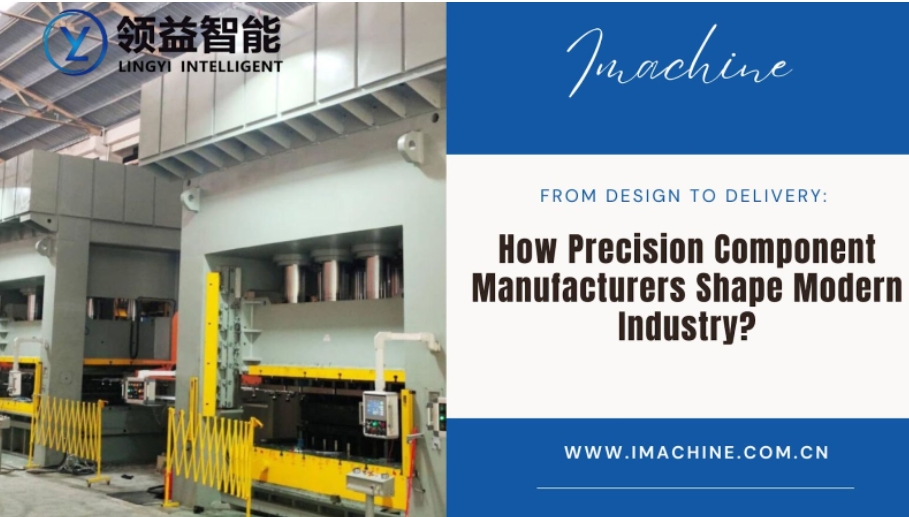
Precision Parts Manufacturing is no longer a back-end process hidden in the shadow of large industrial operations—it is the very engine driving modern innovation across aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and electronics. From intricate aerospace components to life-saving medical devices, the work of a precision component manufacturer ensures that today’s high-performing machines and systems function seamlessly.
As industries embrace tighter tolerances, enhanced performance, and customized functionalities, the role of precision engineering has evolved significantly. This blog explores how precision part manufacturers shape modern industry—from design innovations to delivery precision—and how technologies like Deburring machines and sheet leveling machines are integrated to deliver flawless output.
Did You Know?
“Over 60% of global manufacturers now integrate precision CNC machining into their core production processes.”
Understanding the Role of Precision Component Manufacturers
At its core, a precision component manufacturer designs and produces complex parts with tight tolerances that must meet exact specifications. These are not just nuts and bolts—they are the tiny, often invisible components that power turbines, assemble microchips, and operate surgical tools.
Precision at Every Step
- Micron-level accuracy
- Material integrity across temperature and stress levels
- ISO certifications and industry-grade quality assurance
They combine state-of-the-art precision equipment and expert human oversight to develop components that match exact performance metrics across varying industries.
The Growing Demand for Precision Parts
According to recent market data, the global precision parts market is projected to reach USD 403.22 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 9.43% from 2023 to 2029. This demand is driven by:
- Increasing automation in manufacturing
- Miniaturization in electronics and medical devices
- Rising quality standards in global supply chains
- Shift towards Industry 4.0 technologies
Additionally, the precision manufacturing industry in India is projected to grow at an 8% annual rate, showing a clear global inclination toward accurate, reliable, and high-functioning parts.
Stages of the Precision Manufacturing Lifecycle
The journey from design to delivery includes several meticulous steps. Each phase reflects the discipline, technology, and innovation characteristic of the precision manufacturing industry.
1. Conceptual Design
Design engineers collaborate with clients to translate concepts into CAD models. This phase focuses on:
- Material selection
- Feasibility assessments
- Prototyping possibilities
2. CAD Modeling and Simulation
Software like SolidWorks and AutoCAD is used to build highly detailed digital prototypes. Virtual stress tests and functional simulations ensure zero errors before production begins.
3. Precision Machining
This is where Precision manufacturing equipment like CNC machines, laser cutters, and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machines) come into play.
4. Post-Processing
Once parts are machined, they undergo finishing processes like:
- Deburring (removing residual material)
- Sheet leveling (ensuring uniform flatness)
- Surface coating, polishing, or heat treatment
5. Inspection & Quality Control
Metrology tools measure each component with micron-level precision, ensuring strict tolerance limits.
6. Packaging & Delivery
Cleanroom packaging, anti-static bags, and shock-resistant packaging ensure safe delivery to industries worldwide.
Precision Manufacturing Technology: The Driving Force
Modern precision manufacturing technology integrates automation, AI, and digital twins into production workflows. Below are the tech trends transforming the industry:
- Smart Manufacturing: IoT-enabled machines monitor wear and tear in real time.
- AI-Driven Quality Control: Automated systems detect sub-millimetre flaws.
- Additive Manufacturing: Also known as 3D printing, allows for rapid prototyping and low-volume high-precision runs.
