurate or inconsistent labels can lead to models that appear performant during testing but fail when applied to new patient data.
The role of annotation in medical AI training
Most medical AI systems rely on supervised or semi-supervised learning. This means models learn from examples where the desired output is explicitly defined. In imaging applications, this output is provided through annotation.
Medical annotation services may involve:
- Segmentation of anatomical structures or lesions
- Classification of images or regions by pathology
- Localization of findings using bounding boxes or contours
- Pixel-level labeling for detailed tissue analysis
Each of these tasks requires careful alignment with clinical definitions and diagnostic criteria.
Annotation accuracy directly affects clinical reliability
In healthcare, annotation errors have consequences beyond reduced model accuracy. Mislabeling a lesion boundary, misclassifying tissue, or inconsistently defining anatomical regions can lead to false positives, missed diagnoses, or misleading risk assessments.
Because medical AI outputs may influence clinical decisions, annotation workflows must meet a higher standard than those used in many other AI domains. Precision, traceability, and consistency are essential.
Why medical annotation requires domain expertise
General-purpose annotation approaches are often insufficient for medical imaging. Many tasks require knowledge of anatomy, pathology, and clinical context. For example, defining tumor margins or identifying subtle imaging artifacts often demands input from trained professionals.
Consistency across annotators
Even experts may interpret images differently. Without clear guidelines and structured review processes, inter-annotator variability can introduce noise into training datasets. Over time, these inconsistencies degrade model performance and make results harder to reproduce.
Effective medical annotation workflows therefore emphasize:
- Detailed annotation protocols aligned with clinical objectives
- Reviewer calibration to ensure consistent interpretation
- Multi-stage quality assurance and validation
- Documentation of annotation decisions and edge cases
These practices help create datasets that support reliable model learning.
Deep learning amplifies annotation quality issues
Deep learning models are powerful pattern learners. They can extract complex features from large datasets and generalize across diverse inputs. However, this power also amplifies weaknesses in training data.
When annotations are inaccurate or inconsistent, deep learning models learn those errors at scale. The result may be a model that performs well on training data but behaves unpredictably in clinical settings.
Understanding how deep learning for medical image segmentation depends on high-quality labeled data highlights why annotation is such a critical component of medical AI pipelines. Segmentation models, in particular, are sensitive to boundary definitions and class consistency. Small annotation errors can propagate into large performance differences.
Scaling medical AI requires structured annotation pipelines
As medical AI projects grow, annotation challenges increase. Early research datasets are often small and manually curated. Scaling to larger, more diverse populations requires systematic processes that can handle volume while maintaining quality.
Key elements of scalable medical annotation
Successful medical AI teams typically implement structured pipelines that include:
- Standardized annotation guidelines reviewed by clinical experts
- Controlled label taxonomies with versioning
- Quality metrics to monitor annotation accuracy over time
- Feedback loops between model performance and data refinement
- Secure data handling to meet regulatory requirements
These elements ensure that datasets remain reliable as projects evolve.
Regulatory and compliance considerations
Medical AI development operates within strict regulatory environments. Standards related to data privacy, clinical safety, and auditability influence how training data is collected and annotated.
Annotated datasets must often support:
- Traceability of labeling decisions
- Documentation of annotator qualifications
- Reproducibility of training processes
- Clear separation between training, validation, and test data
Annotation workflows that lack structure or documentation can become obstacles during regulatory review, even if model performance appears strong.
From research models to clinical deployment
Many medical AI systems show promising results in research settings but encounter difficulties during clinical deployment. Differences in patient populations, imaging protocols, and operational workflows expose limitations in training data.
Organizations that successfully deploy medical AI treat data annotation as an ongoing process. Rather than labeling data once and moving on, they continuously refine datasets as new cases and edge conditions emerge. This approach helps models adapt to real-world variability and maintain performance over time.
Specialized partners such as DataVLab support medical AI teams by delivering high-quality annotated imaging datasets designed for clinical applications. By combining domain expertise with scalable annotation workflows and rigorous quality control, such approaches help organizations bridge the gap between research and deployment.
Data quality as a strategic asset in healthcare AI
In healthcare, trust is essential. Clinicians must understand and rely on AI outputs before integrating them into care pathways. High-quality annotated data contributes directly to this trust by enabling models that behave consistently and transparently.
Organizations that invest early in robust medical annotation capabilities benefit from:
- More reliable model validation results
- Faster regulatory readiness
- Reduced need for costly dataset rework
- Greater confidence among clinical stakeholders
As medical AI adoption accelerates, the ability to manage training data effectively becomes a key differentiator.
Conclusion: accurate annotation underpins medical AI success
Medical AI development depends on more than powerful algorithms and large datasets. It depends on the quality of the annotations that define what models learn.
Accurate, consistent, and clinically grounded image annotation is essential for building AI systems that perform reliably in healthcare environments. By prioritizing structured annotation workflows, domain expertise, and quality control, organizations can unlock the full potential of medical imaging data and bring AI solutions closer to real clinical impact.