Municipalities across various jurisdictions are under pressure to accelerate housing development while maintaining compliance with zoning, environmental, and infrastructure policies. Pre-approval permit systems are increasingly seen as an efficient solution, allowing developers to bypass prolonged discretionary review for projects that meet predetermined planning criteria. By shifting approvals to a standardized, criteria-based framework, municipalities can speed up the permitting process while ensuring design consistency and policy alignment.
One notable example is Pickering City Centre, where a master-planned redevelopment featuring high-density residential and mixed-use spaces illustrates the need for robust pre-approval mechanisms. With multiple towers, retail components, and proximity to major transit hubs, permitting delays could stall not only construction timelines but also broader economic and civic goals. Projects of this scale demand a pre-approval system that reduces uncertainty and ensures consistent application of planning principles across all phases.
Legal and Regulatory Foundations
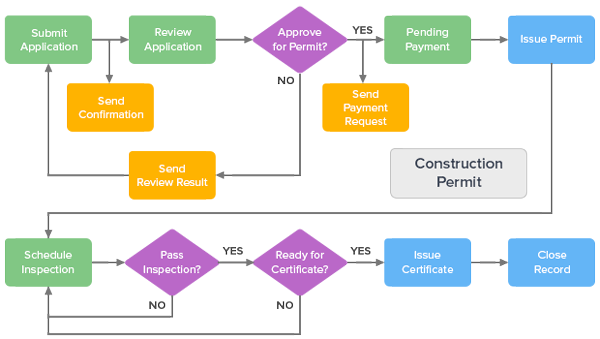
The authority for pre-approval systems is rooted in planning legislation that permits local governments to adopt Community Planning Permit Systems (CPPS). These frameworks consolidate zoning, site plan control, and minor variance approvals into a unified process. To launch a CPPS, municipalities must amend their official plans, engage in public consultation, and enact comprehensive implementing bylaws.
The implementation period for these systems generally ranges from 18 to 36 months, depending on municipal capacity, scope, and the degree of public engagement. Timelines are further influenced by external reviews from conservation authorities, infrastructure providers, and occasionally, provincial ministries. Careful sequencing of plan approvals and staff training is essential to prevent legal challenges and ensure the system is operationally ready.
Administrative and Technological Readiness
Successful pre-approval systems hinge on administrative preparedness and digital integration. Municipalities must modernize their permitting workflows, often by adopting digital permitting platforms that support submission, review, and tracking of applications in real time. These platforms enable automation of zoning checks, flagging of non-compliant designs, and faster interdepartmental coordination.
Implementation of these systems involves several steps: assessment of existing processes, procurement of technology, training of planning and building staff, and onboarding of external stakeholders such as developers and architects. Some municipalities opt to pilot pre-approval processes in specific growth areas before scaling citywide. Metrics such as permit processing time and application compliance rates are used to evaluate effectiveness.
While digitization enhances transparency and efficiency, its success depends on complete and accurate zoning data, user support infrastructure, and system interoperability with other municipal platforms. Cybersecurity protocols must also be embedded from the outset to protect sensitive project and ownership data.
Challenges in Rollout and Compliance
Common obstacles to implementing pre-approval systems include delays in plan adoption, lack of technical expertise, staff turnover, and inconsistent interpretation of design guidelines. Legal appeals to zoning changes or site-specific exemptions can also stall progress. Moreover, during early rollout, some municipalities may need to run parallel legacy and pre-approval permitting streams, placing strain on staff and resources.
To address these challenges, municipalities should invest in legal review of proposed systems and engage third-party planning consultants for technical support. Standardized design templates, detailed submission guidelines, and public education campaigns can further minimize compliance errors and encourage adoption.
Municipalities must also consider how pre-approval standards interact with existing development agreements or heritage overlays. Amendments or transitional provisions may be required to avoid legal conflicts and ensure consistent treatment of applications.
Stakeholder Engagement and Governance
Gaining public and developer support is essential for long-term viability. Transparent governance frameworks, stakeholder advisory panels, and public access to planning dashboards enhance accountability. Periodic review of pre-approval criteria and performance metrics ensures the system remains responsive to emerging design, demographic, and environmental considerations.
Municipal councils and planning committees must be briefed regularly on the system’s operation and impact. Developer associations and legal professionals also play a role in refining processes through constructive feedback and advocacy. Ensuring the pre-approval permit system can withstand political shifts and economic cycles requires strong interdepartmental governance and continuous policy evaluation.
Final Thoughts
Pre-approval permit systems offer municipalities a strategic opportunity to accelerate development approvals without sacrificing planning integrity. When well-implemented, these systems streamline predictable development while reserving resources for complex or sensitive applications. Timely and legally sound implementation of pre-approval systems is essential to support urban growth and streamline housing delivery across expanding urban centres.