The development of artificial intelligence has become one of the most critical topics in business and technology discussions over the past two years. Corporations are investing millions in the advancement of neural networks, competing for breakthroughs in AI capabilities. Companies across different countries are integrating AI in various ways, delegating routine tasks to it, while employees assess how the widespread adoption of neural networks will reshape the job market.
According to Business Research, AI’s impact on the entertainment industry is expected to reach $34.86 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate of 26.3%. Within the creative sector, AI has also sparked intense debate. Content creators worldwide are grappling with issues of copyright, a potential crisis of originality, the value of human creativity, and the concepts of uniqueness and artistic identity. The rapid advancement of AI challenges the traditional structure of the creative world and the long-established rules that govern it.
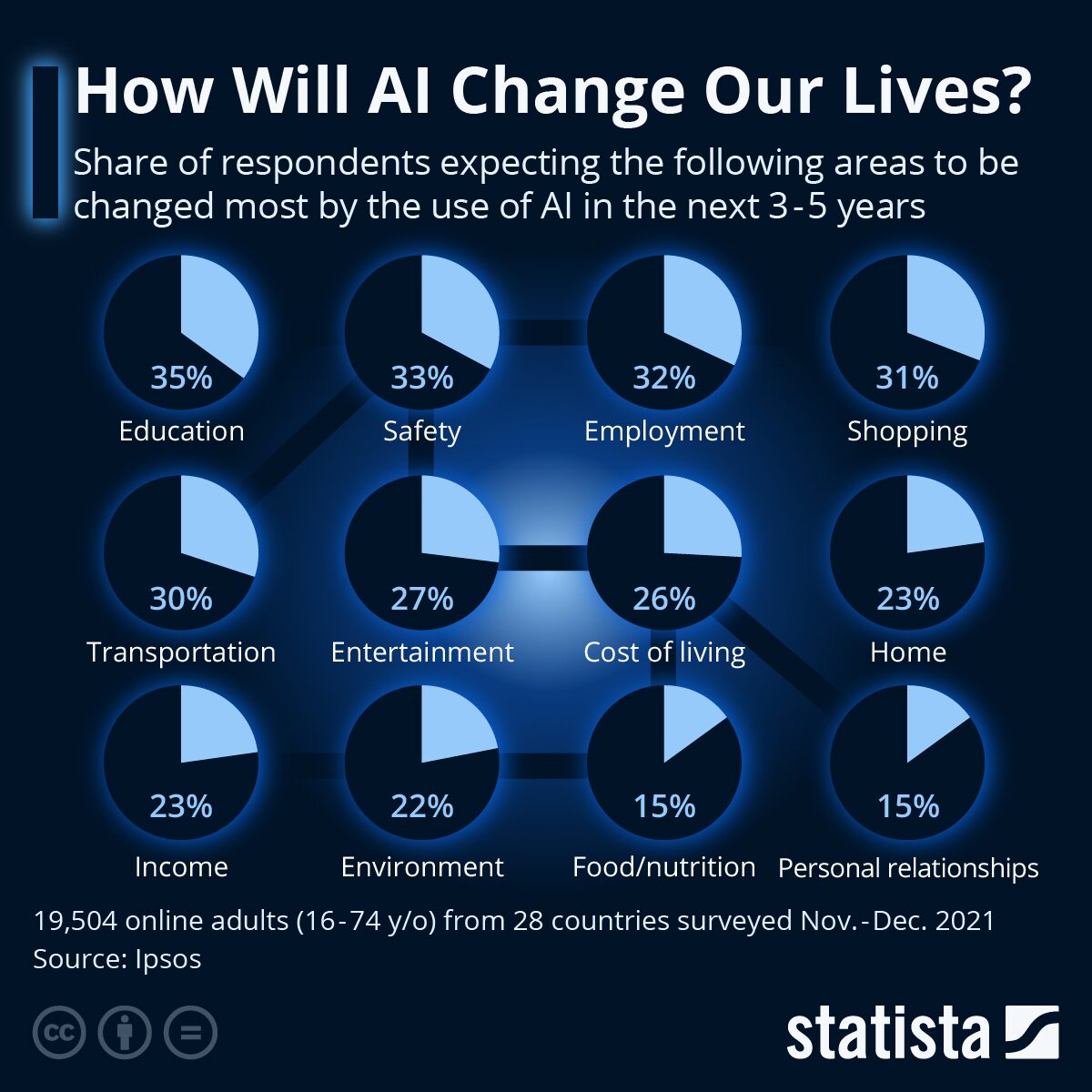
Source: Statista
Discussions about the use of AI in video content creation are also gaining momentum among creators. The primary debates revolve around how AI simplifies the processes of video production and editing, as well as the challenges and ethical concerns associated with its implementation. AI is already significantly transforming our lives, and this trend is only expected to accelerate in the near future.
