Since the market competition becomes more and more fierce, companies have to respond to the market demand more accurately and quickly to win and survive. Good product function and appearance are important factors to catch customers’ eyes. So product development engineers need to make prototypes to verify the function and appearance characteristics. Prototyping plays an important role in the product lifecycle.
How to get a prototype that accurately represents your design? Though many companies might have their machining centers, lots of products need to go through a series of post-processing processes such as painting, anodize, and polishing to have a requested appearance. Besides, most middle and small companies do not have equipment and experience of rapid prototyping. As a result, it is of great importance to choose a prototype manufacturer with rich manufacturing experiences. Wayken Rapid Manufacturing headquartered in Shenzhen, China, is a good choice.
For prototype manufacturing, the first thing to be considered is the choice of material and manufacturing process. Although for many prototypes, such as functional or engineering prototypes, they must be made from materials that are consistent with the final mass production, some prototypes used only for concepts or exhibitions can be made from cheaper materials and processes. A good prototype manufacturer will try to gain more project details and provide appropriate suggestions.
What Would be the Material for Prototype Stage?
The functional verification prototype material must be machined from the same material as the final product. But in some cases, without requests such as strength, stiffness, it can use similar materials to make a prototype. For example, CNC machined aluminum and steel parts can be used for automotive assemble prototypes, as well as to simulate the appearance and mechanical fit function properties of the final products.
Polyurethane
The material used for urethane casting is polyurethane. It could choose different brands and different functional characteristics of the material according to the project needs. Polyurethane can simulate the characteristics of engineering plastics, such as ABS, PMMA, PP, PA, etc. In addition, for the material with particular shore hardness and color requirements, it can also choose the corresponding material to mix the ratio and finally meet the requests.
Polyurethane casting material has a wide range of properties and can break through the limitations of CNC machining, which makes it a good choice for plastic prototyping.
How to Select a Correct Prototyping Process?
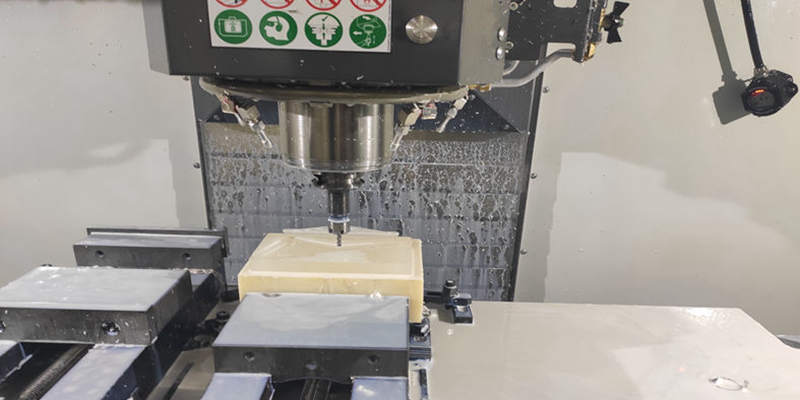

3D printing is a hot and popular prototyping technology at present. However, parts produced by this technique are limited due to the lack of strength, surface quality, and other functional features compared to production parts. Therefore, for plastic prototyping, CNC machining, urethane casting, rapid tooling is still the mainstream choices.
Which process is better for your prototype, CNC machining, or 3D printing?
The most obvious difference between 3D printing and CNC machining is that 3D printing can print complex shapes, such as curved deep holes, internal sharp angles, and completely airtight hollow structures, while CNC machining, on the other hand, offers higher machining accuracy.
Compared with other parts, CNC machined parts are featured with Precision and smooth. CNC mechanical engineers can optimize the design to improve the manufacturability of products, thereby eliminating machining limitations. In addition, if a prototype is made using CNC machining, the prototype can reveal secrets useful for programming machine tool paths.
Of course, CNC machining technology is also widely used in other manufacturing processes, such as mold-making and tool-making. For final production parts produced by CNC technology, materials can be obtained directly from the metal stock for processing, which will save time and avoid multi-step process.
Parts produced by additive technology may have a rough surface finish. For some particular parts, the surface finish would affect its fitting, such as parts with request seal performance. Additionally, 3D printing is not suitable for prototypes that request a high gloss surface. Many metal-additive manufacturing parts need to go through secondary processing after printing. Products printed through an SLA process usually have a more precise surface finishing, but this also depends on the overall dimension of the parts and printing parameters.
