In a world where countries are becoming increasingly interconnected, government policies play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of global trade agreements. From tariffs and quotas to environmental regulations and labor standards, the decisions made by governments can have far-reaching effects on international commerce. Join us as we explore the intricate web of relationships between government policies and global trade agreements, and uncover how these dynamics impact economies around the world.
Introduction to Government Policies and Trade Agreements
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping global trade agreements and impacting international trade. These policies are a set of rules, regulations, and measures that governments implement to regulate the economy and control trade activities within their borders. They can be both domestic or foreign policies, with the latter being more focused on international relations and trade.
In recent years, globalization has led to an increase in interconnectedness between economies, making government policies directly affect international trade agreements. The interdependence of countries in terms of resources, markets, labor, and technology calls for collaborative decision-making through negotiations and agreements.
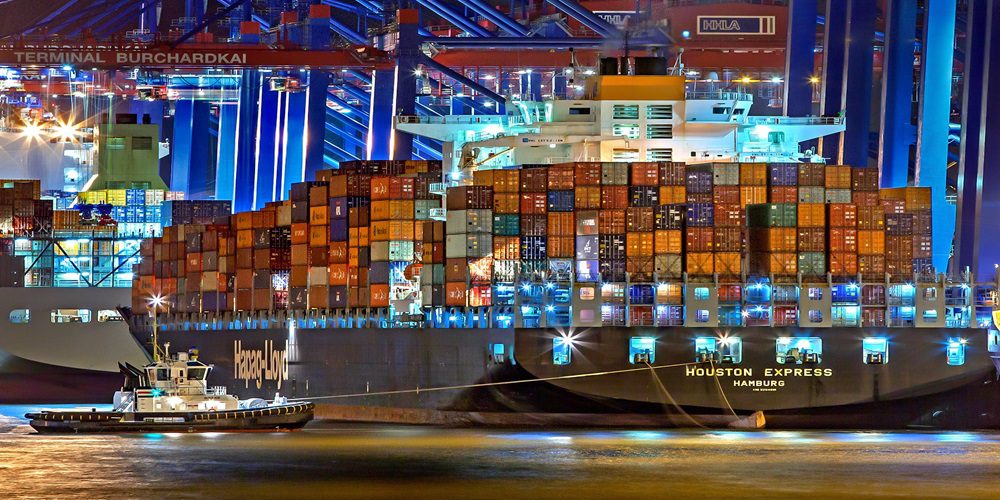
Trade agreements are formal treaties signed between two or more countries to establish mutually beneficial terms for trading goods and services. They aim to reduce barriers such as tariffs, quotas, subsidies, and regulations that hinder free flow of goods across borders. By entering into these agreements, countries commit to specific obligations designed to promote economic growth by increasing exports or imports.
There are various types of trade agreements such as multilateral (between many countries), bilateral (between two countries), and regional (among neighboring countries). Some notable examples include the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), European Union (EU), Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), among others.
The role of government policies in shaping these agreements cannot be overstated. Governments create laws that dictate how businesses operate domestically but also have implications for foreign trade relationships. For instance, imposing tariffs on imported goods may make them less competitive than domestic products but could lead to retaliatory tariffs from trading partners creating an unstable market environment.
Historical Overview of Trade Agreements
The history of trade agreements can be traced back to the ancient civilizations, where merchants and traders established informal agreements for the exchange of goods. However, it was not until the 19th century that formal trade agreements between countries started to take shape.
During this time, colonial powers such as Britain and France began to establish regional trade treaties with their colonies. These early agreements primarily focused on protecting their own economies by imposing high tariffs and quotas on imported goods from other nations.
One of the first major multilateral trade agreements was the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), signed in 1947 by 23 member countries. This agreement aimed to promote international cooperation in reducing tariffs and barriers to trade. As more countries joined GATT over the years, it became a central forum for negotiating global trade policies.
In 1995, the World Trade Organization (WTO) was created as a successor to GATT with a broader mandate for facilitating free and fair international trade. Currently, there are 164 members of the WTO who represent over 98% of world trade.
