There is a specific, eerie silence that falls over a neighborhood when the power goes out. The hum of the refrigerator stops, the HVAC system sighs and goes quiet, and the Wi-Fi router blinks off. For most homeowners, this is the cue to scramble—hunting for flashlights, lighting candles, and wondering if the food in the freezer will survive the night.
But for a select few, that silence lasts only ten seconds. Then, a quiet hum begins outside. The lights flicker back on. The heater kicks back in. The Wi-Fi reconnects. Life resumes as normal, while the rest of the street remains in the dark.
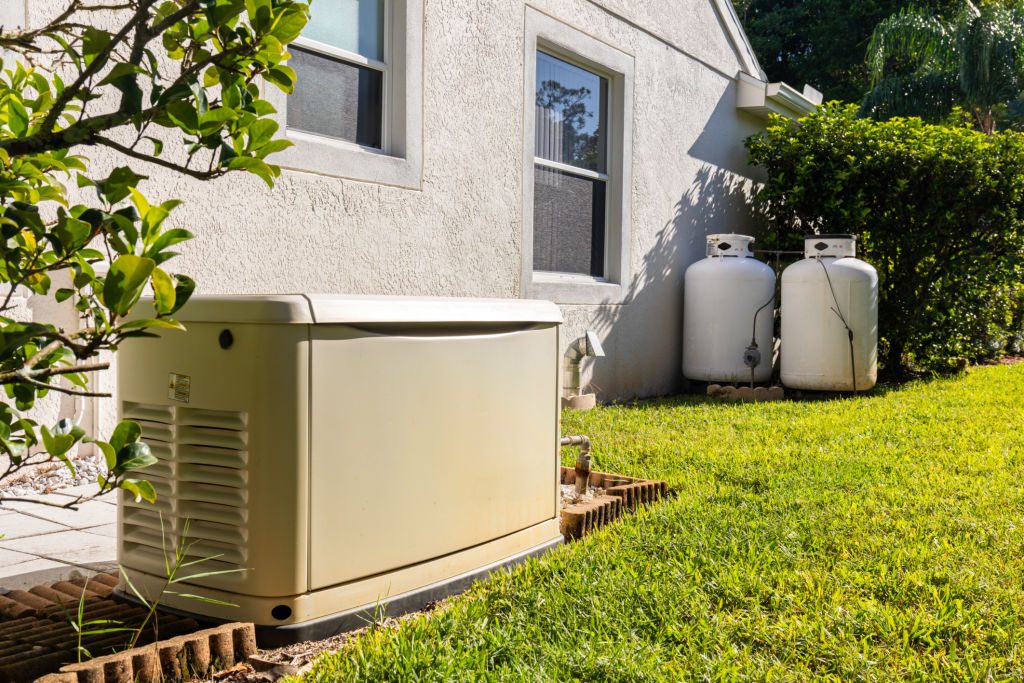
This seamless transition isn’t magic; it is the result of sophisticated technology working in perfect synchronization. A standby generator is not just a bigger version of the loud, gas-guzzling portable unit you drag out of the garage. It is a permanent, intelligent appliance that integrates directly into your home’s electrical panel. However, because this integration involves high-voltage electricity and pressurized fuel sources, it is not a DIY project. It requires professional generator installation to ensure the complex network of sensors and switches functions safely when the grid fails.
If you are considering upgrading your home’s defenses against power outages, it helps to understand what is actually happening under the hood. Here is a look at the technology required to keep your lights on when the world goes dark.
The Automatic Transfer Switch
If the generator is the muscle of the operation, the automatic transfer switch (ATS) is the brain. Without an ATS, a generator is just a motor sitting in your yard.
The ATS is a device installed next to your main electrical panel. Its job is to monitor the voltage coming from the utility grid 24/7. It is hyper-sensitive; it can detect a power loss or a significant voltage drop instantly.
When the ATS senses that the grid has failed, it initiates a sequence of events:
This disconnection is vital. If the generator pushed power into your home while you were still connected to the grid, it would send electricity back down the utility lines (back-feeding), which could electrocute utility workers trying to fix the outage miles away. The ATS technology ensures this never happens.
Load Management Technology
One of the biggest misconceptions about home generators is that you need a massive, industrial-sized unit to power a modern home. Thanks to load management technology, that is no longer true.
In the past, if you wanted to run two AC units, an electric oven, and a hot tub, you needed a generator capable of running them all at once. Today, smart modules allow for load shedding.
Here is how it works: The system monitors the demand. If you are running the AC and you turn on the electric oven, the system recognizes that the demand might exceed the generator’s capacity. It can temporarily shed (turn off) a lower-priority item (like the hot tub heater) to allow the oven to run. Once the oven is off, it allows power back to the lower-priority circuits. This smart distribution allows a smaller, more fuel-efficient generator to power a large home comfortably.
Bi-Fuel Technology
Technology isn’t always digital; sometimes, it’s mechanical. One of the primary tech advantages of a standby unit over a portable one is the fuel delivery system.
Portable generators run on gasoline. This means that during a prolonged outage, you have to go outside every few hours to refill the tank—assuming you can even find an open gas station.
Standby generators utilize bi-fuel technology designed to hook directly into your home’s existing natural gas or liquid propane (LP) supply.
The engineering required to regulate this pressure and ensure a clean burn is precise, ensuring the engine runs smoothly without the gumming and carburetor issues that plague gasoline engines.
Remote Monitoring
Modern generators are part of the Internet of Things (IoT). You no longer have to walk outside in the rain to check if the unit is running properly.
Leading manufacturers now include Wi-Fi and cellular connectivity as standard on their units. This connects the generator to a mobile app on your phone.
Purpose-Built Engines
Finally, the engine technology itself has evolved. You aren’t just strapping a lawnmower engine to an alternator. These are purpose-built engines designed specifically for the rigors of power generation.
They feature hydraulic valve lifters (which require no break-in period or expensive adjustments), specialized cooling systems to prevent overheating during 24-hour run cycles, and advanced alternators that produce clean electricity. Clean power (with less than 5% total harmonic distortion) is essential for modern homes because sensitive electronics—like your smart TV, your laptop, and your HVAC control board—can be fried by the fluctuating power produced by cheap construction generators.
A home generator is more than just a motor; it is a sophisticated ecosystem of switches, sensors, and software. It is a technological shield that keeps your home safe, warm, and connected, no matter what is happening to the grid outside. By investing in the right technology and the right installation, you turn a power outage from a crisis into a minor inconvenience.