AI streamlines video production by automating routine tasks such as editing and video generation based on textual descriptions. AI-powered platforms and tools enable creators to produce content faster and at lower costs, making video production more accessible to a broader audience. YouTube, the world’s leading video platform, is placing significant emphasis on AI integration. According to its official roadmap for 2025, AI will be one of the platform’s key strategic priorities. A wide range of AI tools is already available within the platform itself.
Recently, YouTube introduced the Inspirations tool, designed to support creators during brainstorming and content development. This AI analyzes a channel’s existing content and suggests video ideas. Creators can also input a specific topic, and the tool will generate potential video titles and even structured outlines.
Another major innovation includes the Dream Screen and Dream Track tools. These features allow creators to input a text prompt, and AI will generate a music track or video clip tailored to their content. Currently, these tools are available only for Shorts, but it is likely that they will expand to full-length videos in the future.
One of the most highly anticipated AI-driven features is auto dubbing, which will soon be available to all creators on the platform. This tool promises to revolutionize content dubbing. In the past, creators were limited to audiences speaking their original language, requiring them to create separate channels or hire translators and voice actors to reach a global audience.
Previously, top creators like MrBeast established dedicated channels for different language markets to dub their videos. The Mogol TV team followed a similar approach, launching multi-language versions after acquiring a franchise deal with a major media company.
Later, YouTube introduced the ability to add multiple audio tracks to a single video, allowing viewers to select their preferred language on an English-language channel like MrBeast’s, rather than navigating separate language-specific channels. This eliminated the need to manage multiple accounts and enabled synchronized viewing experiences worldwide.
Now, the auto dubbing feature will leverage AI to automatically translate and generate audio tracks in different languages, eliminating the need for human translators or voice actors. This breakthrough expands audience reach and accelerates channel growth by attracting viewers from new regions. However, this expansion will inevitably lead to increased competition among creators globally.
Additionally, YouTube is considering developing AI-driven tools aimed at enhancing the viewing experience.One such feature is AI-powered video summarization, which would be particularly valuable for educational content. This tool would generate concise summaries of long lectures or podcasts, helping viewers retain key information more efficiently. Another potential feature is a brief interactive quiz that allows viewers to assess their comprehension of the content they just watched. As long-form videos, podcasts, and lectures continue to gain popularity, such tools will be invaluable for audiences seeking to maximize their learning experience.
