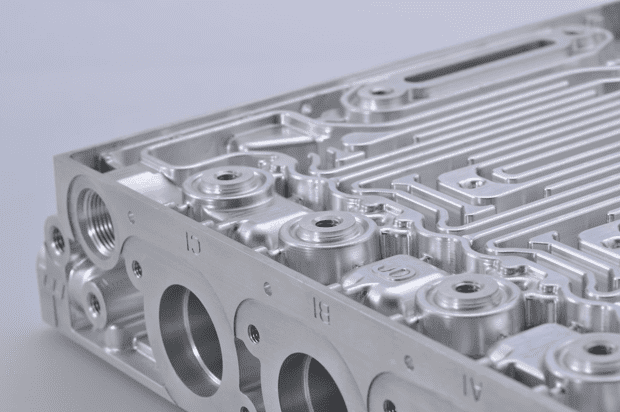
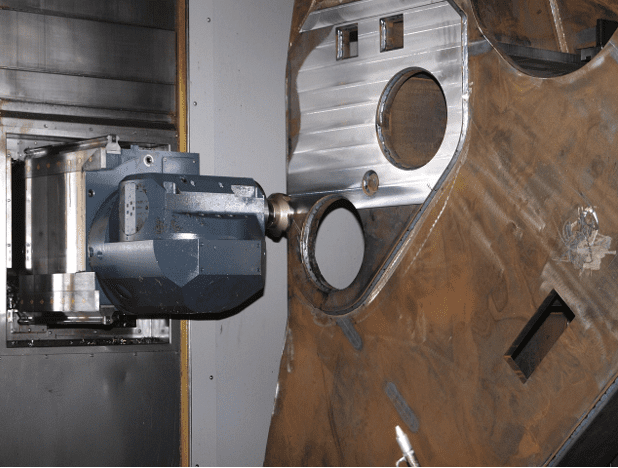
CNC machining remains one of the most fundamental technologies in modern manufacturing, powering precision production from prototypes to high‑volume parts.
But in 2025 and beyond, machine shops aren’t just cutting metals with computer‑controlled tools; they’re transforming how manufacturing works by embracing automation, smart systems, sustainability, and digital‑driven innovation.
These shifts are reshaping the capabilities, efficiency, and competitiveness of CNC machining across global markets.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
One of the most significant trends in CNC machining is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to improve decision‑making and productive output.
New CNC systems embed AI‑driven algorithms that analyze data from sensors and machines in real time to optimize toolpaths, anticipate maintenance needs, and dynamically adjust cutting parameters.
This level of intelligent automation can reduce cycle times, minimize defects, and improve equipment effectiveness (OEE).
AI plays a part in predictive maintenance. Instead of relying on fixed maintenance schedules, AI systems forecast when machine components are likely to fail based on patterns in temperature, vibration, and tooling conditions.
By catching these issues early, manufacturers can avoid costly downtime and extend tool and machine life. In this evolving vista, the industries served by Aerotech Machining are benefiting from these advancements, as machine shops continue to cater to sectors that demand precision and speed, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing. These systems improve quality control by flagging anomalies before parts move downstream.
As datasets grow, machine learning models become more accurate, enabling continuous improvement without manual reprogramming. AI-assisted simulation further reduces trial runs by validating setups virtually before cutting begins.
Smart Factories and IoT Connectivity
Connected Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and devices have made CNC machines smarter and more transparent. IoT integration allows remote monitoring, real‑time diagnostics, and wireless communication between devices on the shop floor.
With sensors feeding data to centralized dashboards, operators can track productivity, spot anomalies, and schedule maintenance before issues worsen.
This connectivity supports Industry 4.0 paradigms, where machines, tools, and systems communicate seamlessly. The result is an intelligent manufacturing environment that reduces waste, improves uptime, and develops agile, data‑driven decision‑making.
Lights‑Out and Fully Automated Machining
Automation has been a part of CNC machining for decades, but the latest evolution is lights‑out machining, where machines operate with little to no human intervention.
Advances in automation, coupled with robotics and smart material handling, allow production runs to continue overnight or during weekends without on‑site labor.
This trend is driven not just by labor savings but by improved consistency and throughput.