- Digital Twins: Simulated models of real-world machines for virtual stress testing and workflow optimization.
Types of Industries Benefiting from Precision Parts
Today’s manufacturing landscape depends heavily on precision part manufacturers across sectors:
| Industry | Applications |
| Aerospace | Jet engines, satellite components, and landing gear |
| Automotive | Gearboxes, engine valves, braking systems |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, implants, diagnostic tools |
| Electronics | Microprocessors, circuit boards, sensors |
| Defence | Surveillance equipment, armoured vehicles |
Each of these sectors requires reliable, scalable, and repeatable manufacturing of parts, where even a fraction of error can cause major functional failure.
Why Precision Matters: Business and Economic Impact
Investing in precision equipment and trained professionals doesn’t just improve component quality—it reduces overall production waste, boosts efficiency, and ensures faster time-to-market.
Key Business Advantages
- Lower failure rates reduce warranty claims and service calls.
- Greater product lifespan enhances consumer trust
- Reduced rework saves energy and resources.
- Scalability becomes easier with repeatable production systems.
In today’s competitive manufacturing space, precision is not optional—it’s a strategic differentiator..
Innovation Through Collaboration
To thrive in this precision manufacturing industry, companies are increasingly forming alliances with research labs, universities, and software providers.
Recent strategic movements include:
- Mergers and Acquisitions to access new tech
- Contract manufacturing for global reach
- Cross-industry partnerships to diversify product offerings
- Increased investments in AI, robotics, and cloud-based MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems)
These collaborations result in agile manufacturing workflows and highly customized client offerings.
Challenges and Solutions in Modern Precision Manufacturing
Despite immense advancements, manufacturers face persistent challenges. However, innovative solutions are paving the way forward.
Common Challenges
- Managing high material costs
- Keeping up with rapid tech changes
- Recruiting skilled labour
- Maintaining tight tolerances at scale
Effective Solutions
- Automating repetitive tasks through robotics
- Using simulation software for predictive maintenance
- Outsourcing component-level tasks to global units
- Continuous upskilling of the workforce
The Role of Specialized Equipment in Precision Engineering
Modern precision engineering is incomplete without cutting-edge precision manufacturing equipment. Some examples include:
- CNC Machines: Provide unmatched repeatability
- Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs): Used for quality inspection
- Laser Cutters & Waterjets: Ensure thermal-free high-speed cuts
- Deburring Machines: Vital for safe, smooth part finishes
- Sheet Leveling Machines: Create consistent component geometries
Together, these technologies help transform raw materials into finely finished, high-performance products.
Looking Ahead: Precision Manufacturing in the Next Decade
The future of Precision Parts Manufacturing lies in hyper-customization, data-driven decision-making, and sustainable production practices.
Emerging Trends to Watch
- Sustainable machining: Reduced water, oil, and energy usage
- Blockchain traceability: Authenticating part origin and production details
- Cloud-based design collaboration: Reduces time from concept to production
- Microfactories: Decentralized production for local delivery and faster iteration
These innovations are shaping how precision parts will be designed, manufactured, and distributed in a fast-changing industrial landscape.
Building the Future One Micron at a Time
From aerospace components to wearable medical devices, precision parts are the silent yet powerful forces shaping the future of technology. The role of a precision component manufacturer is not only to deliver par, s—but to deliver performance, reliability, and innovation in every product.
As the global market continues to expand, fueled by technological advancement and demand for high-accuracy components, the spotlight will remain on those who can build faster, better, and smaller—without compromising quality.
Whether through next-gen precision manufacturing equipment, data-rich AI systems, or collaborative global partnerships, precision manufacturers are redefining what’s possible—one micron at a time.
Key Takeaways
- Precision component manufacturing is critical to industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive.
- The global precision parts market is projected to reach $403.22 billion by 2029.
- Technologies like CNC, deburring machines, and sheet leveling machines are key tools in the manufacturing process.
- Trends like AI integration, sustainability, and additive manufacturing are shaping the future of the industry.
- Precision matters not only for quality but also for cost savings, customer trust, and scalability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What does a precision part manufacturer do?
A precision part manufacturer designs and produces high-accuracy parts with strict tolerances, often used in critical sectors like aerospace, healthcare, and automotive.
Q2. Why is precision important in modern manufacturing?
Precision reduces waste, increases product lifespan, and ensures performance consistency, which is essential for high-functioning and safe machinery.
Q3. How are precision parts inspected for quality?
Inspection tools like Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs), laser scanners, and digital micrometers are used to ensure each part meets dimensional and material standards.
Q4. What industries benefit the most from precision parts?
Sectors such as aerospace, medical, automotive, defence, and electronics heavily rely on precision parts for their performance-critical systems.
Q5. What’s the future of the precision manufacturing industry?
The future will see more use of AI, sustainable machining practices, and decentralized microfactories, offering faster, cleaner, and more customized manufacturing solutions.