Considering the geometric shape and function of the parts, if the parts are blocky and simple in structure, with only simple holes and plane features are needed, CNC machining will be the best. If the parts are complex, require multiple CNC operations to complete the machining, and do not have a high requirement of surface finish, then 3D printing can be efficient and cost-effective.
Urethane Vacuum Casting
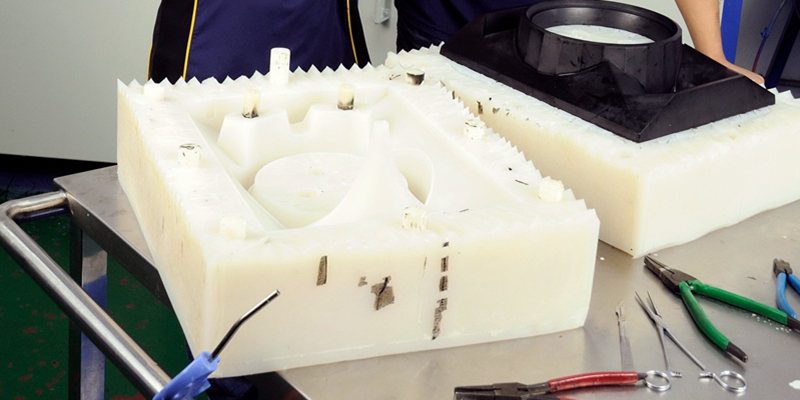
Compared with the injection molding process used in the final production, vacuum casting is a fast and cost-effective method to produce prototypes. When the number of prototypes ranges from 5 to 80, this is the best choice, and of course needs to be evaluated on a project-by-project basis.
For vacuum casting, the first step is to make a master piece by CNC or 3D printing. The surface of this master will ultimately determine the surface finish of subsequent products. Therefore, it is necessary to treat the surface of this master as needed, such as smoothing or polishing or to achieve the surface texture through painting. The next step is to make a silicone mold from this master model. In general, the lifecycle of the silicone mold is 10-12 pieces.
Low Volume Production by Rapid Injection Molding
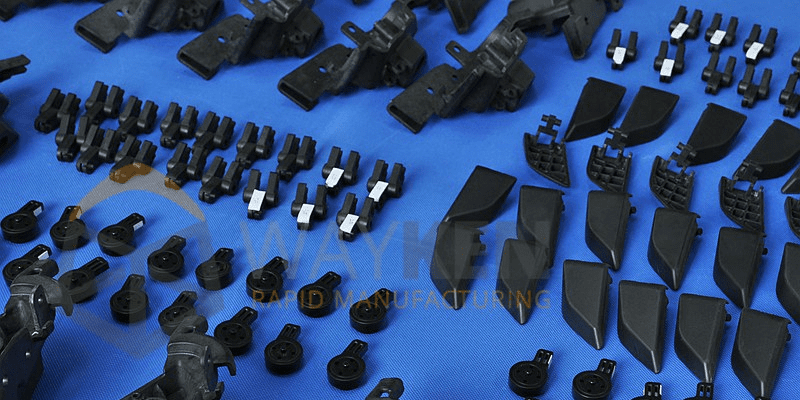

Rapid injection molding uses a metal mold, the life of which ranges from 5k to 20K. Injection molding for low volume manufacturing requires the investment of time and money to cut and polish the mold. The price cost of a single product is not low compared to the cost of mass production. So why use injection molding for prototyping?
In the particular product development stage, prototypes must be made using the same manufacturing techniques as finished parts to ensure the design manufacturability and to check whether these are design defects. This can avoid delays and rework during mass production. Besides, the rapid mold can be used to verify the material choice and to establish initial parameters, such as melt temperature, master material validation, and cooling strategy.
The Role that a Prototype at in Product Development
An effective and accurate prototype will bring great benefits to product development and greatly help to proceed with the project. It allows designers to have a physical sense of their products. At the same time, it could facilitate the product development team to effectively verify the appearance and function of the design, improving the design according to the verification result. This could avoid the potential manufacturability in final production.
Functional prototypes, on the other hand, can be used to test the integrated performance of products such as assembly performance and material properties. This can correct potential problems before finalizing the design. Functional prototypes could be made from different materials at different stages. For example, for mechanical function testing, it only needs to satisfy assembly performance. And the material properties testing is supposed to use the equivalent level of material as the final product. This strategy would optimize the cost of prototyping.
To learn more about prototype manufacturing services, check out WayKen.



































