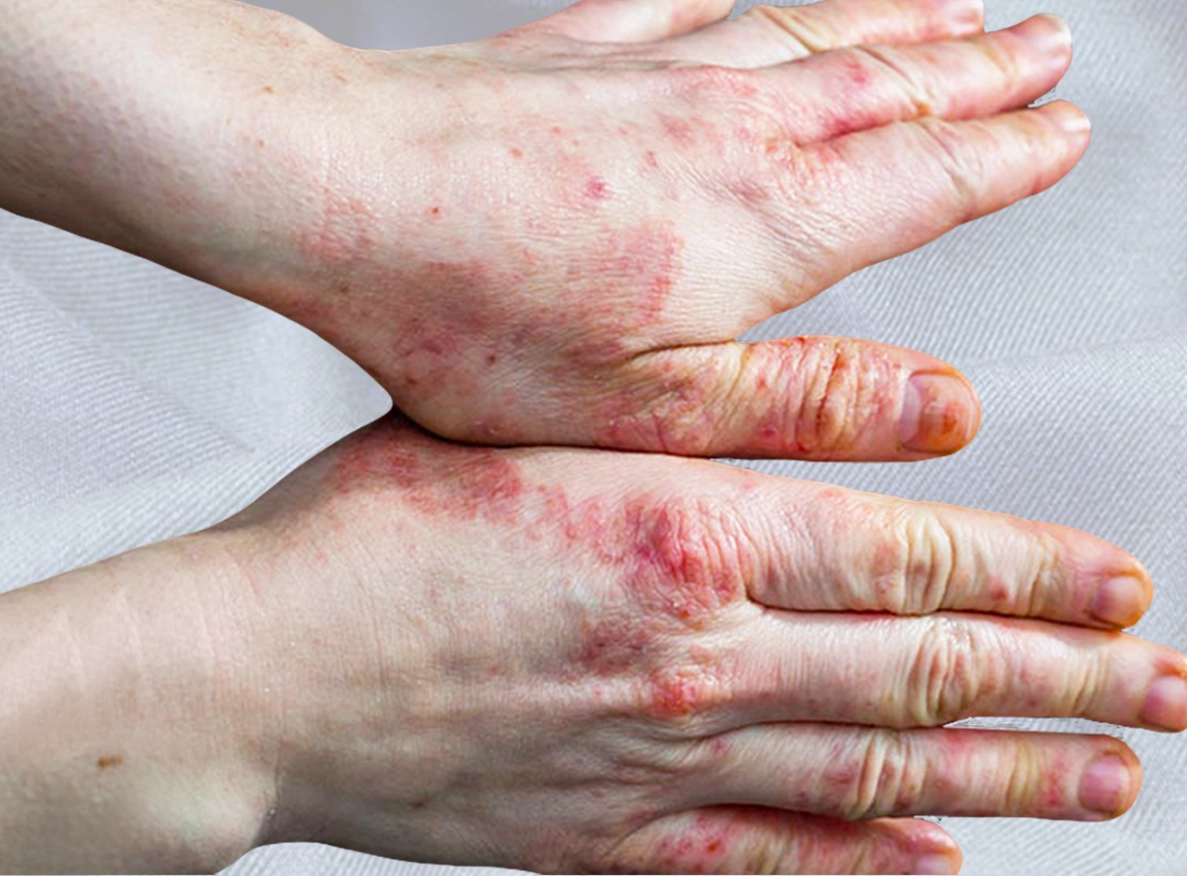
Eczema is one of the most common skin conditions affecting both children and adults in Singapore. Our hot, humid climate intensifies sweating, increases bacterial activity on the skin, and weakens the skin barrier — all of which can trigger or worsen eczema flare-ups. For patients who come to my clinic, the biggest challenge is rarely the diagnosis; it’s learning how to control flare-ups long-term, prevent relapses, and manage the emotional toll of constant itching, dryness, and sleep disruption.
While eczema cannot be “cured” in the traditional sense, it can be controlled extremely well with a proper treatment plan. The goal is not just to suppress symptoms temporarily but to strengthen the skin barrier, reduce inflammation, and equip patients with lifestyle strategies that keep flare-ups to a minimum.
For many patients searching for the best eczema doctor in Singapore, the first step is understanding the range of treatment options available — from quick itch-relief measures to advanced therapies used in dermatology clinics today. Every individual requires a customised plan because eczema varies widely in severity, triggers, and skin responses.