WTO negotiations have led to significant advancements in global trade policy through various rounds of talks since its establishment. One notable example is the Uruguay Round (1986-1994), which resulted in creating several new comprehensive agreements covering agriculture, intellectual property rights, services, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Other regional trade agreements have also emerged throughout history with varying degrees of success. The European Union (EU), formed through economic integration among its member states, serves as one such successful example. It has created a single market for goods and services within its borders while removing barriers to intra-regional trades.
On the other hand, some regional trading blocs like North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) have faced criticisms related to job losses due to outsourcing and unequal benefits distribution among member countries.
As globalization continued to shape our world economy, more nations started recognizing the importance of trade agreements in promoting economic growth and development. Hence, countries began negotiating bilateral trade agreements with the objective of expanding market access and reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
How Government Policies Shape Global Trade Agreements
Government policies have a significant impact on global trade agreements. These policies are created and enforced by governments to regulate, protect, and promote their country’s economy. In this section, we will discuss the various ways in which government policies shape global trade agreements.
1. Tariffs and Trade Barriers:
One of the most common ways in which government policies shape global trade agreements is through tariffs and trade barriers. Tariffs are taxes imposed by governments on imported goods, making them more expensive for consumers. These tariffs are used to encourage domestic production and protect local industries from foreign competition. By imposing high tariffs or creating strict rules for imports, governments can limit the amount of foreign products entering their country, therefore shaping global trade agreements.
2. Subsidies:
Governments also use subsidies to support their domestic industries and make them more competitive internationally. Subsidies are financial assistance provided by governments to businesses or industries with the aim of boosting production or reducing costs. This enables domestic producers to sell goods at lower prices than international competitors, giving them an advantage in global trade agreements.
3. Free Trade Agreements:
On the other hand, governments may also negotiate free trade agreements (FTAs) with other countries to reduce or eliminate barriers such as tariffs and quotas on imported goods. FTAs promote open markets and increase opportunities for international trade by providing businesses with access to new markets without facing high tariffs or other restrictions.
4. Regulatory Policies:
Government regulations also play a crucial role in shaping global trading relationships between countries. Regulatory policies include product standards, health and safety requirements, environmental regulations, etc., that must be complied with before goods can be sold in a particular market.
Deviations from these regulatory policies can result in penalties or prohibitions on imports from specific countries if they do not meet the required standards. These regulations ultimately influence which products can enter a country’s market and affect its trading relationships with other nations.
5.Economic Policies:
Government economic policies such as interest rates, exchange rates, and taxation also have a significant impact on global trade agreements. For instance, a government may devalue its currency to make exports more attractive and imports more expensive, ultimately altering the balance of trade between countries.
6. Foreign Investment Policies:
Governments can also shape global trade agreements through their foreign investment policies. These policies dictate the terms under which foreign companies can invest in domestic industries or acquire domestic companies. Restrictions on foreign investment can limit international competition and protect domestic industries from being acquired by foreign entities.
Case Studies of Successful and Failed Trade Agreements
Trade agreements are a vital component of global trade, as they establish mutually beneficial terms and conditions for participating countries. However, not all trade agreements are successful in achieving their intended goals. In this section, we will examine some case studies of both successful and failed trade agreements to understand the impact of government policies on these agreements.
Starting with successful trade agreements, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) serves as a prime example. Signed in 1994 between Canada, Mexico, and the United States, NAFTA aimed to eliminate tariffs and barriers to trade among its member countries. This agreement led to a significant increase in cross-border trade between the three nations, resulting in job growth and economic development. By implementing favorable government policies such as investor protection laws and removal of non-tariff barriers, NAFTA effectively facilitated smooth trade activities among its member states.
Another noteworthy example is the European Union (EU), which is considered one of the most successful examples of regional integration through trade agreements. The EU started with six member states in 1957 and has now expanded to include 27 nations. The EU operates under a single market system where goods, services, labor, and capital can move freely without any restrictions or barriers within its member states. This regional integration has resulted in increased competitiveness and improved economic performance for its members through harmonization of policies related to taxation, product standards, immigration laws, etc.
