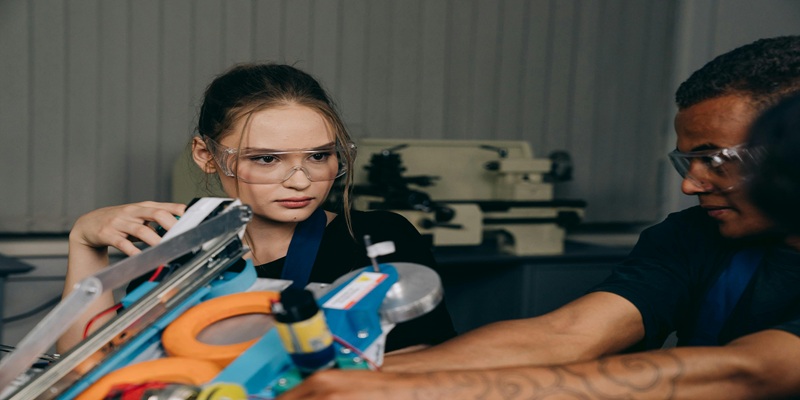
The factory floor has always been a hub of innovation, from the introduction of assembly lines to the integration of industrial robotics. However, recent advances in automation are creating seismic shifts in how products are manufactured, assembled, and distributed. This ongoing transformation is not just enhancing productivity; it is redefining the very structure and dynamics of manufacturing.
The Rise of Smart Factories Driven by Industry 4.0 Technologies
One of the most significant automation trends is the transition toward smart factories, powered by Industry 4.0. These modern manufacturing plants utilize interconnected systems, enabling real-time data exchange between machines, sensors, and operators. The fusion of operational and informational technologies makes production lines more agile, efficient, and responsive.
Through the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and machine learning, smart factories can predict equipment failures, adapt to variable production demands, and optimize energy usage. Moreover, data analytics plays a crucial role in providing actionable insights that guide decision-making on the factory floor.
Not only does this enhance operational performance, but it also reduces waste, minimizes downtime, and boosts overall output.
Cobots: Collaborative Robots Enhancing Human-Machine Synergy
Unlike traditional robots that operate in isolation, collaborative robots (cobots) are designed to work alongside human operators. These smart machines are equipped with sensors, safety features, and AI-driven vision systems, enabling them to respond intelligently to their environment.
Cobots are particularly popular among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) due to their affordability and ease of integration. They can handle repetitive tasks such as packaging, assembly, and inspection while freeing up human workers for more complex and strategic activities.
Additionally, the flexible deployment of cobots allows manufacturers to adjust their production lines quickly, which is crucial in today’s dynamic market landscape.
Predictive Maintenance Through Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Traditionally, maintenance on factory equipment was either reactive or scheduled. This often led to unexpected breakdowns or unnecessary servicing, both of which increase operational costs. However, the adoption of predictive maintenance powered by AI and machine learning has revolutionized maintenance strategies.
By analyzing historical and real-time data, AI can identify patterns that indicate impending equipment failure. Consequently, manufacturers can proactively schedule maintenance, reduce downtime, and extend machinery lifespan. This trend is becoming a game-changer, especially in industries where equipment reliability is critical.
Furthermore, predictive maintenance contributes to better resource allocation and lowers the total cost of ownership over time.
Digital Twins and Simulations Enhancing Operational Efficiency
The concept of digital twins has emerged as a transformative trend in factory automation. A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical system, used to simulate, monitor, and analyze operations in real time. This enables manufacturers to test different scenarios, optimize production schedules, and anticipate potential disruptions before they occur.
Digital twins facilitate better decision-making by providing a comprehensive view of the factory ecosystem. For example, by simulating a new production line layout, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies and improve throughput without having to make costly physical changes.
