Unlike in temperate climates where greenhouses used in the winter, and are heated, greenhouses in tropical climates such as Kenya have no heating and are used all year round. They are covered with UV treated polythene, not glass or fiber glass. In the ventilated sections, white colored low or high density insect nets are used. The choice of white because it reflects much light which deters insect entry. It also reflects off heat
There are various types of greenhouses in Kenya by Grekkon Limited categorized by;
1.Construction material
1.1Galvanised steel greenhouses
The steel bars used in greenhouse construction in Kenya are of various sizes depending on their position in the structure. Thicker and stronger steel bars are placed on the edges as anchors. The lighter steel gauge is placed on the roof, and also acts as the internal crop support system. The choice of thickness of the steel bars adopted depends on the greenhouse location. In windy locations, the steel bars are deliberately stronger than in calm areas.
Food grade aluminum or zinc is what Grekkon Limited uses to galvanise these steel frames to keep them from rust. All vertically placed steel bars that are in contact with the ground have a concrete base. This strengthens the structure, and holds it in place during strong wind, or a storm.
1.2Wooden greenhouses
Treated timber greenhouses are cheaper than galvanized steel greenhouses. However, they have a shorter lifespan, because wood is degraded much faster than galvanized steel. Their design too is less flexible, and so they are designed as vented type models.
Growers are advised not to treat the timber with used motor oil. This is because it will contaminate food crops.
2.By activity
2.1Crop production
Galvanised steel or wooden greenhouses are used for food crop production, and ornamentals. These structures have planting beds to ensure proper drainage, and irrigation is by drip systems.
2.2Seedling production
The have 1meter high tables on which seedling trays are placed. On the roof, a system of misters or foggers to humidify are installed. Vegetable, herb, fruit, cereal, spice, forestry, and ornamental crops are commonly propagated in these structures.
2.3Fish rearing
Fingering production, and fish rearing in greenhouses is a growing practice amongst Kenyan farmers. This commercial venture is driven by the growing demand for fish and fish products locally, and internationally. They are shorter in height than crop production greenhouses, and are warmer. Locally, they are referred to as haygroves
-
The design adopted
3.1. Vented type greenhouses. They have an opening on the roof, and are taller in height. This opening, and additional height allows for more airflow in the structure, creating a higher cooling effect. These are for very hot- where average daily temperatures are beyond 30 degrees Celsius. This is for the mid to low altitude locations
3.2. Tunnel type greenhouses. Their roof is continuous, and have only the side ventilation. They are also shorter in height. Constructed in the highlands, or cool locations. Daily average temperatures here do not exceed 30 degrees Celsius
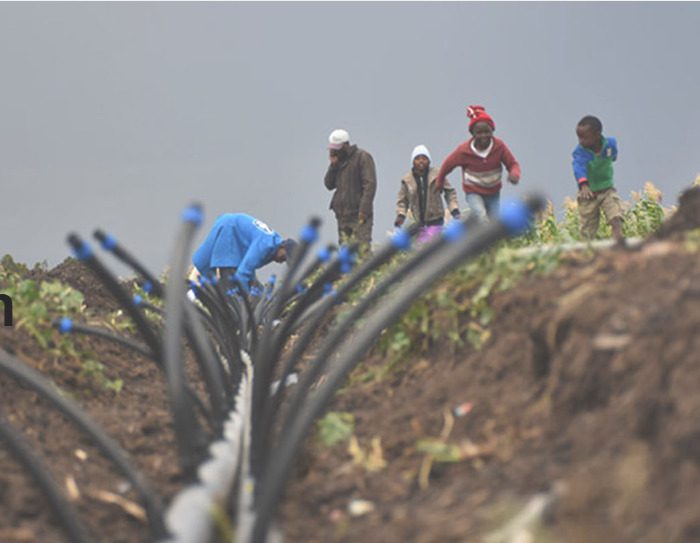
Our drip irrigation system in every greenhouse is through a HDPE main line.