The manufacturing sector stands on the brink of a technological transformation, with industrial drones emerging as a critical innovation driver. As factories evolve into smart, interconnected ecosystems, drones are transitioning from niche tools to essential components of modern industrial operations. The global market for commercial drones is projected to expand significantly, with the industrial segment experiencing particularly rapid adoption. These aerial workhorses are no longer just flying cameras but have become integrated data platforms, automated inspectors, and logistical partners that enhance every aspect of manufacturing from raw material to finished product.
For industry leaders like Jinghong Drone, this represents both a validation of years of specialized development and an exciting frontier for innovation. With over 15 years of manufacturing expertise, we’ve witnessed firsthand how drones have evolved from simple remote-controlled devices to intelligent systems capable of transforming entire production workflows.
Key Applications Transforming Manufacturing Operations
1. Inventory Management and Warehouse Optimization
Modern manufacturing facilities often span hundreds of thousands of square feet, with inventory spread across multiple levels and zones. Traditional manual inventory counting is not only time-consuming and labor-intensive but also prone to human error. Industrial drones equipped with RFID scanners and high-resolution cameras can autonomously navigate warehouse aisles, scanning thousands of items in a fraction of the time required by human teams.
These drones generate real-time inventory data, update management systems automatically, and can identify discrepancies immediately. For large-scale operations, this capability translates to reduced shrinkage, optimized stock levels, and significant labor cost savings. Some facilities report reducing inventory audit times from weeks to mere hours while achieving 99.9% accuracy rates in stock counting.
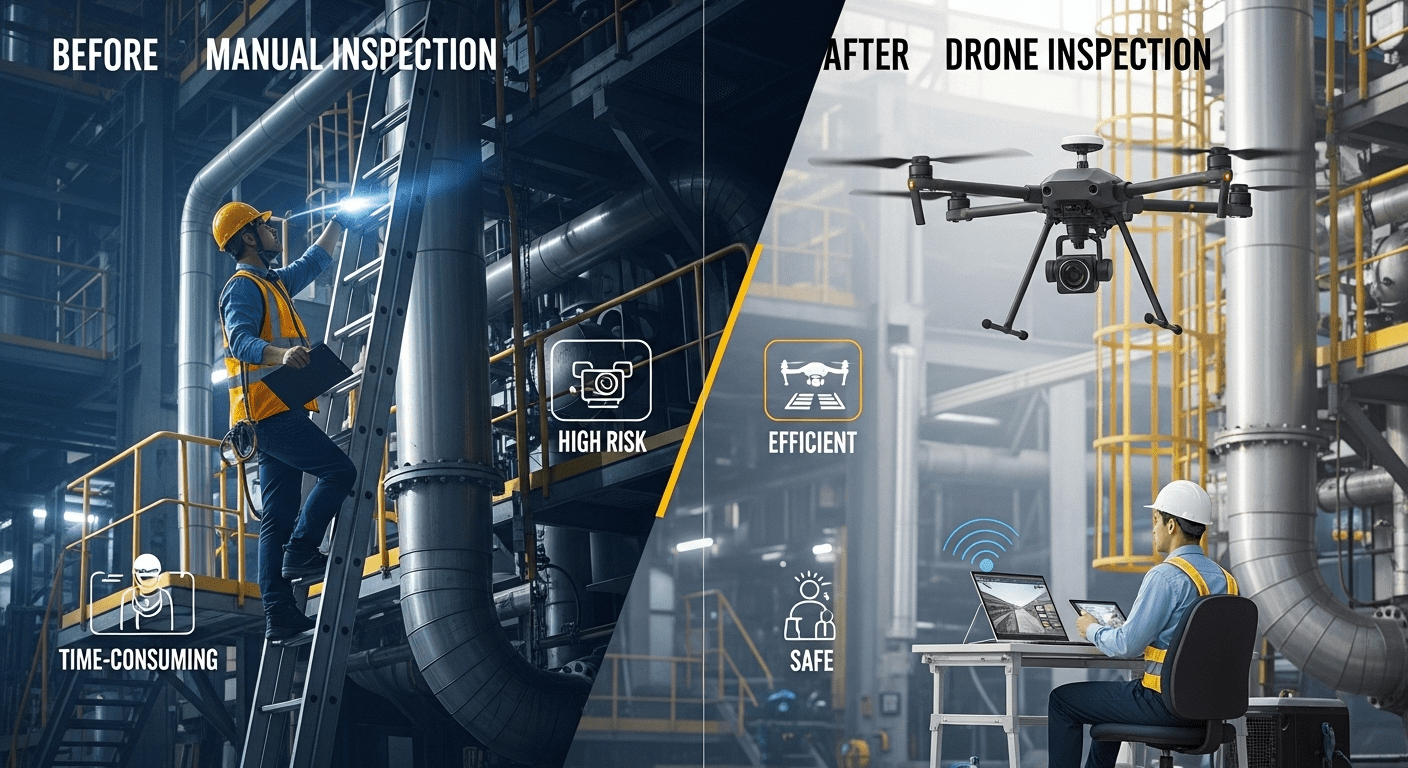
2. Facility and Infrastructure Inspection
Manufacturing plants contain extensive infrastructure that requires regular inspection—from roof integrity and structural beams to piping systems and electrical conduits. Traditional inspection methods often involve scaffolding erection, production downtime, and safety risks for personnel. Industrial drones eliminate these challenges by providing safe, rapid access to hard-to-reach areas without disrupting operations.
Equipped with thermal imaging, LiDAR, and high-zoom cameras, drones can detect issues invisible to the naked eye, such as heat leaks in piping, corrosion on structural elements, or cracks in concrete. This proactive maintenance approach prevents small issues from escalating into costly repairs or production halts. For example, a chemical plant using drone inspections reduced annual maintenance costs by 34% while improving overall facility safety ratings.
3. Quality Control and Production Monitoring
