What is an Online Stock and Trading Broker? Online stock and trading broker is a financial institution that provides services for buying, selling, and trading stocks, options, and other securities. Online brokers allow customers to access their accounts from any device or computer with an internet connection. They can also provide real-time market information and streaming quotes on their websites.
What are the benefits of using an online stock & trading broker? The main benefit of using an online stock & trading broker is the convenience it offers investors. Customers can access their accounts from any device or computer with an internet connection, making it a good choice for investors who want to invest from anywhere. Additionally, online brokers provide real-time market information and streaming quotes on their websites, which can be helpful for investors who want to stay up-to-date on the latest stock prices.
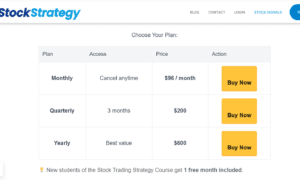
What do you look out for when choosing an online stock and Trading broker? When choosing an online stock and trading broker, investors should look for a provider that has a good track record of providing quality services. Additionally, customers should ensure that the broker they choose offers a wide range of investment options. Finally, investors should make sure the broker they choose has customer support available 24/7 to answer any questions they may have. Judging by this, we will take a look at our top 10 stock and trading broker for this year.
The year so far has been great for both investors and stock brokers. The market has been on a steady uptrend, with stocks prices climbing steadily since the beginning of the year. With this in mind, we have chosen brokers that are well-equipped to handle the current market conditions.
-
TD Ameritrade
TD Ameritrade is one of the oldest and most popular online stock and trading brokers in the United States. The company has more than 13 million customer accounts and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies. TD Ameritrade also offers real-time market information and streaming quotes on its website, making it a good choice for investors who want to stay up-to-date on the latest stock prices.
-
Charles Schwab
Charles Schwab is another well-known online stock and trading broker in the United States. The company has more than 11 million customer accounts and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies.
Charles Schwab also offers real-time market information and streaming quotes on its website, the broker has also significantly slashed fees on its mutual funds and ETFs, eliminated common account fees, reduced commissions to $0 per trade, and allows investors to buy fractional shares of stock, making it extremely affordable..
-
Fidelity Investments
Fidelity Investments is one of the oldest and most well-known stock and trading brokers in the United States. The company has more than $2 trillion in assets under management and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies. Fidelity combines a zero-dollar commission charge, top-notch research, and an excellent mobile app, all in a simple online platform. With as low as $0 account minimums and zero-expense-ratio index and mutual funds, this is perhaps one of, if not the most affordable stock brokers.
-
Interactive Brokers
Interactive Brokers is a well-known online stock and trading broker in the United States. The company has more than 6 million customer accounts and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies. Interactive Brokers also offers real-time market information and streaming quotes on its website, the broker also boasts of some of the lowest commissions and margin rates around making it a good choice for investors who want to stay up-to-date on the latest stock prices.
-
Robinhood
Robinhood is a stock and trading broker in the United States that offers a mobile app and website. The company has more than 5 million customer accounts and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies. Robinhood also offers real-time market information and streaming quotes on its website, With no fees, and access to trade fractional shares and cryptocurrency, Robinhood is a no-frills but efficient brokerage account.
-
E-Trade
E-Trade is a stock and trading broker in the United States that offers a mobile app and website. The company has more than 19 million customer accounts and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies. E-Trade manages to cater to active traders with multiple trading platforms, while also appealing to long-term investors with thousands of mutual funds and ETFs that can be traded for free.
-
RTW Brokers
RTW Brokers is a stock and trading broker in the United States that offers a mobile app and website. The company has more than 5 million customer accounts and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies. RTW Brokers manages to cater to active traders with multiple trading platforms, while also appealing to long-term investors with thousands of mutual funds and ETFs that can be traded for free.
-
Ameritrade U.S.A.
Ameritrade U.S.A. is a well-known stock and trading broker in the United States. The company has more than 12 million customer accounts and offers a wide range of investment options, including options, futures, and cryptocurrencies. Ameritrade is one of our top-rated all-around brokerage accounts with outstanding tools and products, in-depth and comprehensive research, and no account minimums.
-
Webull
Webull is one of the oldest stockbrokers in the world with superb mobile and web platforms. Webull is a mobile-first investing platform that stands out with the quality and simplicity of its experience and no commissions.
-
Merrill Edge
Merrill Edge If you are looking for a broker that offers high-quality tools for trading while still catering to your every trading need, then this is the broker for you. Merrill Edge charges no fees for stock and ETF trades, However, options trades come in at $0.65 per contract.