Data is the lifeblood of any organization and handling data without sacrificing speed of access and processing is essential.
Centralized servers, though easy to operate and maintain, have their limitations in the modern world. Data storage costs are reduced, but at a cost of the user being located physically too distant and therefore, things like latency, bandwidth limitations and network disruptions can have a drastic impact.
The answer? Have multiple data centers so the distance between the data storage and user is reduced to increase efficiency.
Introducing Edge Computing
Edge computing is a form of decentralized data storage and processing system where all operations are handled at the “edge” of a network, ensuring that the user and the data are as close as possible. Hence the name.
A distributed database system sounds like the perfect solution, but it comes with a host of its own problems.
It has a heavy impact financially. A distributed database requires a distributed storage solution, meaning you have multiple physical servers to maintain and look after. While this is something that is unavoidable, other issues start to build up. With users located as close as possible, but still physically away from the data, APIs need to be built, structured and set up that have to ensure load balancing taking into consideration the internal network bandwidth, the internet connection etc. Lastly, all of the data caching and distributed databases have to connect seamlessly to be in sync.
How HarperDB Overcomes Edge Data Issues
The team at HarperDB has been well aware of these issues. Forced to handle the enormous pressure of keeping the system up and running, developers are like firefighters and most of their efforts are concentrated on the upkeep, rather than bringing in innovations.
HarperDB has the privilege of being the only solution provider for the globally distributed database sector. HarperDB makes all this easy to operate by having faster performance, while still having lower latency and a cost efficiency that is unparalleled.
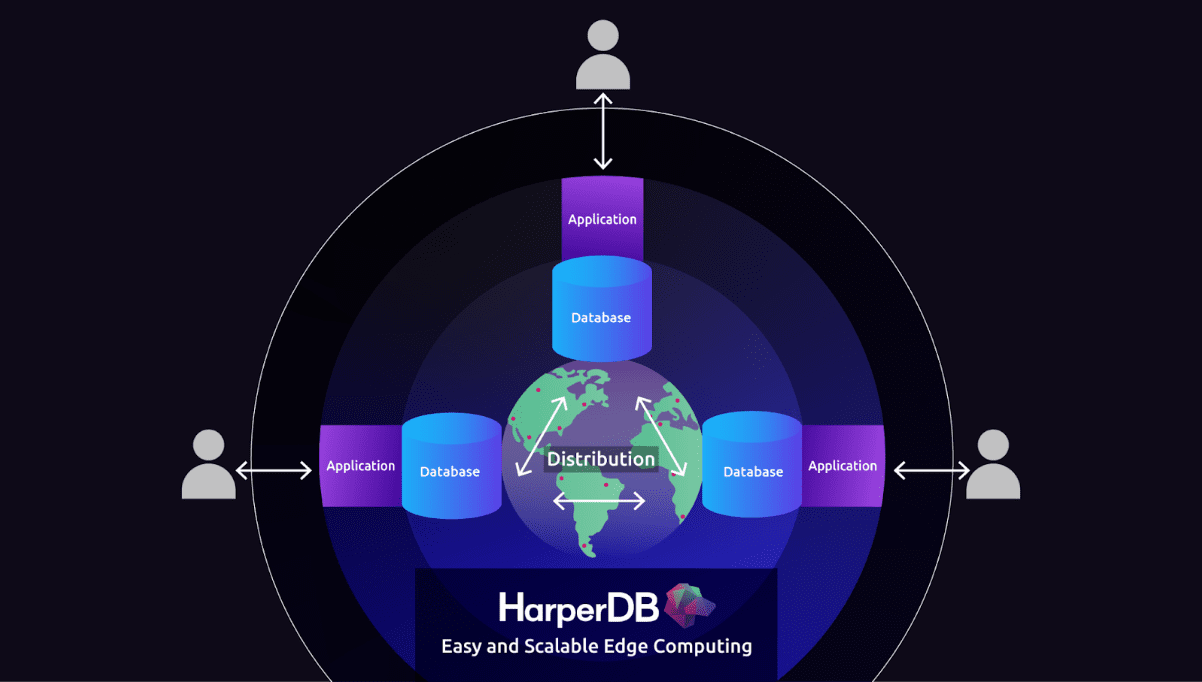
Creating simplicity without sacrificing performance, HarperDB enables three key components of the complete distributed data structure:
- The Application Layer: HarperDB’s Custom Functions access embedded API servers where users can deploy APIs, machine learning and other applications without the need of setting up and deploying additional technologies.
