Health tech has transformed the modern healthcare landscape by introducing digital platforms, connected medical devices, and intelligent data systems. While these advancements improve patient care and operational efficiency, they also introduce complex cybersecurity challenges. As health tech continues to expand, safeguarding sensitive medical information becomes a strategic priority for healthcare organizations worldwide.
The integration of digital systems in hospitals, clinics, and research institutions has created a vast ecosystem of interconnected devices and databases. Protecting this ecosystem requires a structured approach to cybersecurity that addresses vulnerabilities while maintaining accessibility and functionality.
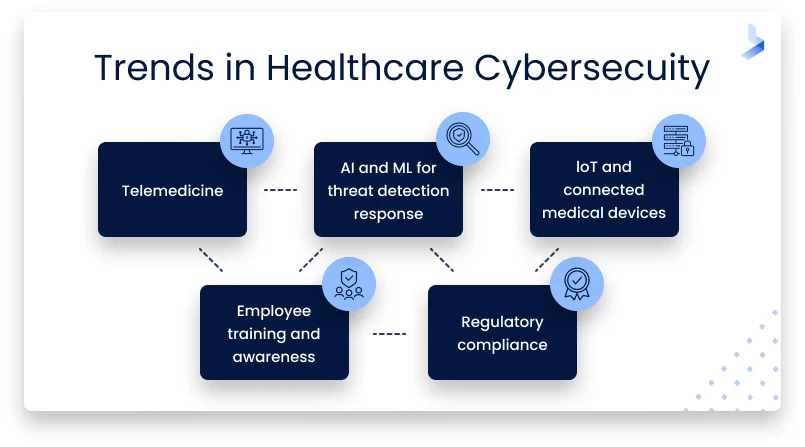
The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity in Health Tech
Health tech relies heavily on electronic health records, remote monitoring systems, telemedicine platforms, and data analytics tools. Each of these components processes large volumes of sensitive patient data, including medical histories, diagnostic results, and treatment plans. This information is highly valuable and must be protected against unauthorized access.
As healthcare systems become increasingly digital, cyber threats evolve in sophistication. Health tech environments are particularly attractive targets due to the critical nature of their services. A disruption in healthcare operations can have immediate and serious consequences, making cybersecurity a matter of patient safety as well as data protection.
The reliance on cloud computing, mobile applications, and connected devices further increases the attack surface. Health tech organizations must therefore adopt comprehensive security frameworks that cover every layer of their digital infrastructure.
Common Cybersecurity Threats in Health Tech
Health tech faces multiple cybersecurity risks that require continuous monitoring and proactive defense strategies.
One significant threat is unauthorized data access. Weak authentication systems or outdated software can create entry points for malicious actors. Once access is gained, confidential patient records may be exposed or manipulated.
Another challenge involves ransomware attacks, where critical systems are locked until demands are met. In a health tech environment, such disruptions can delay treatments and compromise patient care. The urgency of healthcare operations makes these systems particularly vulnerable to pressure-based attacks.
Phishing campaigns also target healthcare professionals by impersonating trusted communications. A single compromised account can grant access to broader networks within a health tech infrastructure.
Medical devices connected to networks present additional risks. Without proper security configurations, these devices can become gateways into hospital systems. Health tech security strategies must therefore extend beyond traditional IT systems to include embedded device protection.
The Impact of Cybersecurity Breaches on Healthcare
A cybersecurity breach in health tech can have far-reaching consequences. Beyond financial losses, organizations may experience reputational damage and loss of patient trust. Healthcare providers depend on patient confidence, and any compromise of data security can weaken that trust significantly.
Operational disruptions are another serious concern. When health tech systems are disabled or restricted, patient scheduling, diagnostics, and treatment workflows may be interrupted. Delays in access to medical records can affect clinical decision-making.
In addition, regulatory penalties may apply if data protection standards are not met. Compliance with healthcare data regulations is essential, and failure to secure patient information can result in substantial legal consequences.
Building a Strong Cybersecurity Framework in Health Tech
Effective cybersecurity in health tech requires a multi-layered strategy. A comprehensive framework addresses prevention, detection, response, and recovery.