On the other hand, not all trade agreements have been as successful. A prominent example is the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), which involved twelve Pacific Rim countries but ultimately failed due to political opposition from some participating nations such as the United States withdrawing from it under former President Donald Trump’s administration in 2017. Despite initial optimism regarding benefits such as increased access to new markets and greater economic opportunities for smaller economies like Vietnam or Malaysia under TPP provisions; concerns over potential job losses due to offshoring prompted protests against this agreement.
Impact of Political Factors on Global Trade
The world of global trade is heavily influenced by political factors, and it’s important to understand how government policies can impact trade agreements. Governments play a crucial role in shaping international trade through various policies and regulations that are put in place. These policies can have both positive and negative effects on global trade, ultimately shaping the economic landscape of countries around the world.
One of the primary ways government policies impact global trade agreements is through tariffs and trade barriers. Tariffs, or taxes imposed on imported goods, are one of the most commonly used tools for governments to protect their domestic industries. For example, if a country’s government wants to promote local production of a certain product, they may impose high tariffs on imports of that product to make it more expensive for consumers and therefore encourage them to buy from local producers instead. On the other hand, if a government wants to increase competition among domestic producers, they may reduce or eliminate tariffs on imports to allow for cheaper foreign products to enter their markets.
Another factor that impacts global trade agreements is investment policies. Governments have control over rules regarding foreign direct investment (FDI), which is when companies invest in another country by setting up operations or acquiring existing businesses. Governments can either restrict or encourage FDI through regulations such as limits on foreign ownership, tax incentives, and protectionist measures. These investment policies influence where companies choose to invest and conduct business, thus impacting international trade flows.
In addition, political stability also plays a significant role in global trade agreements. Countries with unstable political environments may face difficulties in attracting investments due to concerns about security and potential changes in policy direction with different leaderships. This instability can lead to disruptions in supply chains and harm international relations with trading partners.
Government subsidies also have an impact on global trade agreements by creating an uneven playing field for businesses. Some governments provide subsidies to their domestic industries as support for growth and development. However, this practice gives these industries an advantage over their international competitors and can lead to trade disputes if other countries feel unfairly treated.
Future Outlook of Government Policies and Global Trade
The future outlook of government policies and global trade is one that is constantly evolving and adapting to the ever-changing global landscape. In recent years, there have been significant shifts in political dynamics and economic policies, which have had a direct impact on the world of international trade.
One of the major factors shaping the future outlook of government policies is the growing trend towards protectionism. With countries like the United States adopting more nationalist policies and imposing higher tariffs on imported goods, there has been a notable decrease in global trade agreements. This has led to concerns about potential trade wars and increased tensions between nations.
However, it is not all doom and gloom for international trade. Many governments are recognizing the importance of maintaining strong global connections and are actively working towards creating new trade partnerships. For example, Brexit may lead to challenges for both European Union (EU) member states and the UK in terms of their trading relationships but it also presents an opportunity for these nations to forge new trade deals with other countries outside of the EU.
Another key factor impacting government policies and global trade is technological advances. With technology becoming increasingly integrated into various industries, governments are having to adapt their policies to keep up with this changing landscape. Innovation in areas such as e-commerce, digital currencies, and logistics has opened up new avenues for cross-border trade, ultimately leading to a greater volume of international transactions.
Moreover, environmental concerns have become critical drivers for government policies in recent years. Climate change has prompted many countries around the world to prioritize sustainable practices in their economic activities. As such, we can expect to see more regulations being implemented by governments to ensure that businesses engage in environmentally friendly practices when conducting international trade.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that government policies play a crucial role in the development and implementation of global trade agreements. From setting tariffs and regulations to negotiating terms with other nations, governments have a significant influence on the flow of goods and services across borders. While some policies may benefit certain industries or countries, others can create barriers to fair trade practices. As our world becomes increasingly interconnected through international trade, it is essential for governments to carefully consider their policies’ impacts on global trade agreements and strive towards creating mutually beneficial partnerships for all involved parties.