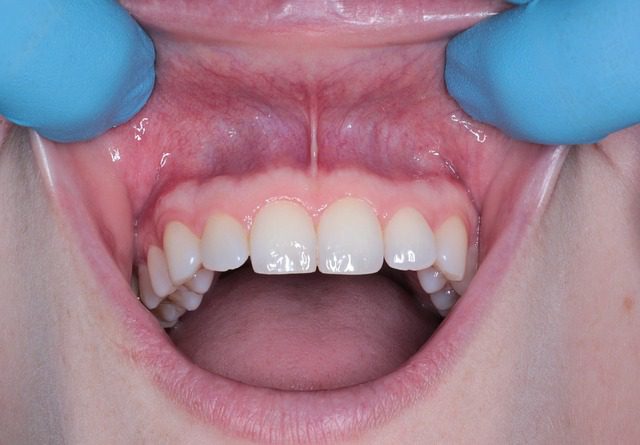
Swollen gums around a tooth can be a sign of underlying oral health issues that require attention. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options to address this condition effectively. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind swollen gums around a tooth, discuss common symptoms to watch for, and provide insights into treatment options and preventive measures for optimal oral health.
Swollen gums around a tooth can occur due to various factors, and recognizing the causes and symptoms is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Let’s explore some common causes and symptoms associated with swollen gums:
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the most common cause of swollen gums. It is an early stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gums. Poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, and bacterial infections can contribute to gingivitis.
- Periodontitis: If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. Periodontitis causes the gums to recede and form pockets around the teeth, leading to swelling, redness, and tenderness.
- Dental Abscess: A dental abscess is a pocket of pus that forms due to a bacterial infection. It can cause severe pain, swelling, and inflammation around the affected tooth. Abscesses require immediate dental attention to prevent further complications.
- Trauma or Injury: Trauma or injury to the gums, such as accidental biting, aggressive brushing, or dental procedures, can result in swelling and tenderness around the affected tooth.
Recognizing the symptoms of swollen gums is essential for early detection and timely treatment. Some common symptoms include:
- Swelling and puffiness of the gums
- Redness or discoloration of the gums
- Tenderness or pain around the affected tooth
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Receding gumline or the appearance of gaps between teeth
Treating swollen gums around a tooth involves addressing the underlying cause and adopting preventive measures for long-term oral health. Here are some remedies and practices to consider:
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial for preventing and treating swollen gums. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristle toothbrush, floss regularly, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash to remove plaque and bacteria from the gumline.
- Rinse with Saltwater: Rinse your mouth with warm saltwater to reduce swelling, inflammation, and kill bacteria. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and swish it around your mouth for 30 seconds before spitting it out.
- Use a Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help reduce swelling and provide temporary relief. Wrap a few ice cubes in a clean cloth and hold it against the swollen gums for 10-15 minutes at a time.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid consuming hot, spicy, or acidic foods and beverages that can irritate the gums further. Also, refrain from smoking, as it can worsen gum inflammation and delay healing.
- Dental Treatment: If the swelling persists or worsens, seeking dental treatment is essential. A dentist will evaluate your condition and determine the appropriate course of action. Treatment options may include:
- Professional Cleaning: A thorough dental cleaning by a dental hygienist can help remove plaque and tartar buildup, reducing inflammation and swelling.
- Scaling and Root Planing: In cases of advanced gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be necessary. This treatment involves removing bacteria and tartar from below the gumline and smoothing the tooth roots to promote gum reattachment.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to control bacterial growth and reduce inflammation.
- Dental Procedures: In situations where a dental abscess or tooth decay is causing the swollen gums, dental procedures such as root canal therapy or tooth extraction may be necessary to eliminate the infection and alleviate symptoms.
Prevention is key to maintaining optimal oral health and preventing swollen gums. Here are some preventive measures to incorporate into your oral care routine:
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Use an Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to kill bacteria and reduce the risk of gum infections.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to detect and address any potential oral health issues before they escalate.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support gum health and overall oral health.
- Avoid Tobacco Use: Tobacco use increases the risk of gum disease and delays healing. Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco products can significantly improve gum health.
Conclusion:
Swollen gums around a tooth should not be ignored, as they can be indicative of underlying oral health issues. Recognizing the causes and symptoms of swollen gums is crucial for seeking timely treatment and preventing further complications. By practicing good oral hygiene, adopting preventive measures, and seeking dental treatment when needed, you can alleviate discomfort, promote oral health, and maintain a healthy smile. If you experience persistent swelling or discomfort, consult with your dentist for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment. Your oral health is key to your overall well-being, so take proactive steps to keep your gums healthy and prevent swollen gums around your teeth.