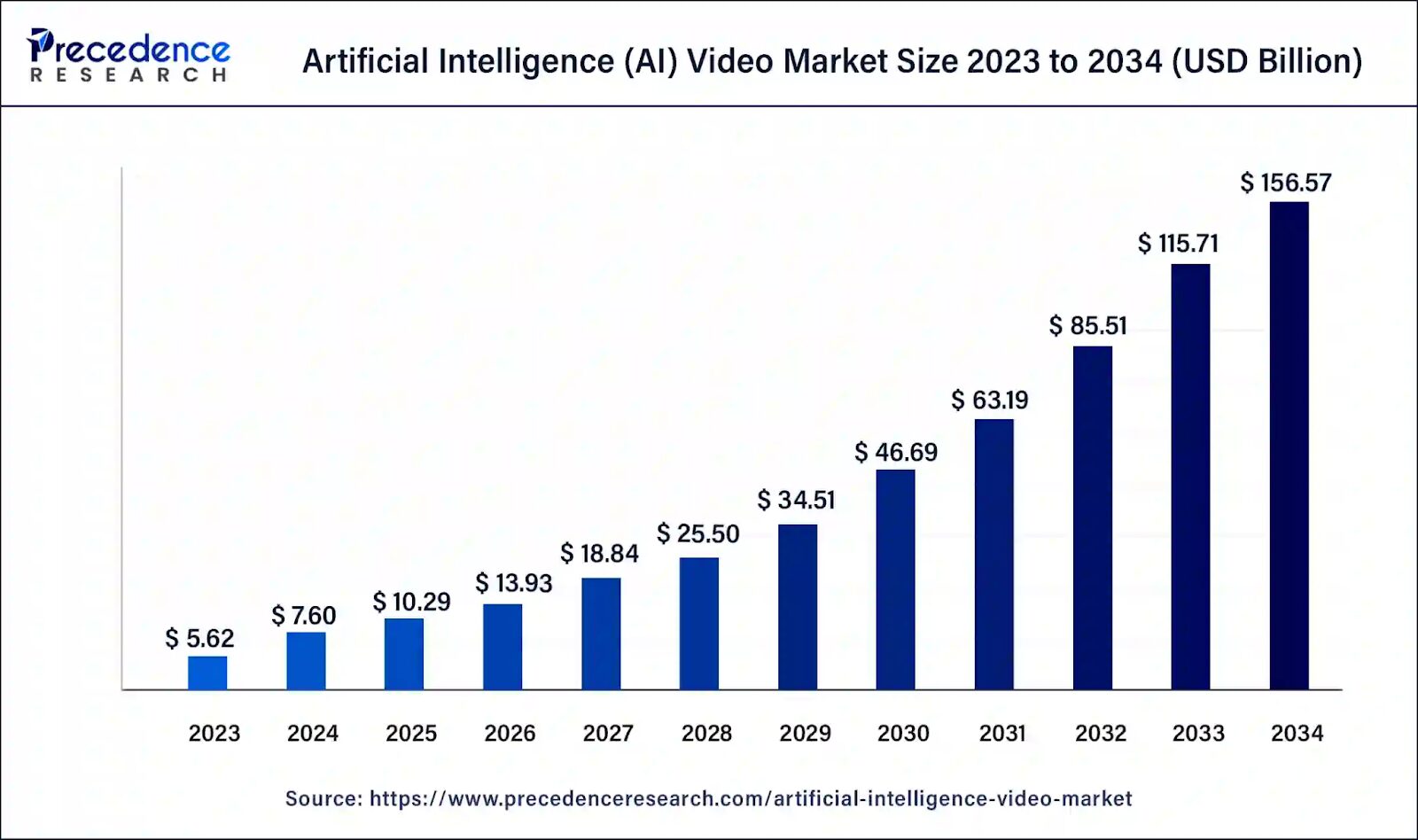
Source: PrecedenceResearch
It is also important to consider the wide range of additional AI-powered tools that go beyond YouTube itself and can significantly enhance the video creation process. For instance, dubbing videos into multiple languages is no longer limited to YouTube’s built-in features—third-party services such as ElevenLabs offer advanced AI-driven speech synthesis. What makes this tool particularly unique is its ability not only to translate text but also to replicate the original speaker’s voice and tone. The result is a seamless experience where it feels as if the same person is speaking fluently in another language. A striking example of this technology in action is the interview with YouTube’s CEO, where AI-powered voice cloning was used for dubbing.
