The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), effective May 25, 2018, has reshaped the global landscape of data privacy, extending its influence far beyond the European Union (EU). As outlined by Jyotirmay Jena in the International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), GDPR standardizes data protection laws across the EU, enhancing transparency and individual control over personal data. Its extraterritorial scope means U.S. businesses interacting with EU residents—through sales, services, or behavioral monitoring—must comply, introducing both opportunities for improved data practices and challenges related to compliance, penalties, and operational adjustments.
Enhancing Data Protection and Customer Trust
GDPR mandates stringent guidelines on data collection, storage, and processing, offering U.S. businesses a chance to strengthen their privacy frameworks. Principles like data minimization—collecting only essential data—and data protection by design encourage robust security measures such as encryption and pseudonymization. By upholding data subject rights (e.g., access, erasure, portability), companies can build trust with EU customers, who increasingly value privacy. Compliance not only mitigates legal risks but also positions firms as privacy leaders, enhancing competitiveness in a data-driven market.
Challenges in Compliance and Data Management
Despite its benefits, GDPR poses significant hurdles for U.S. businesses. The regulation’s complexity overwhelms many, especially small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources. Jyotirmay Jena presented that mapping data flows to identify EU interactions is resource-intensive, while adjusting legacy systems to meet requirements like 72-hour breach notifications adds operational strain. Cross-border data transfers, restricted unless safeguarded by tools like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs), further complicate compliance, particularly after the Privacy Shield’s invalidation. Non-compliance risks fines up to 4% of global revenue or €20 million, plus reputational damage.
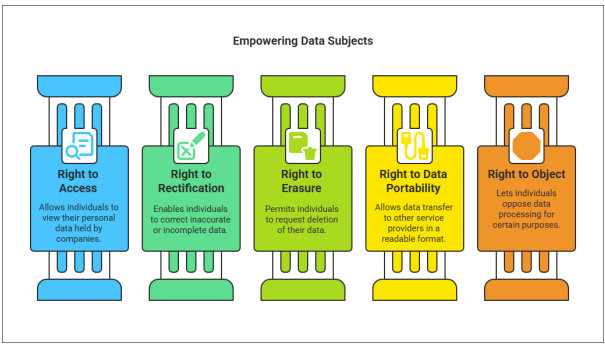
User Rights and Regulatory Expectations
GDPR empowers EU residents with rights to access, rectify, erase, restrict, or transfer their data, challenging U.S. firms to implement responsive systems. According to Jyotirmay Jena, businesses must ensure lawful bases for processing—like explicit consent—while meeting regulatory expectations for transparency and timeliness. Resistance to change, cultural differences in privacy priorities, and the need for employee training can hinder adoption. Companies must also address potential legal scrutiny and class-action risks, necessitating proactive strategies to align with GDPR’s high standards.
System Architecture and Compliance Frameworks
Achieving GDPR compliance requires a structured approach: assessing data activities, embedding privacy into systems, and establishing breach response protocols. U.S. businesses leverage tools like encryption, access controls, and regular audits, often appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee efforts. Frameworks such as SCCs or the EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework facilitate lawful data transfers. Key features—data minimization, storage limits, and security safeguards—are integral to meeting GDPR’s technical and organizational demands.
Performance Evaluation and Future Improvements
Evaluations show GDPR compliance enhances data security and customer trust, with compliant firms reporting fewer breaches and stronger market positions. According to Jyotirmay Jena, studies suggest proactive adopters reduce legal risks by 30-40% compared to non-compliant peers, especially benefiting SMEs targeting the EU. However, gaps remain: inconsistent enforcement, resource disparities, and transfer complexities challenge uniform success. Improving audit frequency, employee training, and transfer mechanisms is critical for sustained compliance and operational efficiency.
Maximizing GDPR Compliance for Future Growth
To fully harness GDPR’s potential, U.S. businesses must refine their strategies. Conducting regular data audits ensures ongoing adherence, while robust security measures like encryption protect against breaches. Training staff on GDPR requirements fosters a privacy-centric culture, and engaging legal experts tailors compliance to specific needs. Strengthening transfer safeguards—via updated SCCs or emerging frameworks—addresses cross-border challenges. By viewing compliance as an opportunity, companies can turn regulatory demands into a strategic advantage, enhancing global credibility.
Conclusion: The Future of GDPR for U.S. Businesses
While challenges persist, Jyotirmay Jena asserts in IJCET that GDPR’s future impact on U.S. businesses is promising. As privacy expectations rise and enforcement tightens, compliance will become increasingly vital. Businesses must prioritize security enhancements, regulatory alignment, and customer trust to thrive under GDPR. By addressing complexities, embracing best practices—like appointing DPOs and refining data policies—and innovating within legal bounds, U.S. firms can transform GDPR from a burden into a cornerstone of success, ensuring resilience and relevance in a privacy-first world.