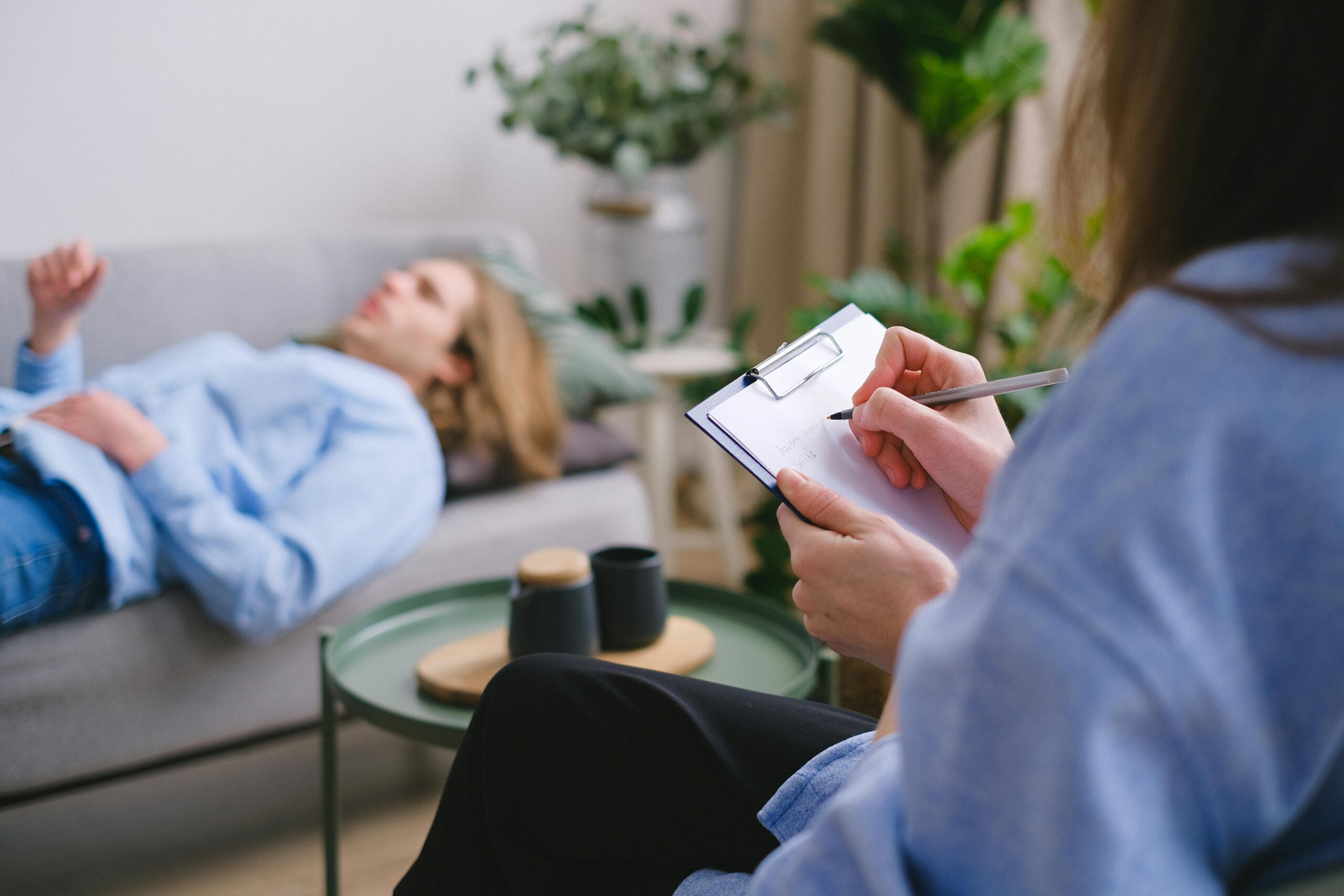
Emotional burnout has become increasingly common as people navigate prolonged stress, high expectations, and limited opportunities for rest or recovery. While burnout is often associated with work or caregiving responsibilities, its effects reach far beyond exhaustion. Emotional burnout can impact mental health, physical well-being, relationships, and the ability to function in daily life.
Mental health treatment plays a critical role in helping individuals recognize burnout, address its underlying causes, and restore emotional balance.
Understanding Emotional Burnout
Emotional burnout is a state of chronic emotional exhaustion caused by prolonged stress without adequate recovery. Unlike short-term stress, burnout develops gradually and can feel difficult to escape without support.
Common signs of emotional burnout include:
- Persistent fatigue that does not improve with rest
- Emotional numbness or detachment
- Irritability or mood swings
- Decreased motivation
- Difficulty concentrating
- Feeling overwhelmed by simple tasks
When left unaddressed, burnout can worsen mental health symptoms and interfere with daily functioning.
How Burnout Affects Mental Health
Burnout and mental health are closely connected. Prolonged emotional stress can contribute to anxiety, depression, and feelings of hopelessness. Individuals experiencing burnout may struggle to regulate emotions, leading to heightened reactivity or emotional withdrawal.
