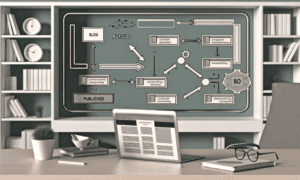
Accurate positioning is at the heart of modern technology, from guiding autonomous vehicles on the road to supporting precision farming in the fields. Yet, Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signals often face issues such as atmospheric disturbances and satellite orbit errors, which can reduce accuracy significantly.
Cloud-based GNSS correction services have stepped in to address this challenge, providing a scalable way to boost positioning accuracy without relying on expensive local infrastructure. Understanding how this system works helps illustrate why it is becoming a driving force behind modern innovation.
Keep reading to learn how cloud-based corrections transform navigation and unlock new possibilities across industries.
Understanding GNSS Corrections in the Cloud
GNSS corrections refer to improving the raw satellite data so that positioning becomes significantly more accurate. While GNSS signals give location information, they are subject to delays and distortions that affect accuracy. In some cases, this can mean several metres of error, which is unsuitable for applications that demand high precision.
Cloud-based correction addresses these issues by drawing on a dense network of ground stations. These stations constantly measure satellite signals, identify errors, and send that data to the cloud. Devices connected via the internet can then access the corrections in real time, achieving positioning down to the centimetre level.
How Cloud-Based GNSS Correction Works
The process begins with ground reference stations that detect errors caused by factors such as ionospheric delay and satellite clock drift. Instead of storing and processing this data locally, the information is transmitted to a central cloud service. From there, the corrections are streamed back to user devices, which apply them instantly to improve positioning.
This method differs from traditional approaches like Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) corrections, which often require users to set up and maintain expensive local base stations. By moving the process to the cloud, the system becomes more flexible and scalable, allowing wider adoption across industries and geographies.
Benefits and Real-World Applications
One of the most notable advantages of cloud-based GNSS correction is its accessibility. Because users only need an internet connection to receive corrections, it eliminates the need for heavy investment in infrastructure. This lowers the barrier for industries looking to implement high-accuracy positioning.
For example, in agriculture, farmers can carry out precision planting and harvesting with reduced waste. Surveyors benefit from consistent accuracy without having to set up extra equipment.
For example, in agriculture, farmers can carry out precision planting and harvesting with reduced waste. Surveyors benefit from consistent accuracy without having to set up extra equipment.
At the same time, autonomous vehicles and drones depend on enhanced positioning to operate safely and reliably. Robotics and logistics also gain from the improved scalability, as multiple devices can connect to the same correction service without added complexity.
Final Thoughts
Cloud-based GNSS correction represents a major leap forward in positioning technology. By combining error detection from reference stations with the scalability of the cloud, it delivers accuracy once out of reach for many industries.
As automation and connected devices continue to expand, the demand for dependable positioning will only grow, and cloud-enabled GNSS corrections are set to remain at the heart of this transformation.