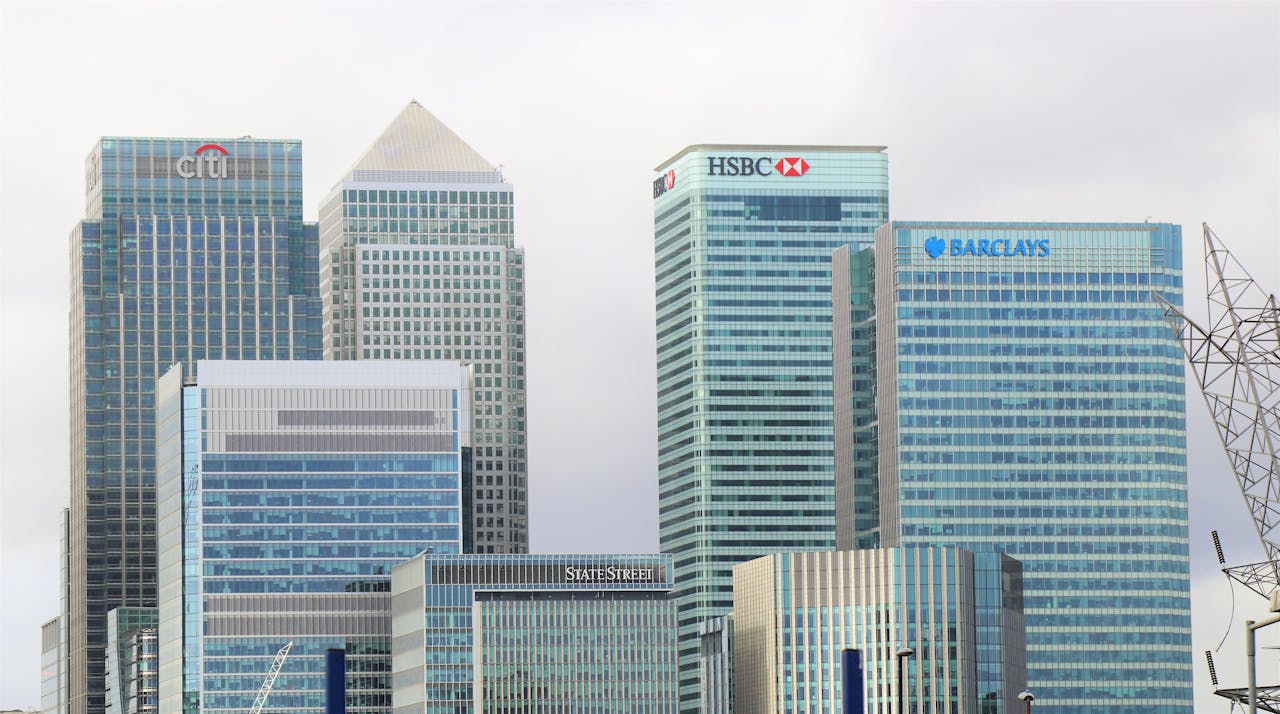
Offshore banking has grown in popularity over recent decades as individuals and businesses seek ways to diversify assets, protect wealth, and sometimes benefit from favourable tax and regulatory environments. Opening an offshore bank account can offer numerous advantages, such as increased privacy, currency diversification, and access to international markets. However, navigating the offshore banking landscape isn’t without its challenges. For many, the complexities of regulatory compliance, cultural differences, and operational hurdles can create barriers to effectively utilizing offshore banking services.
Websites like GlobalBanks provide practical strategies and connections to help you navigate the complexities of offshore bank account opening with ease.
In this article, we explore the most common challenges of offshore banking and provide practical solutions to help you overcome them.
Understanding Offshore Banking
Before diving into the challenges, it’s important to clarify what offshore banking entails. Offshore banking refers to maintaining bank accounts or financial services in a country different from your country of residence. Often, these accounts are located in jurisdictions known for banking secrecy, low taxation, or financial stability, such as the Cayman Islands, Switzerland, Singapore, or Luxembourg.
While offshore banking can be a useful tool for international finance, it requires careful planning and compliance with local and international laws.
Challenge 1: Regulatory Compliance and Legal Risks
The Problem:
One of the biggest challenges in offshore banking is navigating the complex regulatory environment. Governments worldwide have increased transparency measures to combat money laundering, tax evasion, and financial crimes. International frameworks like the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) and the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) require banks to share information about foreign account holders with tax authorities.
Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines, account closures, or even criminal charges.
How to Overcome It:
- Due Diligence: Always work with reputable banks and financial institutions that follow international compliance standards.
- Understand Reporting Obligations: Educate yourself on your country’s tax reporting requirements related to offshore accounts. Consult with a tax professional who understands international tax laws.
- Maintain Transparency: Keep meticulous records of all offshore transactions and declare your accounts when required.
- Legal Counsel: Engage legal experts specialized in offshore finance to ensure you stay within the legal framework.
