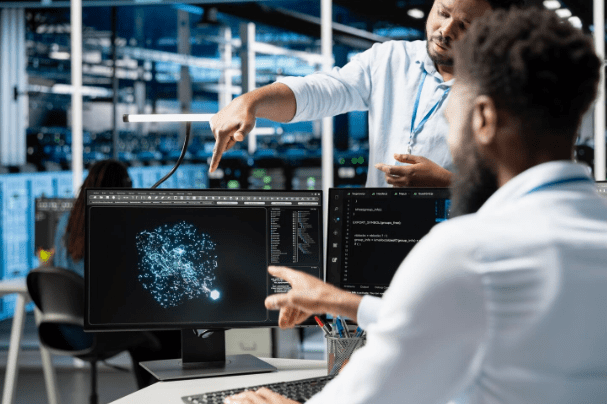
Quantum computing is steadily moving from theory into practical business experimentation, and companies no longer need a physics lab to explore its potential. With cloud-accessible platforms and developer-friendly tools, quantum technology is becoming part of real-world workflows. IonQ, a leader in trapped-ion quantum computing, enables businesses and developers to access quantum power without investing in complex hardware infrastructure. Rather than replacing classical computing, IonQ’s systems enhance it by solving highly complex calculations that traditional machines handle inefficiently. From logistics and finance to cybersecurity and artificial intelligence, organizations are already discovering how quantum resources can unlock smarter decisions, faster simulations, and competitive innovation. This article explores practical, realistic ways businesses and developers can begin applying IonQ’s quantum systems today.
Optimization Problems for Real-World Business Decisions
One of the most immediate and valuable uses of quantum computing lies in optimization. Many industries face problems that involve evaluating massive numbers of possible combinations: supply chain routing, portfolio balancing, workforce scheduling, traffic flow, and logistics planning. Classical computers often rely on approximations because the search space becomes too large to handle efficiently. IonQ’s quantum systems can explore many possibilities at once using quantum states, making them well-suited for these combinatorial challenges.
For example, logistics companies can experiment with optimizing delivery routes across thousands of variables, reducing fuel usage and improving delivery times. Financial institutions can analyze risk distributions across large portfolios more efficiently. Manufacturers can optimize production schedules by considering machine constraints, labor availability, and demand forecasts simultaneously.
Developer Experimentation, Cloud Integration, and Innovation Labs
Perhaps the most practical way businesses can use IonQ today is through developer experimentation. IonQ systems are accessible via cloud services such as AWS Braket, Azure Quantum, and Google Cloud, significantly lowering the entry barrier. Developers can write quantum programs, test circuits, and integrate quantum calls into standard applications without owning specialized hardware.
Innovation teams can build internal quantum labs, running pilot projects in optimization, simulation, and AI without disrupting core operations. Startups can prototype quantum-powered features, while enterprises can train engineers in quantum programming languages like Qiskit or Cirq adapted for IonQ hardware. One realistic approach is using the keyword concept once: teams explore how useful IonQ’s quantum systems become when combined with classical workflows rather than isolated as experimental tools. This mindset shifts quantum from a novelty into a practical extension of existing infrastructure.
Quantum Simulation for Materials, Chemistry, and Energy
Another powerful area where IonQ’s technology shines is simulation. Simulating molecules and materials at the quantum level is extremely demanding for classical computers because quantum behavior is inherently complex. IonQ’s trapped-ion architecture is particularly useful for modeling chemical reactions, electronic structures, and material properties with higher precision.
In practical terms, pharmaceutical companies can use quantum simulations to better understand molecular interactions during drug discovery, reducing trial-and-error in the lab. Energy companies can explore new battery materials, catalysts, and solar components by simulating how atoms behave under different conditions. Even startups in sustainable technology can benefit by testing new compounds digitally before physical production.
Enhancing Machine Learning and Data Analysis
Quantum computing is not meant to replace machine learning, but it can augment certain parts of it. IonQ’s systems can help explore large, complex datasets and improve how models detect patterns, especially when relationships between variables are non-linear and high-dimensional. While fully quantum machine learning is still emerging, practical hybrid approaches already exist.
Businesses can use quantum circuits for feature selection, clustering, and sampling tasks within AI pipelines. For instance, marketing teams can analyze customer behavior across many variables, finding correlations that classical sampling might miss. Financial analysts can model fraud detection scenarios with more nuanced probability distributions. Developers working with IonQ often combine Python, classical ML frameworks, and quantum kernels to accelerate specific computational steps.
Cybersecurity, Cryptography, and Risk Testing
Security is another practical domain for quantum exploration. While quantum computing is known for its potential to break classical encryption in the future, it also offers tools for building and testing stronger security systems today. IonQ’s quantum platforms allow developers to experiment with quantum-safe cryptography, random number generation, and protocol validation.
Organizations can simulate how future quantum attacks might affect existing encryption methods and begin preparing migration strategies toward post-quantum security standards. Banks, governments, and SaaS companies can test authentication schemes, secure communication channels, and key distribution models using quantum principles. Developers use IonQ to prototype quantum key distribution logic and stress-test cryptographic assumptions.
Quantum computing is no longer a distant promise reserved for researchers; it is becoming a practical tool for modern businesses and development teams. As more developers gain experience and more real-world use cases emerge, IonQ’s technology will continue to move from experimentation into strategic application. Companies that begin exploring now position themselves to innovate faster, reduce computational limitations, and stay competitive in a future shaped by quantum computing.