On the production floor, drones offer unprecedented perspectives for quality assurance. Mounted with specialized sensors, they can perform automated visual inspections of products along assembly lines, identifying defects with greater consistency than human inspectors. Advanced systems utilizing machine vision algorithms can detect minute imperfections in products, from paint inconsistencies on automotive parts to micro-fractures in composite materials.
Beyond defect detection, drones provide valuable workflow analytics by monitoring production processes in real-time. They can identify bottlenecks, measure cycle times, and ensure proper adherence to operational protocols. This data-driven insight enables continuous process optimization, directly impacting both product quality and production efficiency.
4. Safety and Security Surveillance
Manufacturing environments often involve hazardous materials, heavy machinery, and complex processes that require constant safety monitoring. Drones serve as aerial safety supervisors, monitoring compliance with safety protocols and identifying potential hazards before they cause incidents. They can patrol perimeter fences, monitor restricted areas, and ensure proper use of personal protective equipment.
In emergency situations, drones provide critical situational awareness without putting human responders at risk. They can assess chemical spills, structural damage from accidents, or fire outbreaks, feeding real-time information to emergency response teams. This capability not only enhances worker safety but also helps facilities maintain compliance with increasingly stringent industrial safety regulations.
5. Logistics and Internal Transport
Within sprawling manufacturing campuses, moving materials between buildings or across large facilities can be inefficient. Drones are increasingly handling internal logistics tasks, transporting tools, parts, or documents between locations faster than ground-based alternatives. For just-in-time manufacturing processes, where minutes matter, this aerial transport capability ensures materials arrive exactly when needed.
Specialized heavy-lift drones, such as the JH M400 Transportation Drone adapted for industrial use, can move payloads up to 200kg between production stations, reducing reliance on forklifts and conveyor systems. This application is particularly valuable in facilities with challenging layouts or where ground transport would interfere with production workflows.
Technological Foundations: What Makes Modern Industrial Drones Effective
Advanced Sensor Integration
The transformative power of manufacturing drones stems from their multisensor capabilities. Modern industrial drones combine visual, thermal, multispectral, and LiDAR sensors to capture comprehensive data about manufacturing environments. This sensor fusion allows a single platform to perform multiple inspection and monitoring tasks that previously required specialized equipment and personnel.