Challenge 2: Access and Communication Barriers
The Problem:
Offshore banks are often located in countries with different languages, time zones, and business customs. This can lead to difficulties in communication and delays in resolving issues. Additionally, some banks require physical presence for account opening or specific transactions, which may not be convenient.
How to Overcome It:
- Choose the Right Jurisdiction: Select offshore banks in countries with good English proficiency and efficient customer service.
- Use Digital Banking Solutions: Many offshore banks now offer robust online banking platforms and mobile apps, enabling you to manage accounts remotely.
- Hire Intermediaries: Employ trusted local agents or offshore service providers who can act as liaisons between you and the bank.
- Plan for Time Differences: Schedule communications and transactions according to the bank’s business hours to minimize delays.
Challenge 3: High Minimum Deposits and Fees
The Problem:
Many offshore banks require high minimum deposits and impose various fees that can make banking expensive, especially for small investors or businesses. These costs may include account maintenance fees, wire transfer charges, currency conversion fees, and more.
How to Overcome It:
- Compare Banks: Research and compare different banks to find one with fee structures and minimum deposit requirements that fit your budget.
- Negotiate Fees: Some banks may be willing to negotiate fees or offer discounts if you maintain higher balances or use multiple services.
- Use Specialized Offshore Banks: Some financial institutions specialize in serving smaller clients with lower deposit thresholds.
- Consolidate Services: Use the bank for multiple financial needs (e.g., investments, loans, currency exchange) to leverage bundled service discounts.
Challenge 4: Currency Risks and Exchange Rate Volatility
The Problem:
Holding funds in foreign currencies exposes you to exchange rate fluctuations, which can erode the value of your assets. Offshore accounts may require you to manage multiple currencies, complicating your financial management.
How to Overcome It:
- Diversify Currency Holdings: Spread your assets across multiple currencies to reduce exposure to any single currency’s volatility.
- Use Hedging Tools: Some offshore banks offer currency hedging products or forward contracts to lock in exchange rates.
- Monitor Currency Markets: Stay informed about economic and political events affecting currency values.
- Plan Currency Conversions Strategically: Avoid frequent currency conversions to reduce fees and losses.
Challenge 5: Perception and Reputation Issues
The Problem:
Offshore banking sometimes carries a stigma due to associations with tax evasion, money laundering, or illicit activities, even though many clients use offshore accounts legally and ethically. This perception can affect your reputation and complicate financial relationships.
How to Overcome It:
- Operate Transparently: Use offshore accounts for legitimate purposes and maintain thorough documentation.
- Communicate Clearly: When necessary, explain the legitimate reasons for offshore banking to business partners, auditors, or financial institutions.
- Comply with Tax Laws: Report all offshore holdings accurately to tax authorities to avoid legal troubles.
- Choose Reputable Jurisdictions: Banking in well-regulated and respected financial centers helps reduce suspicion.
Challenge 6: Limited Deposit Insurance and Protection
The Problem:
Unlike domestic banks that often provide deposit insurance (like FDIC insurance in the U.S.), many offshore banks do not offer the same level of protection. This means that in the event of a bank failure, your deposits might be at greater risk.
How to Overcome It:
- Research Bank Stability: Before opening an account, assess the financial health and regulatory oversight of the bank.
- Diversify Banking Relationships: Avoid placing all your funds in one offshore bank; spread them across multiple institutions.
- Use Trusts and Legal Structures: Consider holding offshore assets within legal entities designed to protect and manage risk.
- Stay Updated: Regularly monitor the economic and political stability of the jurisdiction where the bank operates.
Challenge 7: Difficulty in Opening Accounts
The Problem:
Offshore banks often have stringent Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements. Opening an account can be time-consuming and complicated, requiring extensive documentation such as proof of identity, source of funds, and sometimes references.
How to Overcome It:
- Prepare Documentation in Advance: Gather necessary documents such as passports, utility bills, bank references, and financial statements.
- Seek Professional Assistance: Use the services of international banking consultants or law firms specializing in offshore banking to guide you through the process.
- Be Honest and Transparent: Provide accurate information and be prepared for thorough background checks.
- Choose Banks with Streamlined Processes: Some banks cater to international clients with simplified onboarding procedures.
Conclusion
Offshore banking offers numerous benefits, including asset protection, privacy, and access to international markets. However, it also presents unique challenges ranging from regulatory compliance to operational complexities. By understanding these common hurdles and taking proactive steps, you can safely and effectively utilize offshore banking services to meet your financial goals.
The key lies in choosing the right jurisdiction and financial institution, maintaining transparency and compliance, managing costs wisely, and leveraging professional advice. With proper planning and vigilance, offshore banking can be a powerful tool in your financial strategy.
For those interested in global financial topics, even beyond banking, exploring diverse industries and markets, whether it’s international finance or following the latest in sports like the okc thunder, can broaden your perspective and opportunities.
Read More From Techbullion