Furthermore, professional video editing software is increasingly integrating AI tools to streamline production workflows. A notable example is Adobe Premiere Pro, which now features Generative Extend—an AI-powered function that allows users to extend a clip’s duration. For instance, a five-second shot can be smoothly stretched into an eight-second sequence, with AI seamlessly generating additional frames to maintain visual continuity. The result is so precise that viewers cannot distinguish between the original footage and the AI-generated extension. Additionally, Adobe Premiere Pro’s AI tools assist editors in quickly locating relevant footage within vast amounts of raw material using keyword searches. This is just one of many AI-driven solutions that are transforming video production, making content creation faster, more efficient, and more accessible for creators at all levels.
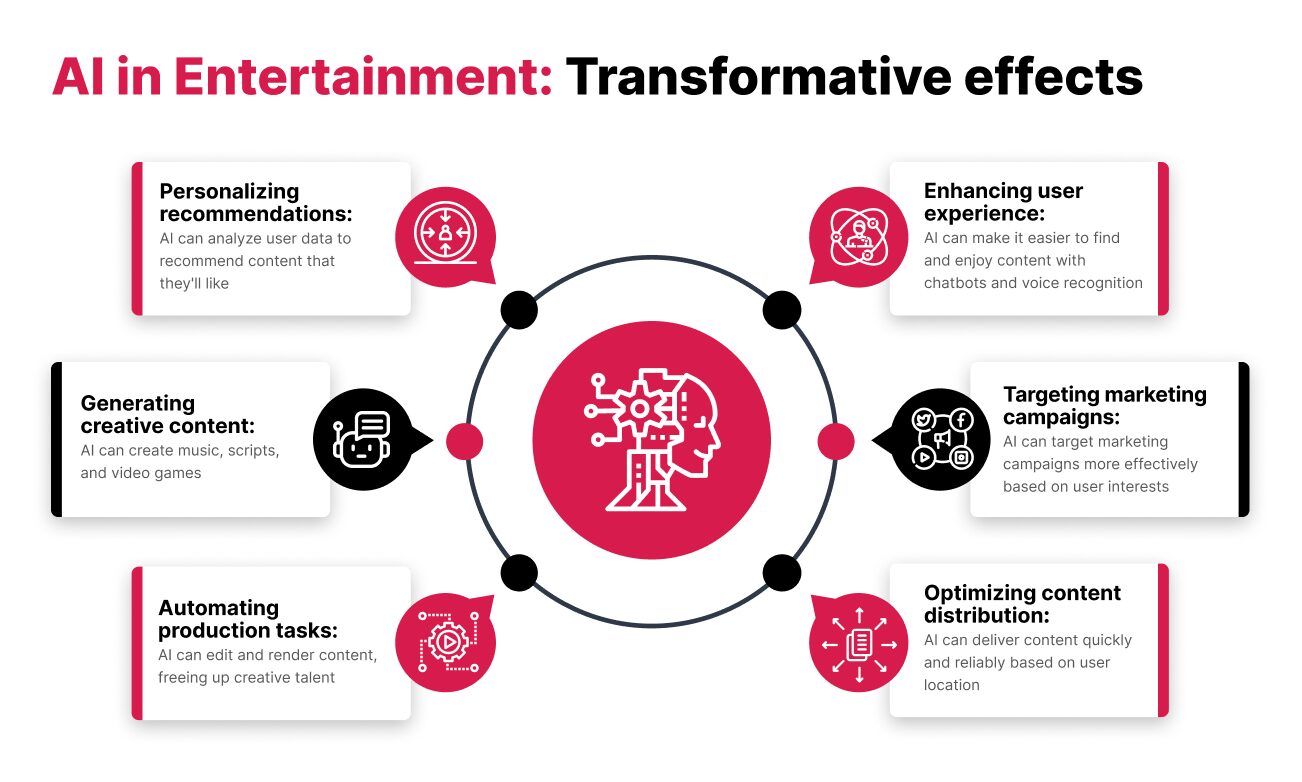
Source: Robosoftin
The use of AI in video content creation has several limitations today. First of all, AI is still not perfect in generating videos. It can create individual frames with decent quality, but when it comes to a sequence of frames with a coherent storyline, the result often falls short. The quality of the generated content can be unstable, and AI-generated frames are easily noticeable, which may deter viewers due to their artificial and unnatural appearance.
