As the global push for energy efficiency and environmental responsibility intensifies, the demand for cleaner, smarter home heating and cooling systems continues to grow. Traditional HVAC systems that rely on combustion fuels are increasingly being replaced with alternatives that reduce carbon emissions, improve indoor air quality, and lower energy bills. One such technology leading this transformation is the electric heat pump.
Unlike conventional furnaces or air conditioners that generate heat or cold through burning fuel or using resistance coils, an electric heat pump transfers thermal energy from one area to another. This method of operation significantly reduces energy consumption while maintaining year-round comfort. But the benefits of this system go far beyond just efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how electric heat pumps work, why they are rapidly becoming the go-to option for both new construction and retrofits, the types available, and what you need to know before installing one in your home or business.
Understanding the Electric Heat Pump
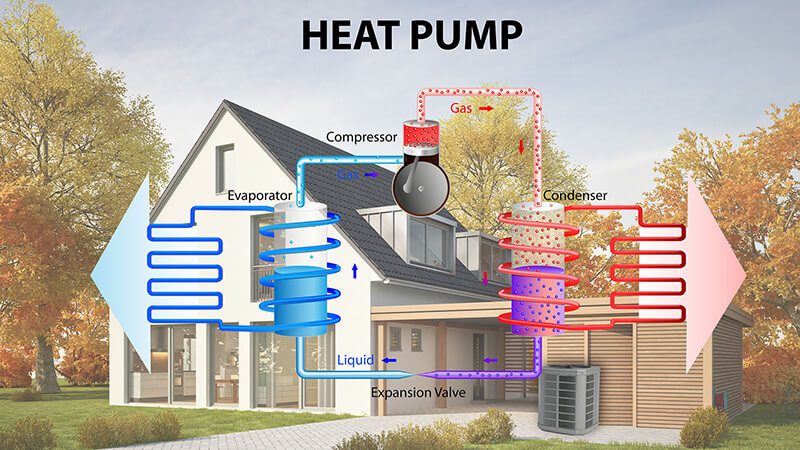
At its core, an electric heat pump operates on the principle of heat transfer. It extracts heat from the air or ground and moves it into a building during colder months. During warmer months, the process is reversed, expelling heat from the inside to the outside, thereby cooling the space.
The system consists of a compressor, refrigerant, expansion valve, and a series of coils. These components work together in a closed loop to move heat rather than generate it. Because of this fundamental difference, the energy consumed is significantly lower than conventional HVAC systems.
Two-in-One System
One of the most attractive aspects of an electric heat pump is its ability to act as both a heater and an air conditioner. This dual functionality means fewer appliances, reduced maintenance, and lower installation costs over time.
Key Advantages of Electric Heat Pumps
Switching to a heat pump system may seem like a big change, especially for those used to traditional gas or oil heating. However, the advantages are numerous and long-lasting.
1. Exceptional Energy Efficiency
An electric heat pump is one of the most energy-efficient climate control systems available today. Instead of consuming energy to create heat, it simply moves it from one place to another. This allows the system to deliver up to three or four times more energy in the form of heat than it consumes in electricity.
This results in:
- Lower monthly utility bills
- Less strain on the electrical grid
- Improved sustainability
Even in colder climates, modern units with inverter-driven compressors and enhanced cold-weather performance features maintain impressive efficiency.
2. Reduced Carbon Emissions
Using electricity instead of fossil fuels to regulate temperature drastically reduces greenhouse gas emissions, especially when paired with a clean energy grid or home solar panels.
As more governments and homeowners prioritize eco-conscious living, adopting technologies like the electric heat pump becomes a critical step toward reaching long-term sustainability goals.
3. Low Maintenance and Long Lifespan
Compared to gas furnaces or traditional HVAC units, heat pumps have fewer mechanical parts that are prone to failure. Regular maintenance typically involves cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and annual inspections by a certified technician.
When maintained properly, electric heat pumps can last anywhere from 15 to 20 years, providing consistent performance with minimal upkeep.
4. Enhanced Indoor Air Quality
Because electric heat pumps do not rely on combustion, they don’t produce indoor pollutants like carbon monoxide or nitrogen dioxide. They also offer the ability to filter, dehumidify, and circulate air, which contributes to a healthier living environment.
Types of Electric Heat Pumps
There are several different configurations available, each suitable for specific applications and building types.