Robotic arms can load and unload parts, perform in‑process inspection, and handle fixturing tasks traditionally done manually. For manufacturers facing labor shortages, this capability is a game‑changer.
Hybrid Manufacturing
CNC machining is increasingly blending with other manufacturing technologies to form hybrid systems. Hybrid manufacturing combines subtractive machining with additive manufacturing (3D printing) in a single integrated process.
For example, a part might be built up additively near net shape and then CNC‑finished to achieve tight tolerances.
The hybrid approach offers advantages such as reduced material waste, faster production of complex geometries, and greater design flexibility.
These systems are particularly beneficial for aerospace, medical, and high‑performance engineering parts where complex features and precision are both important.
Multi‑Axis and Ultra‑Precision Machining
The traditional 3‑axis CNC machines have now been surpassed by multi‑axis machining centers that offer more flexibility and precision.
Machines with 5 or more axes can approach a part from multiple angles in a single setup, reducing the number of fixture changes and improving accuracy on complex contours.
Alongside multi‑axis machines, ultra‑precision machining techniques are gaining traction. These involve extremely fine control over tool motion, enabling surface finishes at micro‑ or even nano‑scale tolerances.
Such capabilities open doors for advanced optics, high‑performance bearings, and precision medical components.
Cloud‑Based Systems and Digital Thread Integration
Cloud computing is transforming CNC operations. Cloud‑based CNC platforms allow secure storage of programs, real‑time collaboration across sites, and access to advanced analytics without heavy local infrastructure.
Engineers and operators can share CAD/CAM data instantly, improving design‑to‑production workflows.
This digital thread links design, manufacturing, and quality data across the lifecycle of a part, breaking down silos and enabling end‑to‑end traceability. With this transparency, manufacturers can better manage revisions, improve quality control, and respond faster to changes in demand.
Advanced Materials & Tooling Technologies
The CNC industry is expanding beyond traditional metals like aluminum and steel into advanced materials such as composites, superalloys, and high‑performance polymers.
These materials present machining challenges, including higher tool wear, thermal stress, and surface integrity issues, driving innovation in tooling materials and coatings.
Cutting‑edge carbide, ceramic, and polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tools extend life and performance, and smart tool monitoring systems help detect wear before it affects quality.
These advances make it feasible to machine parts that were once too difficult or costly to produce.
Sustainability and Green Machining
Sustainability is no longer an afterthought in CNC machining. Manufacturers are adopting green machining practices that reduce energy consumption, recycle coolants, and minimize scrap material.
Energy‑efficient servo drives, near‑dry machining techniques, and coolant recovery systems help reduce environmental impact without sacrificing performance.
This shift aligns with broader corporate sustainability goals and increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. Customers are pushing for suppliers that can demonstrate eco‑friendly manufacturing credentials, making sustainability a competitive advantage.
Improved CNC Programming & Next‑Gen Interfaces
CNC programming is evolving beyond traditional G‑code. Modern CAM softwareincluding platforms integrated with AI‑assisted toolpath generation, makes programming easier and more intuitive.
Tools that automatically generate optimized code help reduce errors and shorten setup times. Emerging standards like STEP‑NC, which embed richer design data directly into machining instructions, aim to replace legacy G‑code with a more semantic and flexible file format.
As adoption is still emerging, such advances represent a long‑term shift toward smarter, model‑based manufacturing.
Quality Control & In‑Process Inspection
Advanced CNC systems now integrate quality control directly into the machining process. High‑resolution probes, laser measurement systems, and machine vision verify part dimensions as they are made, allowing immediate correction or rejection of out‑of‑tolerance features.
This reduces the need for separate inspection steps, accelerates throughput, and improves first‑pass yield. For industries with strict compliance, such as aerospace and medical, in‑process inspection is important to guarantee consistent quality.
CNC machining is undergoing a broad technological transformation. From AI and IoT to hybrid manufacturing and sustainable practices, these trends are pushing the boundaries of what precision manufacturing can achieve.
As production demands evolve and industries seek faster, more capable, and greener solutions, CNC machining will continue to adapt and innovate, creating opportunities for businesses that embrace these emerging technologies.
Read More From Techbullion