Secondly, there are several limitations imposed by YouTube regarding the use of generated content, particularly videos. For several months now, creators have been required to indicate whether their video contains “altered or synthetic content,” meaning whether the content was modified or created using AI. If such elements are present, the creator must mark it during upload, and the video will display a special label “Altered or synthetic content.” This provides viewers with a clear understanding that certain parts of the content were generated by AI.
It is also worth noting the importance of regulating the use of AI in video content. Specifically, attention should be drawn to the nuances of creators marking their content as being AI-generated. The introduction of rules and restrictions for AI usage on the platform is undoubtedly an important and positive step. AI is developing at a rapid pace, and its regulation is becoming necessary. We are all familiar with examples where fraudsters used AI to create fake images of public figures or to deceive people with fake voices of famous performers, creating realistic tracks without their participation. YouTube, as one of the largest streaming services, must respond to these challenges and establish new rules that will protect both viewers and content creators.
Creators are not required to mark the use of AI in all cases. YouTube provides guides explaining when a label is required and when it is not. However, as with legislation, the rules are often open to interpretation, especially when it comes to a technology company where norms change quickly. For example, YouTube requires a label if realistic changes are made to the content but does not require it for minor adjustments, such as beauty filters. However, what about comedic videos where one person’s head is replaced with another’s? This depends on the viewer’s perception of humor.
Another case is when the video generates a “realistic scene that never actually happened.” For instance, a generated video with a historical figure like Napoleon might require a label, as viewers may perceive it as a real event. On the other hand, if the scene is used for educational content, marking it as AI-generated might be unnecessary.
YouTube’s rules allow for a lot of interpretation, which puts creators in a difficult position. If a label is not applied, but the platform considers it necessary, the consequences can be severe, ranging from video removal to exclusion from the partnership program. Therefore, it is important to observe how the rules will work in practice and what nuances will arise in real situations.
AI in video content is also being used to protect creators and viewers. For instance, YouTube is already using and will continue to develop AI tools for security. For example, AI helps detect unauthorized use of content by third parties, allowing for effective monitoring of copyright compliance—both musical and audiovisual. AI tools will also help protect creators from unauthorized use of their AI-generated images. This is a problem that some well-known creators on the platform have already faced. Furthermore, YouTube plans to use AI to protect viewers. For example, the system will determine the user’s age and block dangerous or inappropriate content for children and young audiences, thus increasing safety.
Industry representatives are concerned that some creators will use AI to generate large amounts of completely “artificial,” non-original content. There is a risk that from start to finish, the content will be created by AI—from the script to the visuals. This content is produced very quickly and costs almost nothing to make. Many viewers may start to notice that videos on different platforms are becoming more and more alike, which, in turn, may affect their interest in this content. In such a case, AI could lead not to a revolution but to a crisis of originality in video production.
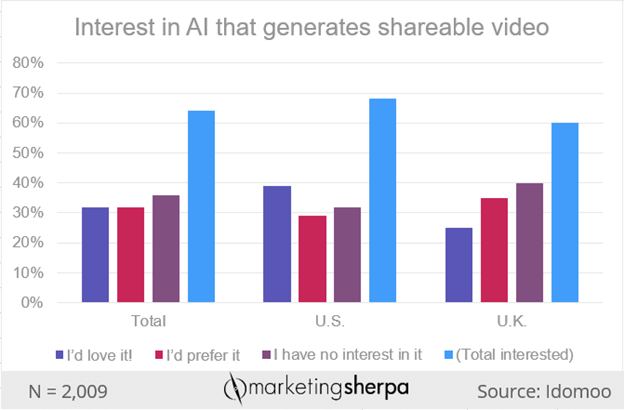
Source: MarketingSherpa
Currently, AI tools exist that not only assist with specific stages of video production but also generate entire videos based on a given text (for example, Invideo AI). All that’s required is to upload a prepared text prompt, and the AI itself will create the visuals, voiceover, music, transitions, and ultimately deliver a finished video. Of course, the result is often generic and lacks creativity. However, such content may still find its audience. Given the low production costs and fast turnaround, this process could flood platforms with monotonous, AI-generated content.