1. Air Source Heat Pumps
These are the most common and extract heat from the outdoor air. They are relatively easy to install and ideal for homes that don’t experience extremely cold winters.
2. Ground Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps
These systems draw heat from the stable underground temperature. Though more expensive to install, they offer even greater efficiency and are suitable for areas with significant seasonal temperature changes.
3. Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Perfect for homes without existing ductwork or for adding heating and cooling to new additions, these systems allow for zoned temperature control in different parts of the home.
Each system has its own set of benefits and limitations, and choosing the right one depends on factors such as budget, climate, and the size and design of the property.
What to Expect During Installation
Proper installation is essential to ensure your electric heat pump performs efficiently and lasts its full service life. A typical installation process involves the following steps:
- Site Assessment
An HVAC professional evaluates your home’s heating and cooling requirements, insulation quality, existing ductwork (if applicable), and electrical system.
- System Selection and Sizing
Based on the assessment, the appropriate model and capacity are chosen. Incorrectly sized systems are one of the most common causes of poor performance and energy waste.
- Unit Placement
Indoor and outdoor components are strategically placed to maximize airflow and accessibility for future maintenance.
- Refrigerant and Electrical Connections
The technician installs the refrigerant lines and electrical wiring, ensuring all connections are properly insulated and sealed.
- System Testing and Calibration
Once everything is installed, the system is tested for leaks, correct refrigerant levels, and proper electrical function. The thermostat is calibrated to ensure accurate temperature control.
A professional electric heat pump installation should take anywhere from a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the complexity of the system and whether any upgrades (such as electrical panels or duct modifications) are needed.
Common Misconceptions
Despite their growing popularity, there are still misconceptions surrounding electric heat pumps. Let’s clear up a few:
“They don’t work in cold climates.”
This was once true, but advancements in technology have made modern electric heat pumps capable of operating efficiently in sub-zero temperatures. Cold-climate models are designed specifically to handle harsh winters without performance loss.
“They are too expensive.”
While the initial cost can be higher than traditional systems, the long-term savings on energy bills and the availability of tax incentives and rebates often make up for the upfront investment.
“They can’t heat large homes.”
Many systems are scalable and can handle large or multi-zone properties. Multi-split systems or dual fuel systems can also be installed to accommodate varying heating needs across different rooms.
Environmental and Economic Impact
Installing an electric heat pump doesn’t just benefit your home—it contributes to broader environmental and economic progress.
- Lower emissions mean cleaner air and a healthier planet.
- Less reliance on fossil fuels contributes to national energy security.
- High efficiency reduces the strain on energy grids, especially during peak seasons.
As nations push toward net-zero carbon goals, widespread adoption of electric heating and cooling technologies will play a crucial role.
Financial Incentives
To encourage homeowners and businesses to transition to efficient systems, many governments offer incentives for electric heat pump adoption. These can include:
- Tax credits
- Utility rebates
- Low-interest loans
- Special financing programs
These incentives can substantially reduce the cost of installation, making it more accessible for a wider range of budgets.
Is an Electric Heat Pump Right for You?
Whether or not this system is the right choice depends on several factors:
- Do you want an all-in-one heating and cooling solution?
- Are you interested in lowering your energy bills?
- Is sustainability a priority in your household?
- Do you want to reduce your reliance on fossil fuels?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, it’s worth exploring your options with a qualified HVAC contractor. They can provide a detailed assessment of your property and help you choose the right system for your needs.
It’s also important to consider how the electric heat pump integrates with other smart technologies in your home. Many modern units can connect to smart thermostats, home automation platforms, and energy monitoring systems—allowing you to take full control over your energy use.
Final Thoughts
The shift to more efficient, sustainable heating and cooling solutions is no longer a niche trend—it’s the new standard. The electric heat pump stands at the forefront of this transition, offering unmatched efficiency, dual functionality, and environmental benefits.
By investing in a quality system and ensuring it is installed correctly, homeowners can enjoy year-round comfort, long-term savings, and peace of mind. As technology continues to evolve and incentives make adoption more accessible, the electric heat pump is quickly becoming the system of choice for modern homes and businesses.
Whether you’re upgrading an outdated HVAC system or building from the ground up, don’t overlook this versatile and future-ready technology. With the right planning and professional support, it could be the smartest home improvement decision you make this decade.