Blockchains are an emerging technology that is already changing the world and will continue to disrupt many industries. When a conversation turns toward Bitcoin, it is only natural to mention blockchain technology. If you’re someone new to the crypto world, questions like ‘What is blockchain technology?’, ‘How does it relate to cryptocurrencies?’ and ‘What are the different types of blockchain technology?’ are common occurrences.
So before we get into much detail about blockchain technology, first, let’s understand the basics of blockchain technology.
Defining Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger. Blockchain keeps track of all transactions and assets in a business network. These assets can be either tangible (a house, car, or land) or intangible (Intellectual property patents, patents, copyrights). Businesses and individuals have started using blockchain technology to track things of value because the process is easy and secure.
Blockchain technology has changed the game for businesses. Information is what makes a business, and due to blockchain technology, getting the most accurate information in the fastest way possible has become extremely easy. Learn more about blockchain technology and become an expert on blockchain technology.
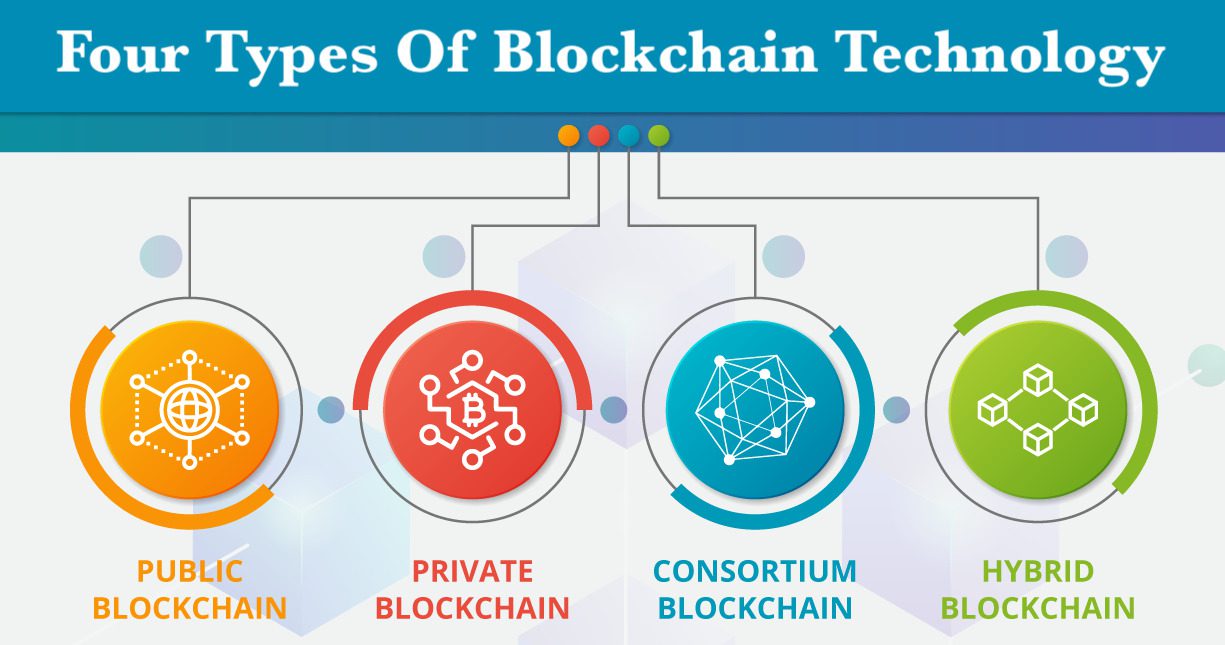
The 4 types of Blockchain Technology
There are different types of blockchain technology for a variety of purposes. You can choose which type you want to use based on what you need it for. There are 4 types of blockchain technologies so far. They are private blockchain, public blockchain, permissioned blockchain, and consortium blockchain.
1. Private Blockchain
Businesses and organizations use private blockchain networks because they tend to work on closed networks. Private networks give companies the ability to customize the accessibility of their blockchain network as it suits their organization. In addition, they can set the parameters for their network and manage the security as per their needs.
Privacy becomes extremely important for organizations if they don’t want their competitors to get access to any of their data. A competitor organization can disclose private information about an organization to the media, ruining the business’s plans for itself.
Pros:
- Quicker than other blockchain networks
- Tighter in security
- Minimum change of hacking
- One company is entirely in charge of the network
Cons:
- Risky for smaller organizations
- Less number of participants can collapse the entire network
Examples:
- Multichain
- Corda
2. Public Blockchain
A public blockchain has no restrictions on who can participate in the network. Anyone who wants to join the network can sign onto a blockchain platform with their device and internet connection. There is no need for anyone’s permission to distribute the ledger system.
Public blockchains are common for mining. They are also common for exchanging cryptocurrencies. Once a person is part of the network, they are authorized to access records and transactions from a block.
Public blockchain networks do not lose their security if all users follow the rules and do not jeopardize the network’s security. After all, you must realize that it is tough for someone to modify once-validated data on a public blockchain network. So while it might look riskier than a private network, the data is still unchangeable.
A public network is even said to be the perfect model for blockchain due to decentralization.
Pros:
- Multiple nodes are linked together, adding an extra layer of security
- Every transaction comes with transparency
Cons:
- The more nodes, the more time it takes to verify transactions
- There is a risk of hackers
- Public blockchains like bitcoin are safe, but a less decentralized network would be risky.
Examples:
- Bitcoin
- Ethereum
- Litecoin
3. Permissioned Blockchain
A permissioned blockchain is also known as a hybrid blockchain because it combines private and public blockchain networks. In a permissioned blockchain network, users can control who can get access to what information. Not all the data that goes on the blockchain is made public. Whoever manages the data can make it public or keep it private and only accessible to certain people.
A permissioned blockchain also allows users to join a private network while being part of a few public networks; when a user tries to join a private network, they usually have to be verified and permitted into the network by someone inside the network.
Pros:
- They are resistant to 51% of hacker attacks
- This is a high-performing network
- They are scalable and cost-effective
Cons:
- It does not provide incentives for network participation
- There are issues with transparency
Examples:
- Dragonchain
4. Consortium Blockchain
As a semi-decentralized network, more than one organization manages the blockchain network. So it’s unlike a private blockchain network with only one authority. Here in the consortium blockchain network, the authority is shared among organizations.
So organizations that are part of a consortium blockchain network can carry out transactions, exchange information, and even do crypto mining. You will find a lot of government organizations or banks using a consortium blockchain network.
Pros:
- They are faster than public blockchain
- And offer control to more authorities than a private blockchain
Cons:
- There is a lack of transparency
- Nodes can get compromised and risk the collapse of the entire network
- It does not provide incentives for network participation
Examples:
- Energy Web Foundation
- R3
Conclusion
Blockchains are not only innovative and revolutionary, but they have proven to be an effective solution in today’s digital world. We can see the importance of blockchains being connected to the internet as it is one of the most important benefits that it has.
Blockchain has lots of potentials when working with big and small businesses. You decide to make which blockchain technology will serve your organization the best. Public networks are easier to manage if you know everything about blockchain. Then, you will make the right moves and won’t risk any data you’re putting on the public blockchain network. Hopefully, this article was informative enough that now you better understand different types of blockchain technology and networks.