Autonomous Operation and AI Processing
Today’s industrial drones increasingly operate with high levels of autonomy, following pre-programmed flight paths while adapting to environmental conditions. Onboard AI processors enable real-time data analysis, allowing drones to make immediate decisions—like flagging a potential defect or adjusting their inspection pattern based on initial findings. This reduces the need for constant human supervision and enables scaling of drone operations across large facilities.
Integration with Industrial IoT Systems
The true power of drone technology emerges when it integrates with existing Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) ecosystems. Drones serve as mobile sensor nodes within smart factories, feeding data directly into Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms, and predictive maintenance algorithms. This creates a closed-loop system where aerial data informs decisions that optimize the entire manufacturing value chain.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Regulatory Compliance and Airspace Management
Manufacturers implementing drone programs must navigate complex regulatory environments, particularly in facilities near airports or in urban areas. Developing comprehensive airspace management plans, obtaining necessary certifications, and implementing geofencing solutions are essential steps for successful drone integration.
Data Management and Analysis
The volume of data generated by regular drone operations can be overwhelming. Successful implementations require robust data management strategies, including cloud storage solutions, automated processing workflows, and clear protocols for transforming raw data into actionable insights. Many companies are developing digital twin models of their facilities that continuously update based on drone-collected data.
Workforce Training and Change Management
Introducing drone technology requires upskilling existing personnel and sometimes creating new roles like drone operators and data analysts. Successful implementations involve comprehensive training programs and change management strategies that help workers understand how drones augment rather than replace human expertise.
The Future of Drones in Smart Manufacturing
As manufacturing embraces Industry 4.0 principles, drones will become increasingly integrated with other emerging technologies. We can anticipate:
- Swarm operations where multiple drones collaborate on complex tasks
- Enhanced AI capabilities enabling predictive analytics and truly autonomous decision-making
- 5G integration providing real-time, high-bandwidth data transmission
- Advanced human-drone collaboration through augmented reality interfaces
These developments will further blur the lines between physical and digital manufacturing, creating more responsive, efficient, and adaptive production systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What safety features do manufacturing drones have?
Industrial drones are built for safety with geofencing, obstacle avoidance sensors, and automated return-to-home functions. Facilities also create specific no-fly zones and operating procedures to ensure safe integration with existing workflows.
Q: How do drones navigate indoors without GPS?
For indoor navigation, drones use vision-based systems, LiDAR, and ultra-wideband (UWB) positioning. These technologies provide precise location data in warehouses and factories where GPS is unavailable.
Q: What is the average ROI for drone implementation?
Most manufacturing facilities see a positive return on investment within 6 to 18 months. Savings come from faster inspections, reduced downtime, more accurate inventory counts, and improved safety outcomes.
Q: How do drones connect to factory management software?
Drones integrate via APIs and middleware. This allows them to feed data directly into systems like MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and ERP software, automatically updating maintenance schedules and inventory logs.
Q: What training do operators need?
Beyond basic pilot certification, effective operation requires training in specific data collection methods, sensor use, and inspection protocols for manufacturing applications. Many drone providers offer this specialized training.
Conclusion
Industrial drones are fundamentally reshaping the manufacturing landscape, offering unprecedented capabilities in inspection, monitoring, logistics, and safety. As technology continues to advance, these aerial systems will become increasingly autonomous, intelligent, and integrated into the manufacturing ecosystem.
For forward-thinking manufacturers, the question is no longer whether to adopt drone technology, but how to implement it most effectively to gain a competitive advantage. By starting with specific pain points, building internal expertise, and selecting the right technological partners, manufacturers can harness the power of aerial intelligence to create safer, more efficient, and more responsive operations.
At Jinghong Drone, we’re committed to developing the next generation of industrial drone solutions specifically tailored to manufacturing challenges. Our expertise in creating robust, reliable UAV platforms positions us as an ideal partner for manufacturers embarking on their digital transformation journey.
Read More From Techbullion