Burnout can also impair cognitive function, making it harder to problem-solve, make decisions, or engage meaningfully in relationships. Over time, these effects may compound, increasing the risk of more severe mental health challenges.
Addressing burnout early is essential to prevent long-term consequences.
Identifying the Root Causes of Burnout
Effective mental health treatment goes beyond symptom management by identifying the root causes of emotional burnout. Burnout often develops from a combination of factors rather than a single stressor.
Contributing factors may include:
- Chronic workplace stress
- Caregiver fatigue
- Unresolved trauma
- Perfectionism or unrealistic expectations
- Lack of boundaries
- Insufficient emotional support
Understanding these underlying contributors allows treatment to target the true sources of burnout rather than offering temporary relief.
Creating Space for Emotional Recovery
One of the first steps in addressing burnout is creating space for emotional recovery. Mental health treatment provides a structured environment where individuals can step away from constant demands and focus on healing.
This space allows individuals to rest emotionally, reflect on stress patterns, and begin rebuilding emotional resilience. Without intentional space for recovery, burnout often persists or worsens.
Structured support creates the conditions needed for emotional restoration.
Therapy as a Tool for Burnout Recovery
Therapy is a cornerstone of burnout treatment. Through therapeutic support, individuals can explore stressors, challenge unhelpful thought patterns, and develop healthier coping strategies.
Therapy helps individuals:
- Recognize emotional limits
- Develop emotional awareness
- Process feelings of guilt or pressure
- Learn stress-management techniques
- Rebuild motivation and purpose
These skills support both immediate relief and long-term emotional health.
Rebuilding Boundaries and Self-Regulation
Burnout often develops when personal boundaries are repeatedly ignored or overridden. Mental health treatment helps individuals identify where boundaries have been compromised and how to restore them.
Learning to say no, set realistic expectations, and prioritize self-care are essential components of recovery. Treatment supports emotional regulation by helping individuals respond to stress more intentionally rather than reactively.
Stronger boundaries reduce emotional depletion and prevent burnout recurrence.
Addressing Co-Occurring Mental Health Conditions
Emotional burnout frequently co-occurs with anxiety, depression, or trauma-related conditions. Treating burnout without addressing these conditions can limit recovery progress.
Comprehensive mental health treatment integrates care for co-occurring conditions, ensuring emotional stability and resilience are rebuilt holistically. This integrated approach supports sustained improvement rather than temporary relief.
For individuals seeking structured support, options such as mental health facilities in Lexington KY, provide environments designed to address burnout alongside broader mental health needs.
Restoring Emotional Energy and Motivation
Burnout often drains emotional energy and diminishes motivation. Mental health treatment focuses on restoring emotional reserves by addressing chronic stress patterns and reconnecting individuals with personal values.
As emotional energy returns, individuals often experience renewed interest in activities, improved engagement with others, and greater clarity around goals. Motivation becomes intrinsic rather than driven by pressure or obligation.
Restored motivation supports long-term emotional well-being.
The Role of Education in Burnout Recovery
Education helps individuals understand burnout as a legitimate mental health concern rather than a personal failure. Learning how stress affects the brain and nervous system reduces shame and encourages proactive care.
A trusted source for research-based information on mental health and stress-related conditions is the National Institute of Mental Health. Evidence-based education empowers individuals to recognize burnout early and seek appropriate support.
Understanding the science behind burnout supports healthier self-perception.
Developing Sustainable Coping Strategies
Mental health treatment emphasizes the development of sustainable coping strategies rather than quick fixes. These strategies support long-term emotional balance and resilience.
Coping strategies may include:
- Mindfulness practices
- Emotional regulation techniques
- Time management skills
- Stress-reduction routines
- Healthy communication patterns
Sustainable coping reduces vulnerability to future burnout.
Preventing Burnout Recurrence
Recovery from burnout includes planning for prevention. Mental health treatment helps individuals identify early warning signs and develop plans to address stress before it becomes overwhelming.
This proactive approach supports long-term emotional health and reduces the likelihood of repeated burnout cycles. Prevention planning reinforces self-awareness and self-care as ongoing priorities.
Reframing Rest and Recovery
Many individuals experiencing burnout struggle with guilt around rest. Mental health treatment helps reframe rest as a necessary component of health rather than a reward.
Learning to value rest and recovery supports emotional sustainability. This mindset shift allows individuals to maintain balance even during demanding periods.
Rest becomes part of a healthy lifestyle rather than an afterthought.
Healing Emotional Burnout Through Intentional Care
Emotional burnout is a signal that the mind and body need support. Mental health treatment addresses burnout by restoring balance, building resilience, and supporting emotional healing.
Through therapy, education, and structured support, individuals can regain emotional energy and clarity. Addressing burnout with intention and compassion creates space for renewed well-being and long-term mental health.
Moving Forward With Emotional Resilience
Burnout does not have to define the future. With appropriate mental health treatment, individuals can move beyond exhaustion and rebuild a life that feels manageable and meaningful.
By addressing the emotional, psychological, and behavioral aspects of burnout, treatment supports lasting change. Emotional resilience grows when care is proactive, comprehensive, and rooted in self-compassion.