Below is a comprehensive, expert-level guide that walks through what patients can expect, how treatment decisions are made, and what long-term control really looks like.
Understanding the Eczema Landscape in Singapore
Eczema affects people differently, but there are patterns clinicians repeatedly see in Singapore:
- Patients experience more frequent flare-ups during hot months
- Stress from work or school often intensifies symptoms
- Sweat, dust mites, and fragrances are common triggers
- Many patients have a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies
- Over-scratching leads to secondary bacterial infections
- Some patients develop lichenified (thickened) skin from chronic inflammation
Most importantly, many patients try to self-manage for too long — relying solely on moisturisers or over-the-counter creams — before finally seeking professional evaluation. By the time they arrive, the eczema is often severe or complicated by infection.
A proper treatment plan requires breaking the itch–scratch cycle, targeting inflammation, and strengthening the barrier from within.
How Dermatologists Diagnose & Assess Eczema
During an eczema consultation, I begin by examining several aspects:
1. Severity and distribution
Is the eczema localised to certain areas (e.g., hands, eyelids) or widespread?
2. Presence of infection
Crusting, oozing, or yellow scabs may signal a bacterial overgrowth.
3. Chronic vs acute stages
Acute flare-ups look red and swollen, while chronic eczema appears dry, thickened, and leathery.
4. Trigger identification
This is crucial. Triggers may include:
- environmental allergens
- chemicals
- sweat
- fragrances
- stress
- certain fabrics
- excessive bathing
- temperature changes
5. Patient lifestyle
A strategy for a busy office worker differs from a plan for a child with severe atopic dermatitis.
Once the evaluation is complete, we determine a tiered treatment plan, which may range from mild topical therapies to advanced systemic options.
Immediate Relief: Treatments for Acute Eczema Flare-Ups
When patients come in with intense itching, painful skin, or visible weeping lesions, the first priority is rapid, effective relief.
1. Medicinal Moisturisers & Ointments
These are different from regular moisturisers. Medical-grade emollients contain:
- ceramides
- humectants
- occlusive agents
- barrier-repair compounds
These formulas restore the skin’s barrier, reduce water loss, and soothe inflammation. They are the foundation of any eczema plan.
2. Topical Steroids (TCS)
Steroids remain one of the most reliable tools for stopping inflammation quickly.
We prescribe:
- mild steroids for the face and thin skin
- medium-to-strong steroids for arms, legs, and trunk
- short courses tailored to severity
Misuse can cause side effects, but appropriate dermatological use is safe and effective.
3. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors (TCIs)
These non-steroidal creams (e.g., tacrolimus, pimecrolimus) help reduce inflammation, especially in sensitive areas like eyelids, neck, or skin folds.
4. Wet Wrap Therapy
This technique dramatically reduces itching for moderate-to-severe flare-ups.
It locks in moisture and medications, speeding up recovery.
5. Antibiotic or Antimicrobial Treatment
If the eczema is infected, we treat the infection first.
Symptoms of infection include:
- yellow crusting
- pus
- fever
- painful swelling
This is extremely common because scratching breaks the skin barrier.
6. Antihistamines for Itch
These support sleep and reduce scratching at night.
Moderate to Severe Eczema: Advanced Clinic-Based Treatments
When standard topical treatments aren’t enough, dermatologists escalate care to modalities that offer stronger, longer-lasting relief.
1. Phototherapy (NB-UVB)
Narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) is one of the most effective non-invasive treatments for chronic eczema.
Performed 2–3 times a week, it:
- reduces inflammation
- improves skin thickness
- helps itching
- supports long-term remission
It is safe for both adults and children under dermatological supervision.
2. Immunomodulators & Systemic Medications
For severe eczema that affects quality of life, oral medications may be required.
These include:
- immunosuppressants (short-term or long-term)
- targeted oral anti-inflammatory agents
- allergy-modulating medications for atopic individuals
These drugs are carefully monitored with regular blood tests.
3. Biologic Therapy for Severe Atopic Dermatitis
Biologics are one of the biggest advancements in eczema care.
They target specific inflammatory pathways responsible for eczema rather than suppressing the entire immune system.
