The rapid shift toward connected and autonomous vehicles presents both unprecedented opportunities and formidable cybersecurity challenges. Traditional security models, built on centralized architecture, leave modern vehicle networks vulnerable to cyber threats such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and malicious attacks on critical infrastructure. To address these challenges, blockchain technology is emerging as a game-changing innovation in securing vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications. By offering a decentralized, transparent, and immutable security framework, blockchain ensures tamper-proof data exchanges, robust identity authentication, and automated security enforcement through smart contracts. This article explores blockchain’s potential to redefine automotive cybersecurity, examining real-world use cases, industry adoption, challenges, and future trends shaping the secure mobility ecosystem.
Why Traditional Automotive Security Falls Short
Modern vehicles increasingly rely on digital connections, communicating continuously with other vehicles (V2V) and infrastructure (V2I). Traditional security frameworks, largely centralized, create single points of vulnerability. Cyber attackers exploit these vulnerabilities, leading to risks such as unauthorized access, data manipulation, and compromised vehicle safety. The growing sophistication of cyberattacks demands a robust, decentralized security model that blockchain can provide.
Introducing Blockchain: A Decentralized Solution
Blockchain provides a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions across multiple nodes securely and transparently. Its tamper-resistant nature makes it particularly suitable for securing vehicle communications and transactions.
Benefits of Blockchain in Automotive Cybersecurity:
- Enhanced Security: Eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of hacking.
- Transparency and Trust: All interactions are permanently recorded and auditable.
- Automation and Efficiency: Smart contracts automate and secure routine transactions.
- Decentralized Identity Management: Vehicles authenticate interactions without reliance on a central server.
Literature Review
As the automotive industry embraces digital transformation, blockchain technology is emerging as a cornerstone of cybersecurity innovation. Research underscores its potential in fortifying vehicle communication networks against cyber threats while ensuring trust, transparency, and automation in vehicular transactions.
Dorri et al. (2017) highlight how blockchain establishes a tamper-proof ledger for Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communications. By eliminating vulnerabilities associated with data manipulation and unauthorized access, blockchain significantly enhances the integrity of connected vehicle ecosystems. Similarly, Liang et al. (2018) emphasize blockchain’s role in decentralized identity management, allowing vehicles to authenticate interactions without reliance on centralized servers. This shift not only strengthens privacy but also mitigates risks linked to identity fraud, a growing concern in the automotive sector.
Beyond secure communication, blockchain-powered smart contracts are revolutionizing transactional security. Moinet et al. (2017) explore how these self-executing agreements can prevent fraud in vehicle leasing, insurance claims, and toll payments by ensuring that transactions adhere to predefined security parameters. Their findings suggest that blockchain automation could eliminate intermediaries, making financial and operational transactions in the automotive industry more secure and efficient.
In supply chain security, Wu et al. (2020) present blockchain as a transformative solution for tracking and verifying the authenticity of automotive components. By creating an immutable record of each part’s origin and history, blockchain enhances transparency and trust in manufacturing and vehicle maintenance.
Kristianto et al. (2022) extend this discussion to decentralized Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for V2X communications, an area where blockchain’s cryptographic capabilities excel. Their research demonstrates that a blockchain-backed PKI framework can strengthen identity verification mechanisms without the security loopholes found in traditional PKI models. This advancement is crucial in protecting vehicular networks from cyberattacks aimed at exploiting authentication vulnerabilities.
Collectively, these studies illustrate blockchain’s vast potential in securing connected and autonomous vehicles. As cyber threats evolve, blockchain is positioned not just as a technological innovation but as a key enabler of next-generation automotive cybersecurity, reinforcing the safety and reliability of future mobility solutions.
Practical Applications of Blockchain in Automotive Security
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Security
Blockchain ensures secure and immutable data exchanges between vehicles, significantly reducing spoofing attacks and data breaches. Each vehicle becomes a node within a blockchain network, authenticating all data shared.
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Security
Blockchain allows secure authentication between vehicles and infrastructure components such as traffic lights, road signs, and charging stations. It ensures the integrity and authenticity of data exchanged.
Blockchain in V2X Communications
Blockchain is redefining the security landscape of vehicular networks by introducing a decentralized, tamper-proof system for tracking and validating vehicle interactions. In this system, each vehicle acts as an independent node, continuously verifying and transmitting data within a vast, distributed ecosystem. By eliminating the need for a central authority, blockchain significantly reduces vulnerabilities, ensuring that vehicular communications remain secure and resistant to cyber threats.
One of the fundamental aspects of blockchain-enabled security is decentralized identity management. Each vehicle is assigned a unique cryptographic identifier, allowing it to authenticate interactions without relying on a centralized database. This approach not only strengthens security but also enhances privacy, mitigating risks associated with unauthorized data access and identity fraud.
Smart contracts add another layer of automation and protection. These self-executing agreements enable vehicles to seamlessly interact with infrastructure components, facilitating processes such as secure toll payments, access control, and software verification. By minimizing human intervention, smart contracts significantly reduce the likelihood of fraud and security breaches.
To maintain integrity across the blockchain network, transactions undergo rigorous validation through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG). These processes ensure that only verified data is stored on the blockchain, effectively preventing unauthorized modifications and fraudulent activities. Additionally, advanced cryptographic techniques, such as SHA-256 hashing and elliptic curve digital signatures, provide robust encryption for transmitted data, safeguarding it against interception and unauthorized alterations.