Strong access control measures form the foundation of secure systems. Multi-factor authentication ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data. Role-based permissions limit exposure by granting users access only to the information necessary for their responsibilities.
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting health tech data during transmission and storage. Even if intercepted, encrypted data remains unreadable without proper authorization.
Regular software updates and patch management are equally important. Outdated systems often contain vulnerabilities that cyber threats exploit. Proactive maintenance strengthens the overall security posture of health tech infrastructures.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Health Tech Security
Artificial intelligence enhances cybersecurity within health tech by identifying unusual activity patterns. Advanced algorithms analyze network behavior and detect anomalies in real time. This capability enables early intervention before threats escalate.
Predictive analytics can also anticipate potential vulnerabilities. By analyzing historical data, artificial intelligence tools within health tech systems identify weak points and recommend targeted improvements.
Automated monitoring reduces the burden on IT teams and ensures continuous oversight. With increasing data volumes, manual monitoring becomes insufficient. Health tech security solutions powered by artificial intelligence improve both speed and accuracy in threat detection.
Strengthening Employee Awareness and Training
Human error remains a significant factor in cybersecurity incidents. Health tech organizations must prioritize employee education to reduce risks. Training programs should focus on identifying suspicious communications, secure password management, and safe data handling practices.
Regular awareness sessions reinforce the importance of cybersecurity in daily operations. When healthcare professionals understand the impact of data breaches, they become active participants in maintaining security.
Clear internal policies further support responsible behavior. Health tech institutions should establish structured reporting mechanisms for potential security concerns, ensuring rapid response and containment.
Securing Connected Medical Devices
The rapid expansion of connected medical devices presents unique challenges for health tech security. Devices such as remote monitors, infusion pumps, and diagnostic tools must meet strict cybersecurity standards.
Manufacturers and healthcare providers must collaborate to ensure that devices are configured securely before deployment. Secure firmware updates and authentication protocols are essential to prevent unauthorized access.
Network segmentation is another effective strategy. By isolating medical devices from general administrative networks, health tech organizations reduce the risk of widespread system compromise.
Continuous device monitoring ensures that performance anomalies are detected promptly. Health tech security teams must treat medical devices as integral components of their cybersecurity ecosystem.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance in Health Tech
Compliance with healthcare data protection regulations is fundamental to health tech operations. Regulatory frameworks outline strict guidelines for data storage, access control, and incident reporting.
Health tech organizations must conduct regular audits to verify compliance with established standards. Documented security policies and incident response plans demonstrate accountability and preparedness.
Data minimization practices also support compliance efforts. By collecting only necessary information, health tech providers reduce exposure and enhance data protection.
Collaboration between legal, technical, and clinical teams ensures that security measures align with regulatory expectations while maintaining efficient service delivery.
Incident Response and Recovery Planning
Despite preventive measures, no system is entirely immune to threats. Health tech organizations must therefore develop structured incident response plans. Rapid identification and containment minimize damage during security events.
Response plans should define clear roles and communication channels. Timely notification to stakeholders ensures transparency and coordinated action.
Backup systems are essential for operational continuity. Secure data backups allow health tech institutions to restore critical services quickly in case of system disruption.
Regular simulation exercises test preparedness and identify improvement areas. Continuous refinement strengthens resilience against evolving cyber threats.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Health Tech
As health tech continues to evolve, cybersecurity strategies must adapt accordingly. Emerging technologies such as blockchain-inspired data validation methods, advanced biometrics, and zero-trust architectures may enhance protection levels.
Investment in cybersecurity infrastructure is becoming a core component of digital healthcare strategy. Leaders recognize that innovation must be supported by strong security foundations.
Collaboration across industry stakeholders will further strengthen health tech security standards. Shared knowledge and coordinated responses improve defense mechanisms across the healthcare ecosystem.
Cybersecurity is a critical pillar of modern health tech. As digital transformation accelerates, protecting patient data and ensuring operational continuity become increasingly complex challenges.
Through comprehensive security frameworks, artificial intelligence integration, employee training, device protection, and regulatory compliance, health tech organizations can build resilient systems that safeguard both information and patient trust.
Sustained commitment to cybersecurity ensures that health tech innovations continue to deliver meaningful improvements in healthcare delivery while maintaining the highest standards of data protection and reliability.