What is 3D printing?
3D printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, is a technique for making objects that uses a method of stacking materials layer by layer to build three-dimensional entities. Unlike traditional Subtractive Manufacturing, where material is removed to form an object (e.g., engraving, milling), 3D printing is a process of adding material.
3D printing technology is based on several key technologies
3D Modeling: The first step in 3D printing is to create a three-dimensional model, which is typically modeled using computer-aided design (CAD) software. CAD software can be used to create geometry, resize, and add details, among other operations, to generate 3D model files ready for printing. Do you know the difference between 3D printing technology and injection molding?
Slicing technique: Before sending a 3D model to a 3D printer, it needs to be sliced into a series of sheets, each representing a layer of objects that the printer will build on top of that layer. The slicing software converts the 3D model into a slicing file composed of many 2D layers, which contains the print path and parameters for each layer.
Print path generation: Once the model is sliced into layers, the print path generation algorithm calculates the print path for each layer based on the specific parameters and requirements of the printer. These paths determine the route by which the print head moves at each level and how the material is added or solidified to build the object.
Material deposition or curing: Depending on different 3D printing technologies, different materials and processes are used to achieve the construction of the object. Common 3D printing materials include plastics, metals, ceramics, resins and so on. For plastic materials, printers deposit melted plastic layer by layer through a nozzle, while metal printing technology involves melting metal powder or wire.
Control systems and sensors: 3D printers are equipped with control systems and sensors to monitor and control the printing process. The sensor can detect parameters such as temperature, position, speed, and adjust the operation of the printer through the control system. This ensures accurate and consistent printing.
In general, 3D printing technology is a method of building objects by layer by layer, generating slice files according to the three-dimensional model, and then controlling the printer through the print path generation algorithm, using the appropriate materials for deposition or curing. Different 3D printing technologies use different processes and materials, but they all follow similar basic principles.

What can a 3D Printer do?
3D printers can manufacture various types of objects and have a wide range of applications. Here are some examples of what 3D printers can do:
Prototyping: A 3D printer is an ideal tool for prototyping. Designers, engineers, and manufacturers can use 3D printers to make physical models of products in order to evaluate designs, perform functional testing, and demonstrate.
Custom manufacturing: 3D printing technology makes custom manufacturing possible. Depending on individual needs and preferences, 3D printers can be used to create personalized items, such as customized shoes, glasses, jewelry, etc.
Education and learning: 3D printers play an important role in the field of education. Students can use 3D printers to transform abstract concepts into physical objects, enhancing their understanding of science, engineering, art and more.
Medical applications: The medical industry is one of the important application areas of 3D printing technology. Doctors and medical professionals can use 3D printers to make medical devices, prosthetics, dental models and more. In addition, 3D printing technology is also used in bioprinting, that is, the method of manufacturing human tissues and organs.
Making complex structures: Some objects have complex structures and geometry that may not be easily achieved with traditional manufacturing methods. And 3D printing technology can build these complex structures layer by layer, making it possible. This includes mechanical parts, architectural models, aerospace components, and more.
Art and creative expression: Artists and designers can use 3D printers to turn their creative ideas and ideas into real artworks and installations. 3D printing technology allows for more freedom and diversity of creative expression.
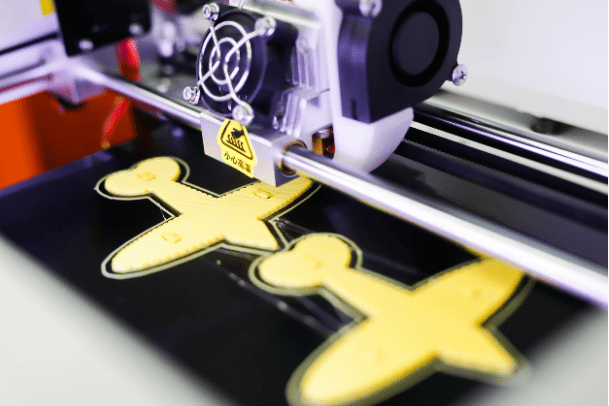

3D printing steps
3D Modeling: First, create or acquire a 3D model using computer aided design (CAD) software. This model can be created from scratch, or it can be obtained by 3D scanning or other means.
Slicing: Next, import the 3D model into the slicing software. Slicing software cuts the model into many thin horizontal layers, each of which is part of the object being built. The slicing software also generates the corresponding print path and parameters for each layer.
Preparation for printing: Before you start printing, you need to prepare a 3D printer. This includes installing the appropriate printing material (such as plastic, metal, ceramic, etc.), setting the printing parameters (such as temperature, speed), and calibrating the printer.
Printing process: Once the preparation is complete, the slicing file can be sent to the 3D printer to begin printing. Depending on the printing technique used, the printer stacks the material layer by layer to build the final object. For plastic printing, for example, the printhead heats and deposits molten plastic on the bottom layer, then gradually stacks the top layer.
Post-processing: After printing is complete, some post-processing steps may be required to improve the quality of the object. This may include removal of support material, surface treatment, painting or other processing.

How much does a 3D printer cost?
The price of 3D printers varies by model, brand, performance and features, ranging from a few hundred dollars to hundreds of thousands of dollars. Here are some common 3D printer price ranges:
Entry-level consumer 3D printers: These printers are less expensive and suitable for personal use and beginners. The price range is usually between $200 and $1,000.
Mid-range consumer 3D printers: These printers have higher performance and functionality and are suitable for professional and educational use. The price range is usually between $1,000 and $5,000.
Professional grade 3D printers: These printers offer increased accuracy, speed, and functionality for professional manufacturing and industrial applications. Prices typically range from $5,000 to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the size and features of the printer.
It is worth noting that in addition to the price of the 3D printer itself, other factors need to be considered, such as printing materials, maintenance costs, and the cost of post-processing equipment. In addition, there are options on the market such as lease and lease purchase, and you can choose the right purchase method according to your needs. Teach you how to choose a reliable 3D printing company for free.
The best choice depends on your budget, needs, and application scenarios. If you are a beginner or individual user, an entry-level consumer 3D printer may be a reasonable choice. For professional users and businesses, printers with higher performance and capabilities may be needed to meet specific needs. Before making a purchase, it is recommended that you research different brands and models of printers and compare their features, performance, user reviews and after-sales support to choose the right 3D printer for you.