One of the most critical applications of blockchain in the automotive sector is securing over-the-air (OTA) updates. By leveraging blockchain, manufacturers can authenticate and distribute software updates with confidence, ensuring that only legitimate patches reach connected vehicles. This approach eliminates risks associated with malware-infected firmware and unauthorized software installations, making blockchain a fundamental pillar of cybersecurity in modern vehicle ecosystems.
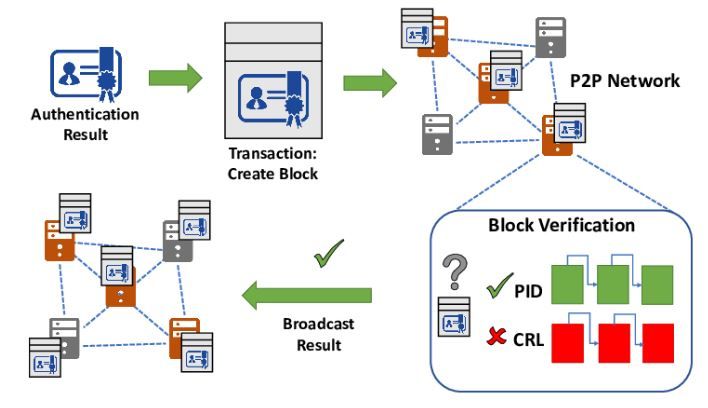
Figure1: Blockchain in V2X Communications
Real-world Implementations and Case Studies
Several automotive and technology companies have embraced blockchain to address cybersecurity concerns. The MOBI Consortium, comprising major automotive manufacturers and technology providers, has pioneered blockchain-based identity verification, facilitating secure data exchanges among vehicles, suppliers, and service providers. Another notable example is BMW’s implementation of blockchain to enhance traceability in its supply chain, significantly improving transparency and security. Pilot projects involving blockchain-enabled charging stations have demonstrated successful secure authentication and payment processing, highlighting blockchain’s potential in practical, everyday automotive scenarios.
Future Trends: What’s Next for Blockchain and Automotive Cybersecurity?
Blockchain is set to play a crucial role in automotive cybersecurity, driven by emerging technologies, industry adoption, and evolving regulations. AI and machine learning will enhance real-time threat detection, shifting security measures from reactive to proactive. Edge computing will further improve blockchain efficiency by reducing latency and enhancing V2X communications.
Regulatory bodies like UNECE and NHTSA are working on blockchain security standards to ensure interoperability across manufacturers, fostering trust and wider adoption. Additionally, industry efforts are focused on enabling seamless data exchange across different blockchain networks to enhance cybersecurity resilience.
The global automotive blockchain market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 30.8% from 2024 to 2030, driven by the rising number of connected vehicles and demand for secure, decentralized data management. Market size is expected to expand from $538.5 million in 2023, with substantial investments in public, private, and hybrid cloud-based solutions. The following image from Grand View Research highlights the anticipated market growth.
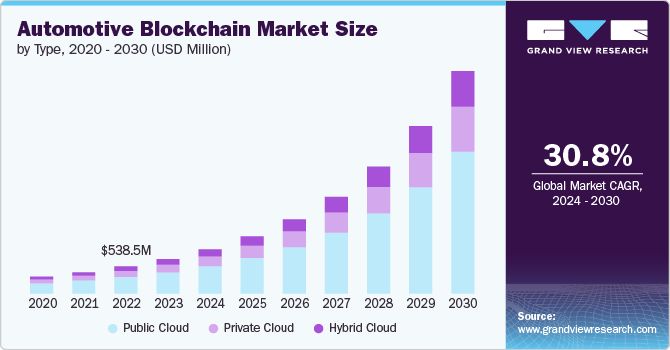
Figure 2: Automotive Blockchain Market Size: Grand View Research – Automotive Blockchain Market size & trends.
One of blockchain’s most critical applications in cybersecurity is securing over-the-air (OTA) updates, preventing unauthorized modifications and malware attacks. As vehicles become more software-driven, blockchain will ensure that only authenticated updates are deployed, making it a key component of future automotive cybersecurity solutions.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology presents substantial potential for addressing automotive cybersecurity challenges by offering decentralized, secure, and transparent solutions for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications. Its adoption promises not only enhanced security but also greater trust and reliability across automotive networks. As blockchain matures and integrates with complementary technologies such as AI, edge computing, and IoT, its role will expand significantly, establishing a robust foundation for secure connected and autonomous vehicle ecosystems. Ongoing research, industry collaboration, and regulatory alignment will be crucial to realizing the full potential of blockchain, ultimately redefining the landscape of automotive cybersecurity.
References
- Dorri, A., Kanhere, S. S., Jurdak, R., & Gauravaram, P. (2017). “Blockchain for IoT security and privacy: The case study of a smart home.” IEEE Pervasive Computing, 17(2), 6-15.
- Liang, X., Zhao, J., Shetty, S., Liu, J., & Li, D. (2018). “Integrating blockchain for data sharing and collaboration in mobile cloud computing.” Future Generation Computer Systems, 78(2), 776-786.
- Moinet, A., Darties, B., & Riviere, J. (2017). “Blockchain-based trust & authentication for decentralized sensor networks.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.01730.
- Wu, J., Li, J., Ye, L., & Peng, W. (2020). “Blockchain-enabled vehicle supply chain management.” Journal of Automotive Research, 89(3), 102-117.
- Kristianto, Edy & Nguyen, Van-Linh & Lin, Po-Ching. (2022). Decentralized PKI with Blockchain in V2X Communications: Promising or only Euphoria?. IEEE Security and Privacy Magazine. 20. 10.1109/MSEC.2022.3141727.



