- The Database Layer: Using auto indexing, HarperDB gives users the ability to have access to the data in a flexible manner that is reminiscent of NoSQL, but still retains the scalability and performance characteristics of RDBMS.
- The Distribution Layer: Users can use HarperDB to replicate distributed data and real time applications in not seconds, but milliseconds. This means data accessing personnel can grab data from the nearest source as fast as possible.
The result is a solution by HarperDB that creates a full stack for edge database management and access for a wide variety of industries, from IoT to Telecom to Gaming. With HarperDB, firms are able to concentrate on bringing innovation and features to their systems rather than focusing on developing and running complex infrastructures.
Exploring the Challenges and Complexities of Deploying Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that brings computation and data storage closer to the users and devices that need them. By moving compute resources closer to the edge of the network, edge computing reduces latency, improves security, and reduces bandwidth costs.
But when it comes to edge computing, there are a few challenges that need to be addressed in order for it to be widely adopted and deployed.
There is the issue of data privacy and security. Since data is stored and processed at the edge, it is more vulnerable to attacks. There needs to be a way to secure data at the edge so that it is not compromised.
There is the challenge of managing and coordinating all the different devices that are connected to the edge network. This can be a daunting task, especially as the number of devices increases.
Bandwidth constraints need to be considered when deploying edge computing solutions. Since data is being processed and stored locally, it will consume bandwidth. This needs to be taken into account when designing edge computing solutions.
Interoperability between different edge computing solutions needs to be ensured. Otherwise, it will be difficult for different solutions to work together seamlessly.
Besides the many potential benefits to using Edge Computing such as improved performance, reduced latency, and increased efficiency, the deployment of edge computing can be a complex process, depending on the specific needs of an organization. In some cases, edge computing may need to be deployed in a distributed manner, with each deployment site having its own dedicated resources. And as stated above, security and networking considerations may need to be taken into account when deploying edge computing systems.
What Does HarperDB Bring to the Table?
Saying something is done better is one thing and being able to do it is a whole other thing. Fortunately, HarperDB is able to do what it says, thanks to its years of development and innovation in the distributed database and edge caching technology.
HarperDB was able to achieve some of the most low latency operations for distributed data handling, such as less than 1 millisecond from API to data, 10 to 50 milliseconds for edge latency and just 100 milliseconds required to deploy database replication anywhere in the world.
But accessing data faster is not just dependent on the API for data latency, but the reading and writing capabilities of the nodes and servers too. HarperDB uses alternatives to NoSQL that are faster, have lower cost of operation and allow for scalability with ease. This gives HarperDB the ability to have 20,000 write operations executed per second for each node, with read stats touching 120,000 per second per node.
The horizontal scaling means HarperDB has one of the least linear cost to capacity ratios, giving firms the ability to reduce costs by as much as 50%, occasionally even more.
Edison Interactive, a DooH advertising platform leveraged HarperDB services to increase its API call speed by 250x. Similarly, the US Army is also using HarperDB to enhance the military’s edge in facial recognition technology to identify foes.
Conclusion
Despite the complexities of deploying edge computing in 2023, organizations need to stay ahead of their competitors and recognize the potential that edge computing has to offer. With careful planning and a comprehensive understanding of the technologies involved, businesses can reap significant rewards from utilizing edge computing. As more companies explore its opportunities, we will see an increased adoption rate for this emerging technology in the coming years.



































