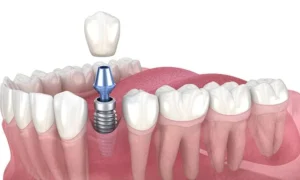
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, affects a significant portion of the population. Four out of five people may have periodontal disease without knowing it, mainly because the early stages of the disease are often painless. Unlike tooth decay, which typically causes discomfort, gum disease can progress silently, making regular dental check-ups and periodontal examinations essential for early detection and prevention.
What Causes Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease begins when plaque—a sticky, colorless film composed of bacteria, food particles, and saliva—accumulates on the teeth and gums. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that inflame the gums and slowly erode the bone supporting your teeth. If not removed through proper brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar (calculus), further contributing to gum disease progression.

Risk Factors for Gum Disease
While poor oral hygiene is a primary cause of gum disease, several other factors can increase the likelihood of developing gingivitis or periodontitis:
- Tobacco Use:Smoking or chewing tobacco significantly raises the risk of plaque and tartar formation, making it easier for gum disease to develop.
- Dental Appliances or Conditions:Ill-fitting bridges, crowded teeth, or defective fillings can trap plaque and bacteria, making it harder to maintain proper oral hygiene.
- Medications:Certain drugs, including steroids, cancer treatments, blood pressure medications, and oral contraceptives, may reduce saliva production, leading to a dry mouth and making plaque adherence easier.
- Hormonal Changes:Pregnancy, puberty, and oral contraceptives can cause hormonal fluctuations that increase the gums’ sensitivity to bacterial toxins, raising the risk of gum inflammation.
- Systemic Diseases:Conditions such as diabetes, blood disorders, and HIV/AIDS can make the body more susceptible to infections, including gum disease.
- Genetics:Some individuals are genetically predisposed to more aggressive forms of periodontitis. If you have a family history of tooth loss, paying close attention to your gum health is crucial.
Signs and Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Early detection is key in managing and treating gum disease. Watch for the following symptoms that may indicate the presence of gingivitis or periodontitis:
- Red and Puffy Gums:Healthy gums should be firm and pink, not swollen or inflamed.
- Bleeding Gums:Gums should not bleed, even when brushing or flossing vigorously.
- Persistent Bad Breath:Bad breath can result from bacteria accumulating in the mouth.
- New Gaps Between Teeth:New spacing between teeth may develop as bone loss occurs.
- Loose Teeth:Bone loss or weakened periodontal fibers can cause teeth to loosen.
- Pus Around the Gums:Pus is a clear sign of infection in the gums.
- Receding Gums:Gum recession is when the tissue around your teeth begins to wear away.
- Tenderness or Discomfort:Plaque, tartar, and bacteria can irritate gums, causing sensitivity and discomfort.
If you notice any of these signs, you must schedule a dental appointment as soon as possible for a comprehensive evaluation.
Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis: What’s the Difference?
- Gingivitisis the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by gum inflammation without affecting the bone or tissue holding the teeth in place. The condition is reversible at this stage with proper oral hygiene and professional cleanings.
- Periodontitisis the advanced stage of gum disease. It occurs when the inflammation spreads deeper into the supporting structures of the teeth, causing permanent damage to the bone and gums. Without treatment, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
Prevention and Treatment of Periodontal Disease
Preventing gum disease requires a combination of daily care and professional dental services. Here are key strategies for reducing your risk of developing periodontal disease:
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene:Brushing twice daily and flossing daily are essential for removing plaque and preventing it from turning into tartar.
- Balanced Diet:A nutritious diet supports your immune system and helps maintain gum health.
- Regular Dental Visits:Scheduling routine check-ups allows your dentist to identify early signs of gum disease and provide timely interventions.
At Affleck Dental, we perform thorough periodontal examinations during every dental check-up to ensure that your gums stay healthy. Our team is here to provide expert guidance and treatment options if you have any concerns about gingivitis or periodontitis.
Consult with Dr. Michael Affleck for Gum Health in Clearfield, Utah
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gum disease or are due for a dental exam, contact Affleck Dental today. As Clearfield’s premier dental practice, we specialize in diagnosing and treating gum disease to protect oral health. Schedule an appointment with Dr. Michael Affleck by calling (801) 614-7013.
Affleck Dental – Keeping Your Gums and Smile Healthy
466 N Main Street, STE 100, Clearfield, UT 84015