As a result, YouTube may see an influx of similar AI-generated videos. However, fully AI-generated content is unlikely to deeply engage viewers due to its generic nature, leading to low watch times, fewer likes, and minimal engagement. This signals to the platform’s algorithm that the video is uninteresting, ultimately resulting in a comparatively low number of views.
Based on interviews with YouTube’s CEO and the company’s public statements, the platform’s strategy regarding AI is clear: YouTube must remain a place for “real” creators who produce authentic content with the help of AI tools. The platform should not become a space for artificially generated content that spreads misinformation, violates copyright laws, or displaces human creators.
At its current stage of development, AI will not replace human creators but will serve as an effective tool in their hands. Those skilled in video editing will only benefit from using AI. As advanced AI tools become available in video editors, creators will be able to improve their work and complete tasks more efficiently.
For instance, if a creator needs to insert a video of a unicorn, they previously had to rely on complex graphics, which was both challenging and expensive. Now, they can generate such a clip in just a few minutes—an incredible advantage that was previously unavailable. AI will take over much of the tedious, technical work, freeing creators to focus on the creative process. As a result, they will have more time to bring their ideas to life, and new AI tools will unlock additional opportunities for creativity and self-expression.
Conclusion:
AI should be seen as an assistant rather than a substitute for human effort. Creativity, ideas, skills, and experience remain at the core of the process. Ultimately, those who are already capable of realizing outstanding ideas will benefit the most from AI, as it allows them to execute their visions faster and more efficiently.
Industry experts worry that creators may start mass-producing unoriginal content using AI. However, due to its lack of uniqueness, such content is unlikely to captivate audiences, leading to low engagement—poor watch times, few likes, and minimal comments.
AI will not replace true creators; instead, it will become a powerful tool for them. It will help reduce production costs across various stages, enabling the realization of ideas that previously seemed impossible or nearly impossible. Those who ignore AI entirely risk becoming uncompetitive. AI will undoubtedly help cut costs in many areas of production. 3D graphics, for example, have always been an extremely complex and expensive aspect of video creation. Today, some of these tasks can be accomplished almost for free in just minutes or hours with AI.
That being said, some creative professions may indeed be replaced by AI. For example, jobs related to drawing storyboards for films or designing backgrounds in animation are already being partially replaced by AI. While these professions may not disappear entirely, the number of specialists in these fields is likely to decrease significantly due to reduced demand.
References:
- Artificial Intelligence for Video Content Analysis: Applications and Challenges. ScienceDirect, K. A. Zahran et al., 2023, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666954423000194.
- How Artificial Intelligence is Impacting Video. Forbes, Kimberly Whitler, 2024, March 26, https://www.forbes.com/sites/kimberlywhitler/2024/03/26/how-artificial-intelligence-is-impacting-video/.
- Video Incoming. TechCrunch, Kyle Wiggers, 2023, August 3, https://techcrunch.com/2023/08/03/video-incoming/.
- Barriers to Industry Adoption of AI Video Generation Tools: A Study Based on the Perspectives of Video Production Professionals in China. ResearchGate, Lijun Zhang et al., 2024, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381946918_Barriers_to_Industry_Adoption_of_AI_Video_Generation_Tools_A_Study_Based_on_the_Perspectives_of_Video_Production_Professionals_in_China.
- AI-Generated Videos: A Blessing or Curse for Your Marketing Strategy. Black Rabbit, 2024, https://www.blackrabbit.pl/post/ai-generated-videos-a-blessing-or-curse-for-your-marketing-strategy
- AI Video Research. Bitmovin, 2024, https://bitmovin.com/blog/ai-video-research/


