Moreover, digital twins are instrumental in enabling remote monitoring and troubleshooting, which has become increasingly important in today’s globalized manufacturing environment.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) Revolutionizing Internal Logistics
Another remarkable automation trend is the deployment of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) for internal logistics. These intelligent machines can navigate complex factory environments, transport materials, and replenish workstations without human intervention.
Unlike Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) that rely on predefined paths, AMRs use advanced mapping and navigation technologies to adapt dynamically to changes on the factory floor. This enhances flexibility and ensures that material handling processes remain efficient even during production shifts or disruptions.
Furthermore, AMRs contribute to safer workplaces by reducing human exposure to hazardous tasks, thereby improving overall operational safety.
Edge Computing Enabling Real-Time Decision-Making at the Source
The integration of edge computing is another pivotal automation trend in modern manufacturing. Unlike traditional cloud computing, edge computing processes data locally—at or near the source. This reduces latency and enables real-time decision-making, which is critical for high-speed manufacturing environments.
With edge computing, manufacturers can instantly analyze machine performance, quality metrics, and process variables. This not only ensures faster response times but also enhances data security and reduces dependence on external networks.
As manufacturing processes become increasingly digitized, the role of edge computing in enabling decentralized, intelligent automation cannot be overstated.
Augmented Reality (AR) Enhancing Workforce Training and Maintenance
As automation technology grows more complex, there is a rising need for efficient training and support tools. Augmented Reality (AR) is stepping in to meet this need. AR systems overlay digital information onto the physical environment, guiding workers through tasks such as equipment assembly, quality inspection, or maintenance procedures.
By using AR glasses or mobile devices, operators can receive step-by-step instructions in real-time, reducing training time and improving task accuracy. Moreover, AR facilitates remote collaboration, allowing experts to provide guidance without being physically present on-site.
This trend not only improves workforce productivity but also bridges the skill gap prevalent in many manufacturing sectors today.
The Emergence of Low-Code and No-Code Platforms in Automation Development
One lesser-known yet highly impactful trend is the use of low-code and no-code platforms for building automation applications. These platforms allow personnel with minimal coding experience to design, test, and deploy automation solutions tailored to their specific processes.
As a result, factory workers and engineers can rapidly prototype new workflows, experiment with process changes, and implement improvements without relying on centralized IT teams. This democratization of development is accelerating innovation and giving factories more control over their digital transformation.
Moreover, such platforms promote agility and responsiveness in operations, helping manufacturers stay competitive in a fast-changing landscape.
Human-Centered Automation and the Future of Work
While automation is often viewed as a job displacer, the reality is far more nuanced. The future of factory work lies in human-centered automation, where technology augments human abilities rather than replaces them. By offloading tedious and repetitive tasks to machines, human workers can focus on areas requiring critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving.
Furthermore, companies are investing in upskilling and reskilling programs to prepare employees for new roles created by automation. This includes positions in robot programming, data analysis, and system integration—roles that are increasingly essential on the modern factory floor.
In this way, automation is not eliminating jobs but rather reshaping the workforce for higher value contributions.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing Through Automation
Environmental sustainability is becoming a key focus for manufacturers worldwide. Automation plays a vital role in supporting green manufacturing practices by optimizing resource usage, minimizing waste, and improving energy efficiency.
For instance, smart energy management systems can track power consumption in real-time and adjust operations accordingly. Automated quality control reduces material defects, and robotics can perform tasks with extreme precision, cutting down on excess material usage.
In short, automation is a powerful tool for helping companies achieve their sustainability goals while maintaining profitability.
Final Thoughts
The transformation of the factory floor through automation is not a distant possibility—it is happening now. From cobots and predictive maintenance to digital twins and edge computing, these innovations are driving unprecedented levels of efficiency, agility, and intelligence in manufacturing.
Yet, success in this new era will depend on how well businesses adapt. Embracing a proactive approach, investing in workforce development, and fostering a culture of continuous innovation will be key.
As automation continues to evolve, the factories of the future will not just be more productive—they will be smarter, safer, and more sustainable than ever before.