Benefits:
- dramatically reduce itch
- heal chronic lesions
- decrease flare frequency
- safe for long-term use
- suitable for patients who failed standard therapy
Patients often report life-changing improvements within weeks.
Long-Term Control: Keeping Eczema Stable
Once an acute flare-up has settled, the real work begins: maintaining remission. Long-term control requires a combination of medical management and lifestyle adjustments.
1. Consistent Moisturisation
Dermatologists recommend moisturizing:
- 2–3 times daily
- immediately after showers
- after hand washing
- during dry or windy weather
Consistency prevents micro-cracks in the skin barrier.
2. Trigger Avoidance
Dermatologists help patients identify and eliminate triggers such as:
- perfumed products
- harsh soaps
- dust mites
- detergents with dyes or fragrances
- wool or synthetic fabrics
- rapid temperature changes
- prolonged sweating
3. Stress Management
Stress is a well-known eczema trigger.
Many patients experience flare-ups during exams, work deadlines, or emotional stress.
4. Maintenance Medications
This may include:
- twice-weekly topical steroids
- twice-weekly TCIs
- barrier-repair creams
- on-demand antihistamines
This strategy prevents micro-flare-ups that could escalate.
5. Regular Follow-Up
Monitoring skin progress helps us adjust treatment, taper medications safely, and prevent relapse.
Special Considerations for Children with Eczema
Singapore has one of the highest rates of childhood eczema in Asia.
Children require more tailored care because:
- Their skin barrier is more delicate
- They may not articulate itch well
- Scratching leads quickly to infection
- Sleep disturbance affects growth and behaviour
Typical paediatric treatment includes:
- steroid-sparing strategies
- gentle cleansers
- wet wraps
- allergen evaluation when relevant
- parental education on daily care
Early intervention dramatically improves long-term outcomes.
Hand Eczema: A Growing Issue Among Adults
With increased handwashing, sanitiser use, and exposure to cleaning agents, hand eczema is on the rise.
Symptoms include:
- cracked fingertips
- red patches
- painful splits
- blisters
- thickened scaly skin
Treatment usually involves:
- strong topical medications
- occlusive nighttime therapy
- barrier-protection strategies
- workplace adjustments (e.g., gloves, barrier creams)
Hand eczema should be treated promptly to avoid chronic thickening.
Eczema & Singapore’s Humid Climate: What Patients Must Know
Humidity is a double-edged sword:
- It prevents the skin from drying out
- But it also increases sweating, which irritates skin and worsens inflammation
Patients often benefit from:
- breathable cotton fabrics
- gentle cleansing after perspiration
- avoiding prolonged sun exposure
- showering briefly with lukewarm water
- avoiding extreme air-conditioning
Lifestyle & Home Strategies Dermatologists Recommend
Besides medical treatments, these home strategies help maintain healthy skin:
1. The “Soak and Seal” Method
A short warm bath followed by immediate moisturisation helps calm flare-ups.
2. Choosing the Right Soap
Use fragrance-free, soap-free cleansers that do not strip the skin barrier.
3. Humidifier Use
Air-conditioning dries the skin.
A humidifier can help prevent night-time itching.
4. Avoid Hot Showers
Hot water strips lipids from the skin and triggers inflammation.
5. Nail Care
Short nails help prevent deep scratches and infections.
When to See a Dermatologist ASAP
Seek immediate evaluation if you notice:
- sudden worsening of eczema
- fever or swollen lymph nodes
- painful, rapidly spreading lesions
- yellow crusts or pus
- eye or eyelid involvement
- severe sleep disruption
- suspected allergic reaction to skincare products
These signs may point to infection, allergy, or severe inflammation that requires urgent care.
What Long-Term Remission Looks Like
With proper dermatological care, patients can achieve:
- fewer flare-ups
- milder symptoms
- stronger skin barrier
- smoother skin texture
- less dependence on steroids
- restful sleep
- significantly improved quality of life
Most importantly, remission is realistic and sustainable.
Final Thoughts
Eczema is a chronic condition, but it is absolutely manageable with the right combination of medical treatment, maintenance care, and lifestyle adjustments. Singapore clinics today offer an extensive range of evidence-based options — from topical therapies to biologics — that can transform a patient’s quality of life.
Whether you are dealing with mild itching or severe, persistent flare-ups, partnering with an experienced dermatologist allows you to regain control and achieve long-lasting skin stability.